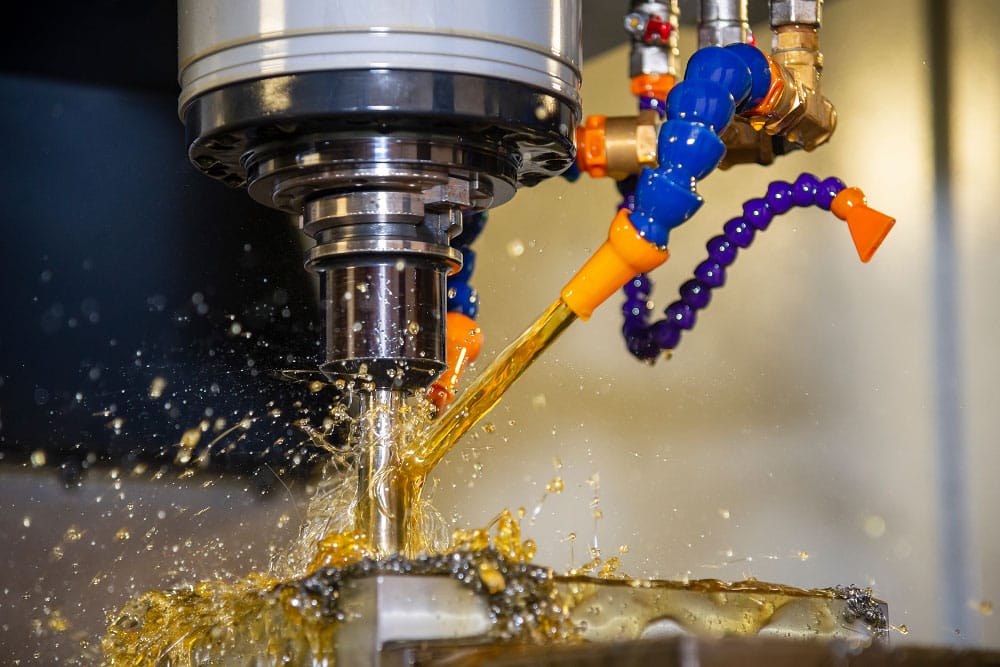
Why do the cutting fluid stink or corrode?
The main reason cutting fluid deteriorates and becomes smelly is that it contains a large number of bacteria, primarily aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic bacteria live in environments containing minerals, such as water, cutting fluid concentrate, and leaked machine oil.
In the presence of oxygen, they divide into two every 20 to 30 minutes. Anaerobic bacteria, on the other hand, live in an oxygen-free environment and divide into two every hour. Their metabolism releases SO₂, giving them a rotten egg smell and turning the cutting fluid black. When the number of bacteria in cutting fluid exceeds 10⁶, the fluid will begin to smell.
Bacteria enter the cutting fluid mainly through the following channels:
1 ) Bacteria invade during the preparation process, such as bacteria in the water used to prepare the cutting fluid.
2) Bacteria in the air enter the cutting fluid.
3) The transfer of workpieces between processes causes the contamination of cutting fluid.
4) The operator’s bad habits, such as littering.
5) The cleanliness of machine tools and workshops is poor.

Cutting fluids are widely used in cutting processes due to their cooling, lubricating, cleaning, and rust-preventing properties. However, cutting fluids often experience deterioration, odor, corrosion, foaming, and skin allergies in operators. Based on our practical experience, the following discusses these issues and their solution
Methods for controlling bacterial growth
1) Use high-quality and stable cutting fluid.
2) Using pure water to prepare concentrated fluid is not only easy to prepare, but also can improve the lubricity of the cutting fluid, reduce the amount carried away by chips, and prevent bacterial erosion.
3) When using, the ratio of concentrated liquid in the cutting fluid should not be too low, otherwise it will easily cause bacterial growth.
4) Since the oil used in machine tools contains bacteria, it is necessary to minimize the mixing of oil leaked from machine tools into the cutting fluid.
5) When the pH value of the cutting fluid is between 8.3 and 9.2, bacteria cannot survive, so new cutting fluid should be added in time to increase the pH value.
6) Keep the cutting fluid clean and do not allow it to come into contact with dirty oil, food, tobacco and other contaminants.
7) Use fungicides frequently.
8) Keep the workshop and machine tools clean.
9) If the equipment does not have a filtering device, the floating oil should be skimmed off regularly to remove dirt.

Methods for preventing and controlling corrosion
1) Use pure water to prepare cutting fluid, and the proportion of cutting fluid should be used according to the recommended value in the instructions of the cutting fluid used.
2) Use anti-rust liquid when necessary.
3) Control the number of bacteria and avoid the production of bacteria.
4) Check the humidity and make sure the humidity in the working environment is within an appropriate range.
5) Avoid contamination of cutting fluid.
6) Avoid contact between dissimilar materials, such as aluminum and steel, cast iron (containing magnesium) and copper, etc.