Introduction
Injection molds and blow molds are two common types of plastic molds. Although the difference between the two is only one letter, there are significant differences in their structure and purpose, and the mold opening prices are also different.
Generally, the price of injection molds is higher than that of blow molds. Why is that?
The price of injection molds is usually higher than that of blow molds, which is mainly determined by the significant differences between the two in molding principles, mold structure, precision requirements, material strength and production process.
The difference between the molding principles and functions of the two molds
1.Injection mold
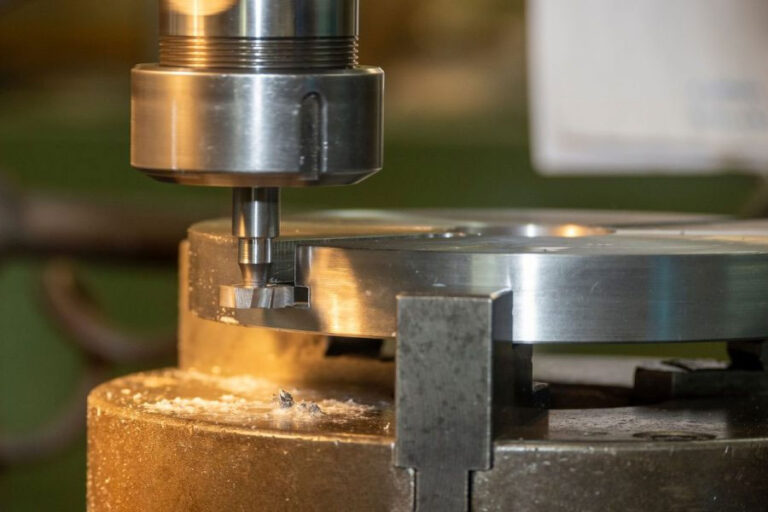
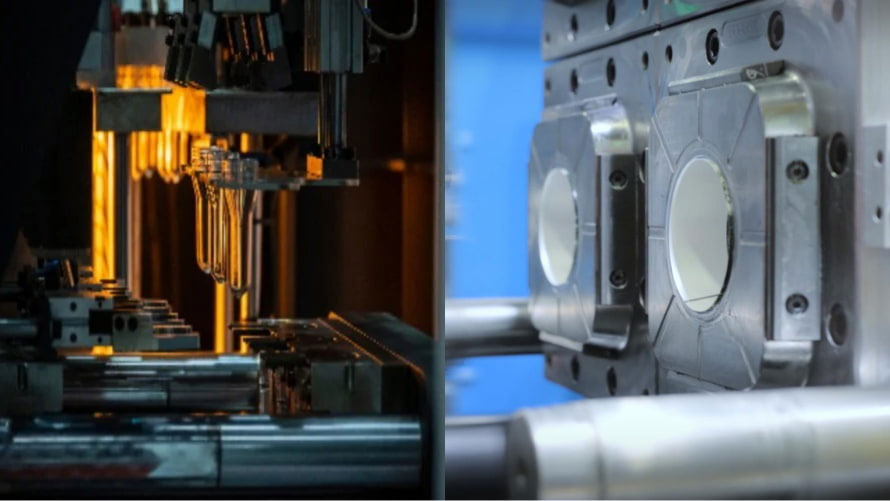
Injection molding is the process of injecting molten plastic into a closed mold cavity at high pressure (100-150MPa) through an injection machine, and then forming it after cooling and solidification.
The mold needs to completely wrap the melt and withstand high pressure, so it must have a high-strength structure, precise parting surface design and complex auxiliary systems (such as pouring, cooling, and ejection) to ensure part dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
2.Blow mold
Blow molding is to first extrude or inject the plastic melt into a tubular parison, then put it into a mold and blow it into the mold cavity with compressed air (0.2-1MPa) to form a hollow product (such as a bottle or container).
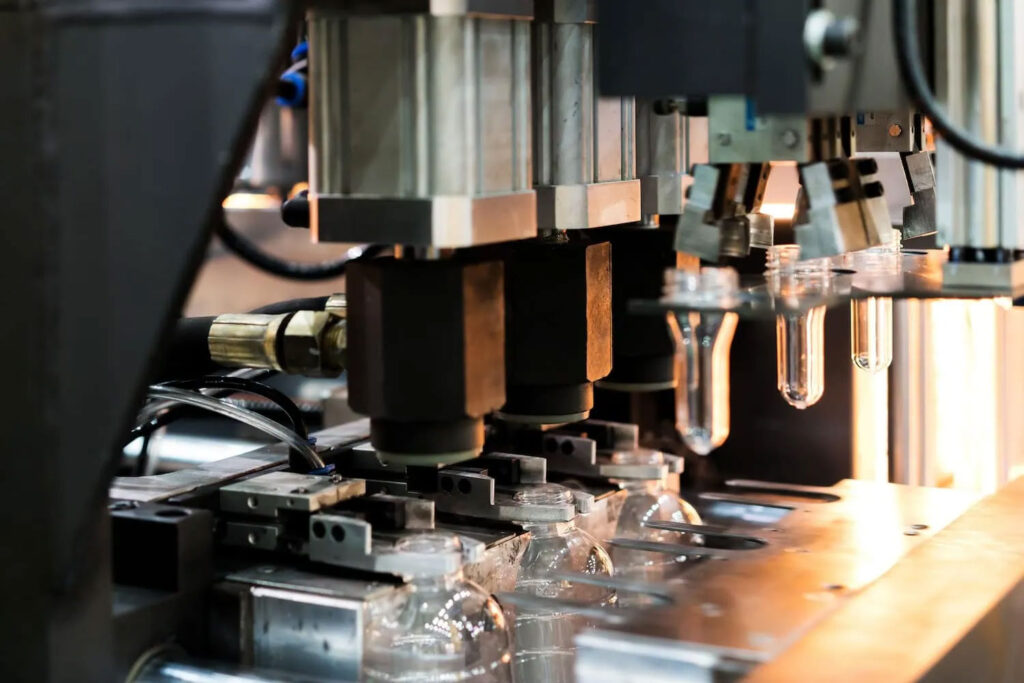

The mold only needs to provide a hollow outline and does not need to withstand high pressure. Its function focuses more on heavy blank clamping and gas channel design, and its structural complexity is much lower than that of an injection mold.
The difference between the two molds
1.Differences in mold structure
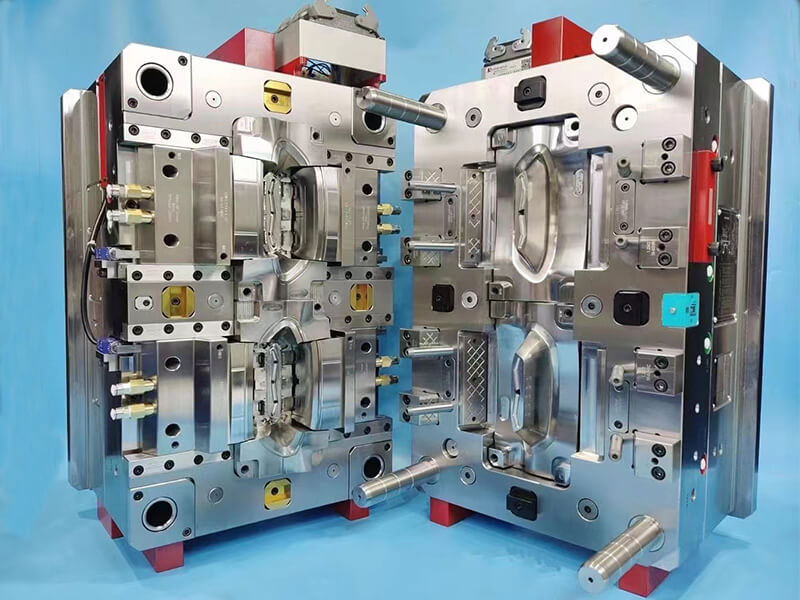
The injection mold is a sophisticated complex that integrates multiple systems. Its structure includes a fixed mold, a movable mold, a pouring system (main channel, branch channel, gate), cooling water channel, ejection mechanism (ejector pin, push plate) , etc. Complex parts also require a lateral core pulling mechanism (slider, inclined ejector).
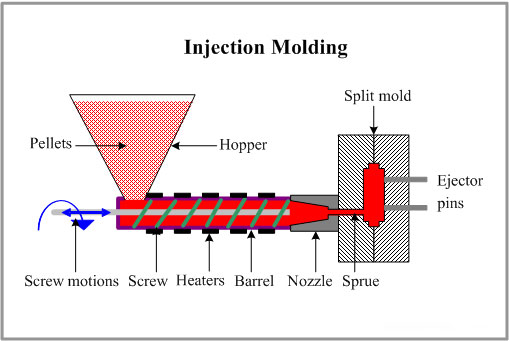
For example, the gate of the mobile phone case mold needs to be concealed, the cooling water channel needs to be arranged along the curved surface of the shell, and the ejection mechanism needs to avoid leaving marks on the exterior surface, all of which increase the difficulty of processing.
Therefore, the number of parts in an injection mold is large. A set of injection molds usually consists of dozens of parts, and the matching precision requirements of each component are high and the structure is relatively complex.
Blow molds , on the other hand, are simple opening and closing structures, primarily consisting of two mold halves (male and female), supplemented by a parison inlet and blow nozzle . The mold’s simple opening and closing motion eliminates the need for complex gating or ejection systems, and typically contains fewer than 10 parts.
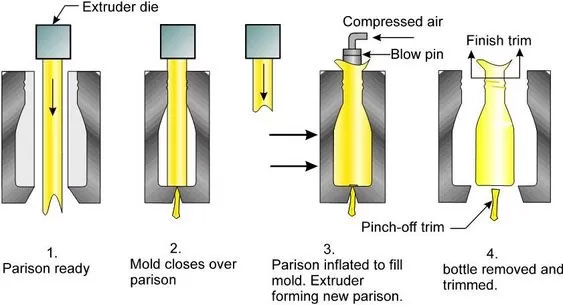
For example, a mineral water bottle blow molding mold only needs two half molds to clamp the parison, and air is introduced into the mold through a blowing nozzle. The structure is similar to a “clip” and the processing difficulty is relatively low.
Obviously, the more complex the mold structure is, the more difficult it is to design and process, and the higher the cost will naturally be.
2.Differences in material requirements
Since injection molds need to withstand high pressure during the injection process, they must use high-hardness mold steel (such as 718H, H13) , and may also need to undergo heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering to prevent cavity deformation or wear.
For example, the injection mold for automobile bumpers requires the use of pre-hardened steel, and the material cost is 3-5 times that of ordinary steel.
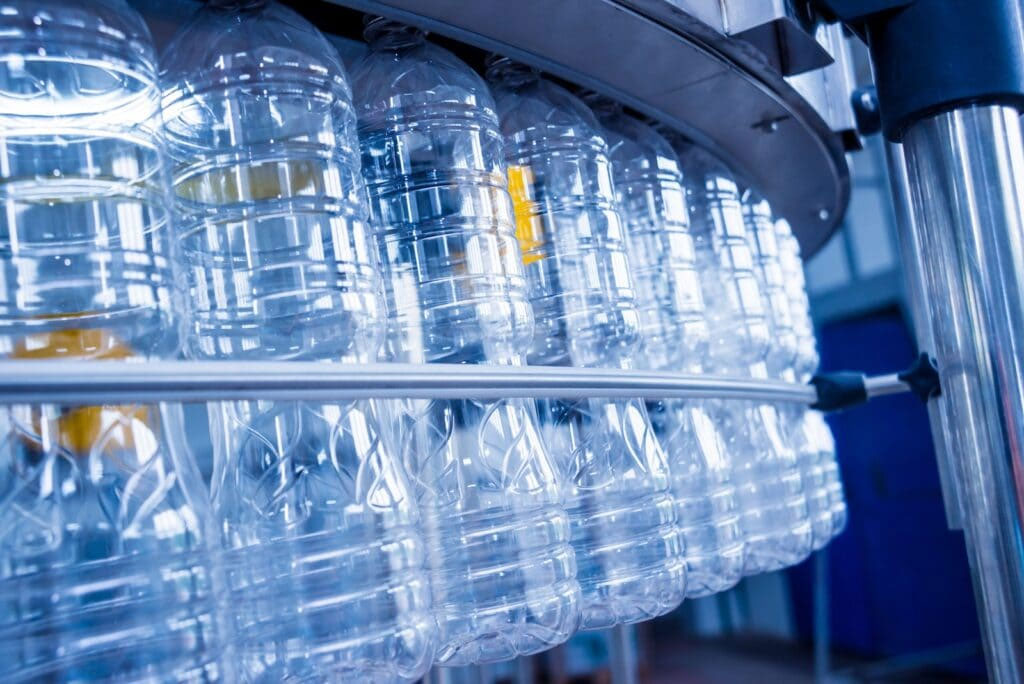

Blow molds withstand low pressure and are often made of aluminum alloy or ordinary carbon steel (45# steel) . They require no complex heat treatment and can even be machined directly. Aluminum alloys have low density and excellent machinability, and their cost is only half or even one-third of that of injection mold steel.
3.Differences in accuracy requirements
Injection molds usually have higher precision requirements because injection molded parts also require high precision. For example, the tolerance of electronic connectors is usually required to be within ±0.05mm. Therefore, the cavity of the injection mold needs to be processed through precision processes such as five-axis milling, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and wire cutting . The surface roughness must reach Ra0.8μm or less (mirror polishing).
If the parts have surface requirements such as leather grain and etching, laser engraving or chemical etching is also required, and the cost of a single process can reach thousands of yuan.
The precision requirements for blow-molded products are lower. For example, for plastic barrels, the tolerance is allowed to be ±0.5mm. The mold processing is mainly ordinary milling and turning, and no high-precision equipment is required. The surface roughness Ra1.6μm can meet the requirements.
Due to the high precision requirements, the processing cycle of injection molds is also longer, which may take 20-30 days, while the processing cycle of blow molds may only take 5-10 days.
4.Differences in design complexity
Injection mold design requires Moldflow analysis to simulate melt flow, predict weld lines, and predict warpage. Cooling system design ensures a cavity temperature difference of ≤5°C. These analyses can take weeks. For example, mold design for thin-walled products (such as disposable lunch boxes) requires repeated optimization of gate locations to avoid short shots and deformation.
The core of blow mold design lies in matching the parison dimensions with the mold cavity. The blow-up ratio (typically 2-4 times) is calculated using empirical formulas, eliminating the need for complex simulations. For example, when designing a beverage bottle mold, the cavity dimensions simply need to be determined based on the bottle capacity. This streamlined process can reduce the design cycle to just one or two days.
The higher the design complexity and the longer the time spent, the higher the price of the injection mold.
5.Differences in application scenarios
Injection molds have a wider range of application scenarios and are often used in the production of plastic products such as daily necessities, medical supplies, consumer electronics, and automotive parts. They are also suitable for solid or semi-solid parts with complex structures.
The core application of blow molding molds is to produce hollow products, such as plastic bottles, daily chemical bottles, fuel tanks, etc.
Conclusion
Due to the high-pressure molding requirements, precise structural design, high-hardness materials and complex processing technology, the price of injection molds is usually 3-5 times that of blow molds of the same specifications.
If the product is a high-precision solid part, injection mold is a must; if it is a hollow thin-walled product, blow mold has the advantage of low cost and high efficiency.