Introduction
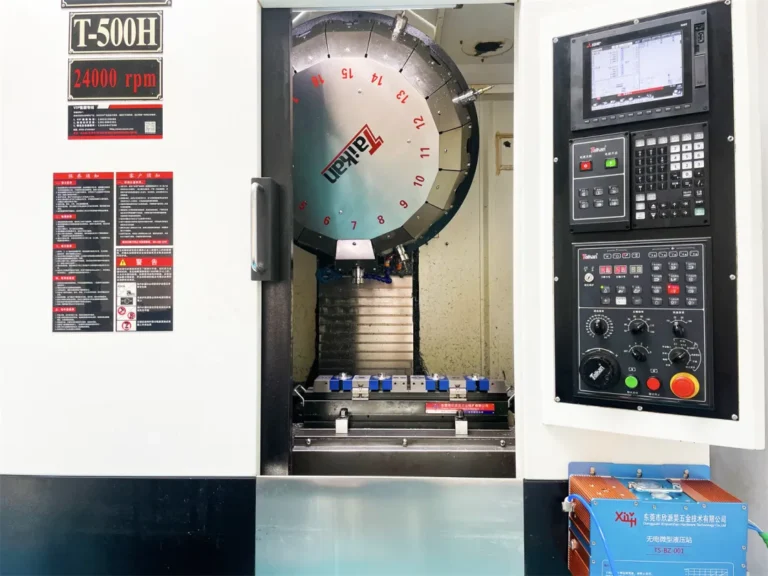
Prototype making is a process of rapidly transforming design concepts into physical models. Prototypes can be used to verify appearance, test structure, evaluate functionality, and conduct market research. So it is is an essential step in prototyping to provide suitable 3D files to a prototype manufacturer. Among the file formants, STP and STL are the two most frequently mentioned ones, each with its own characteristics and uses.
Below, we will explain why 3D files are needed for prototype making and provide a detailed comparison of the differences between STP and STL formats, hoping to help you better prepare your prototyping materials.
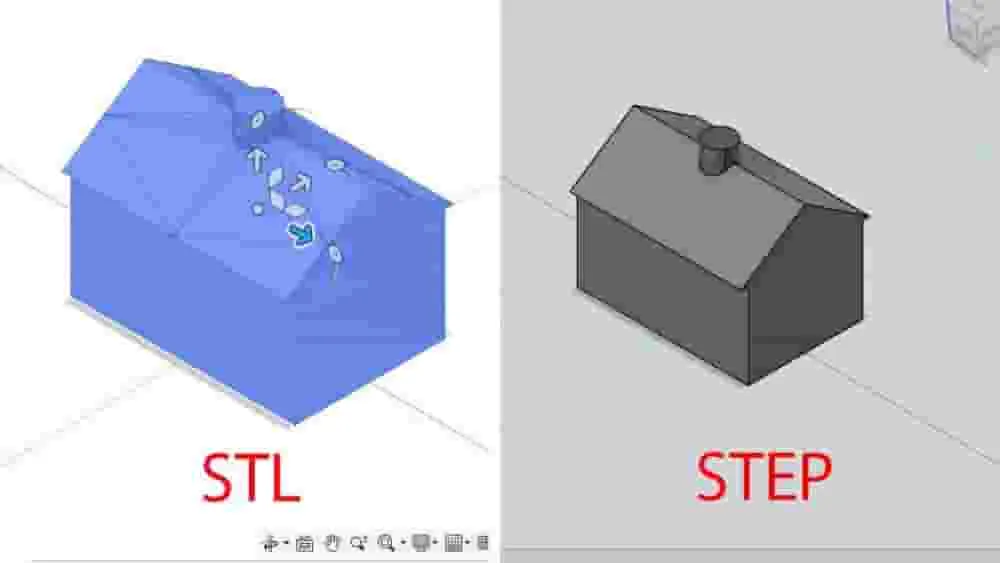
Why must 3D files be provided for prototype making?
Prototype making, whether through CNC machining, 3D printing, or vacuum molding, essentially relies on a digital model to accurately replicate a physical entity. The 3D file acts as a “blueprint” in this process, and its necessity is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1, Accurate Assessment and Quotation:
Prototype manufacturers need 3D models to understand the product’s dimensions, structural complexity, internal details, and appearance requirements. This allows them to determine the production process, required materials, processing time, and to provide accurate costs and delivery dates. Without 3D models, accurate assessment and quotation are difficult to achieve.
2, The foundation of CNC programming:
Modern prototype manufacturing relies heavily on digital technologies such as CNC machining and 3D printing. These devices all require programming based on 3D files.
- CNC machining: Toolpath planning (including cutting paths and non-cutting idle paths) needs to be set according to 3D drawings.
- 3D printing: Based on digital model files, objects are constructed by printing and bonding materials layer by layer. Although silicone molding directly uses physical prototypes to make molds, the prototypes themselves are also obtained through CNC or 3D printing, and thus also rely on 3D files.
3, Ensuring accurate communication and consistent results:
3D files are the most accurate and unambiguous communication tool between designers and manufacturers. Combined with ID drawings (process drawings), BOM (Bill of Materials), and other documents, it ensures that the final prototype model meets design expectations in terms of dimensions, assembly, appearance, and functionality, avoiding rework and losses due to misunderstandings.
What if there are no 3D files available? If you only have the physical product, you can obtain data through 3D scanning (digitization) and draw a 3D model, or find a prototype manufacturer with design capabilities to assist in completing the drawing design.
The core differences between STP and STL files
STP (or STEP) and STL are both file formats used for 3D models, but they differ significantly in nature, the information they contain, and their uses. You can quickly understand their key differences using the table below:
| Feature Dimension | STP (STEP) file | STL file |
|---|---|---|
| nature | CAD design data(Equivalent to the original electronic document) | Surface mesh data(Equivalent to a scanned image) |
| Data composition | It contains rich information such as precise geometry (e.g., B-Rep boundary representation), topology, assembly relationships, and material properties. | It consists only of triangular facets (triangular meshes) and describes the geometry of an object’s surface. |
| Editing | highParametric modification and editing can be performed directly in CAD software. | LowIt cannot be directly edited parametrically, making modification difficult. |
| Information content | highIt supports storing information on various aspects such as color, material, precision, and product structure. | LowIt only contains geometric information and does not include attributes such as color and material textures. |
| File size | Relatively large (due to abundant information) | Relatively small (but high-precision meshes can also result in very large files). |
| Main uses | CAD Data ExchangeCollaborative design, archiving, and serving as the source of process design. | 3D printingRapid prototyping, Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) |
| Accuracy guaranteed | highPreserve the original design intent and precise dimensions | The accuracy is compromised depending on the degree of mesh refinement; it is only an approximate representation. |
| Compatible software | Mainstream CAD software (such as SolidWorks, UG, CATIA, Pro/E, etc.) | Almost all 3D printing software and slicing software |
To understand this more intuitively, consider this analogy: An STP file is like an editable original Word document, while an STL file is like a PDF or image obtained by scanning that document after it has been printed on paper . You can easily edit the text and formatting in a Word document, but it’s difficult to directly modify the text in a scanned image.
How to prepare suitable documents for prototype making
Having understood the differences above, you will be more confident in preparing your prototype documentation:
1, We prioritize providing STP format files:
Because STP files retain complete design information and parametric features, they are ideal for CNC programming and mold making . They maximize the accuracy of the prototype model and facilitate necessary minor adjustments or checks by the prototype manufacturer during processing. We also accept various commonly used CAD formats such as STP, IGS, and PRT.
2, Clearly define processing requirements:
When providing 3D files, please be sure to provide detailed technical requirements , such as:
Accurate ID process drawings : specifying surface treatment requirements (such as Pantone color code, gloss level, electroplating effect, etc.).
Material requirements : Specify the required materials (such as ABS, PC, nylon, aluminum, stainless steel, etc.).
3, Post-processing:
Whether spray painting, screen printing, oxidation, polishing, etc. are required.
Critical dimensional tolerances : Dimensions that require strict protection and their tolerance ranges are specifically noted.
Use cases for STL files : When your prototype is primarily made using 3D printing processes (especially SLA/SLS), providing the STL format is standard practice. When exporting an STL file, please ensure you set a sufficiently high resolution (precision) to minimize detail loss and sharp edges caused by triangular faceting.
Summary and Recommendations
In summary, 3D files are needed for prototype making because they are the foundation of digital manufacturing , affecting cost assessment, production processing, and the final result .
STP files are CAD formats containing rich design information , suitable for high-precision machining and data exchange , and are the preferred source files for prototype manufacturing .
STL files are triangular mesh formats designed for 3D printing . They have poor editability but excellent compatibility .
For GaoFeng HK, we have the capability to process 3D files in various formats. To ensure your prototype project is completed efficiently and to a high standard, we strongly recommend that you prioritize providing STP format 3D design files, along with clear and concise process requirements. This will allow us to provide you with the most accurate quote and produce a high-quality prototype model that perfectly matches your design ideals.
If you have any questions about file formats, process selection, or any other aspects, please feel free to contact our technical advisors.