Introduction
Injection molds, stamping molds, and die-casting molds are three common types of molds in industrial production. Their working principles, applicable materials, and production scenarios vary. The following are the product types and characteristics they are applicable to.
Characteristics of three molds
Injection mold
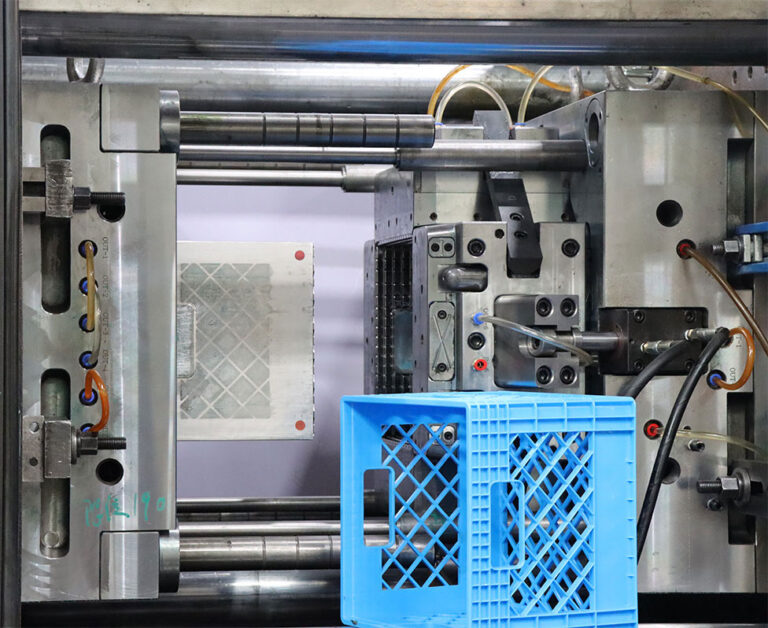
Injection molds are tools that inject molten plastic raw materials into the mold cavity and obtain products after cooling and solidification. They are suitable for the molding of thermoplastics (such as PP, PE, ABS, PVC, etc.) and some thermosetting plastics.
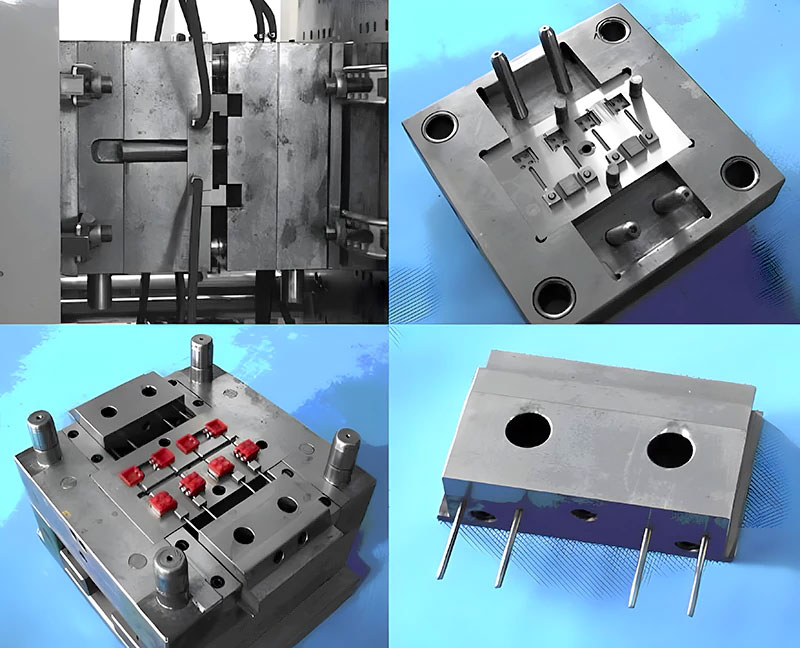
Its product features are: complex shape, high precision, can have details such as inner cavity, thread, boss, etc., and good surface quality.
Stamping die
Stamping dies are used to apply pressure to metal sheets (in a few cases, non-metal sheets) through a press to cause them to undergo plastic deformation or separation, thereby obtaining products of the desired shape and size . They are mainly suitable for metal materials (such as steel plates, aluminum plates, copper plates, stainless steel plates, etc.).
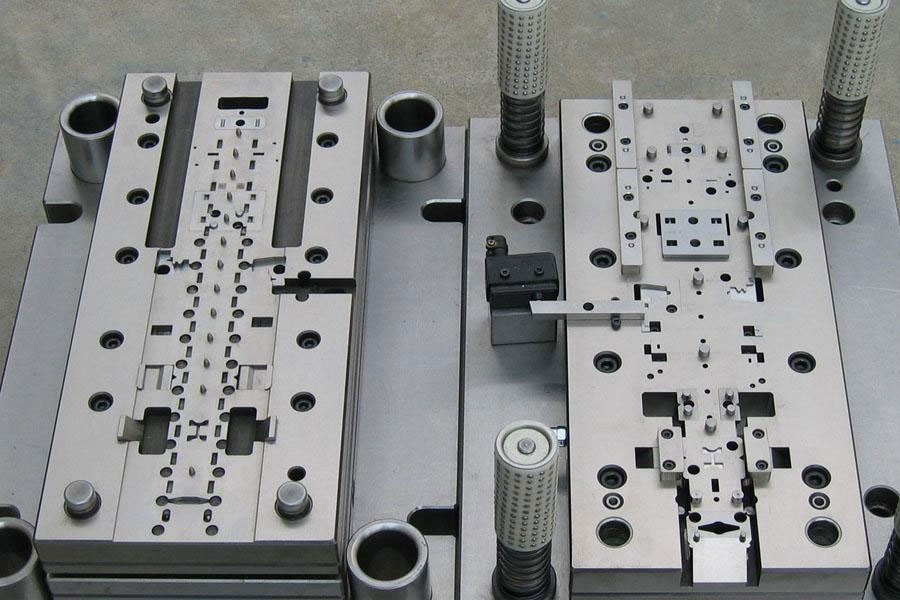
Its product features are: relatively uniform thickness, mass production, high precision (especially precision stamping), and suitable for flat or curved structures.
Die casting mold
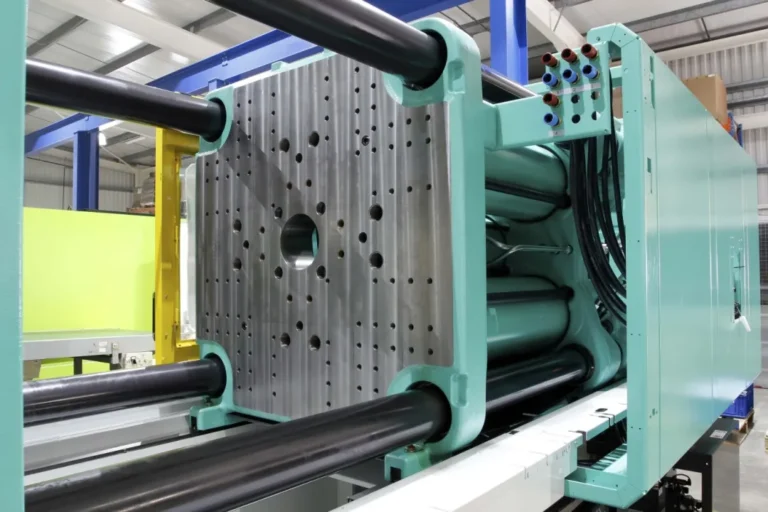
Die-casting molds are made by quickly pressing molten metal (mostly non-ferrous metals) into the mold cavity under high pressure, and then cooling and solidifying to obtain the product. They are suitable for low-melting-point non-ferrous metals and their alloys (such as aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, magnesium alloys, copper alloys, etc.).
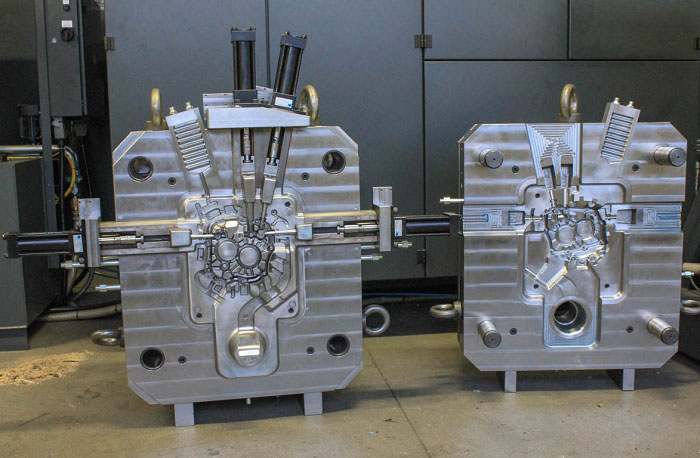

Its product features are: high casting density, good strength, the ability to form complex thin-wall structures, high dimensional accuracy, and suitable for replacing some metal processing parts to reduce costs.
Application products of three molds
Common application products of injection molds
Daily necessities: plastic cups, toothbrush handles, toys, storage boxes, plastic tableware, etc.
Electronic appliances: mobile phone casings, computer keyboards, charger casings, TV casings, connectors, plastic gears, etc.
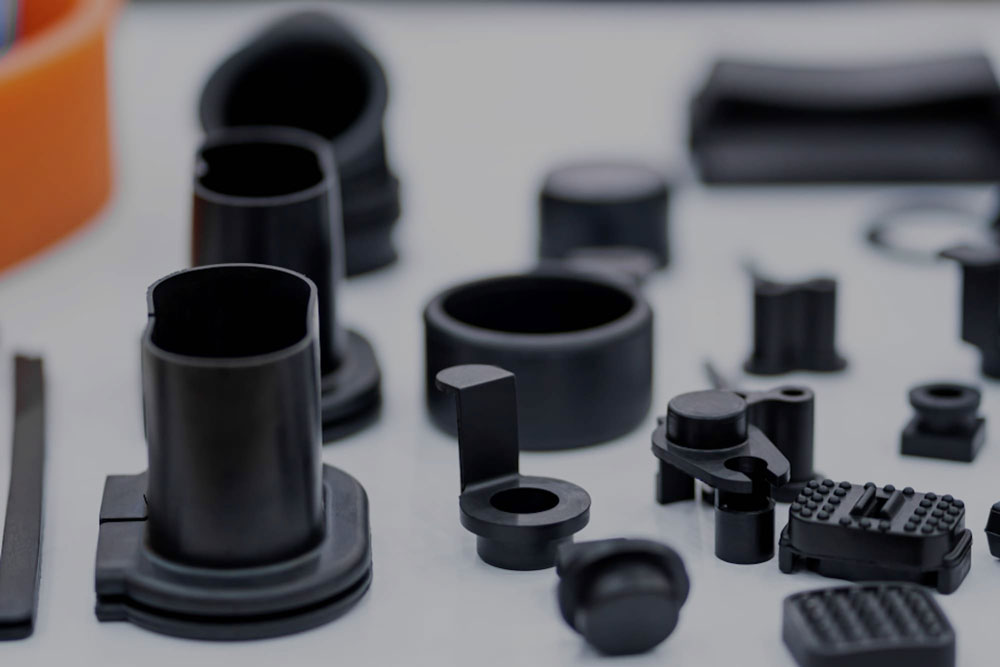

Auto parts: car dashboards, door handles, bumpers (plastic parts), interior parts (such as seat adjustment knobs), etc.
Medical supplies: syringes, infusion set parts, plastic medicine bottles, medical instrument housings, etc.
Common application products of stamping dies
Automobile industry: body panels (such as doors, hoods), frame parts, brake pad steel backs, automobile radiator fins, etc.
Electronic appliances: motor core (stamped and laminated silicon steel sheets), battery shells, mobile phone SIM card trays, connector shrapnel, heat sinks, etc.
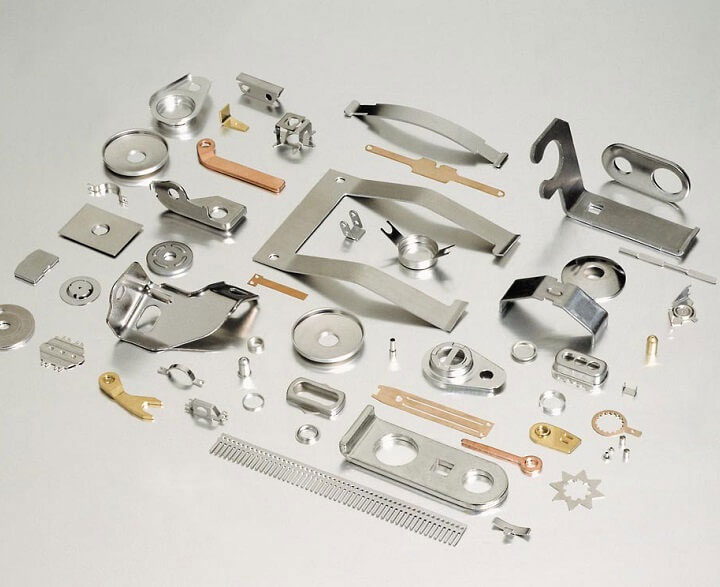

Hardware products: nails, nuts, washers, scissors blades, key blanks, metal mesh (such as anti-theft window mesh), etc.
Daily necessities: cans (can bodies and lids are stamped), metal lunch boxes, stainless steel tableware (such as the initial forming of spoons and forks), etc.
Common application products of die-casting molds
Auto parts: engine block, gearbox housing, aluminum alloy wheel, steering knuckle, water pump housing, etc. (structural parts that bear certain mechanical properties).
Electronic appliances: laptop computer casings (magnesium alloy), camera bodies (zinc alloy), LED radiators (aluminum alloy), motor casings, etc.
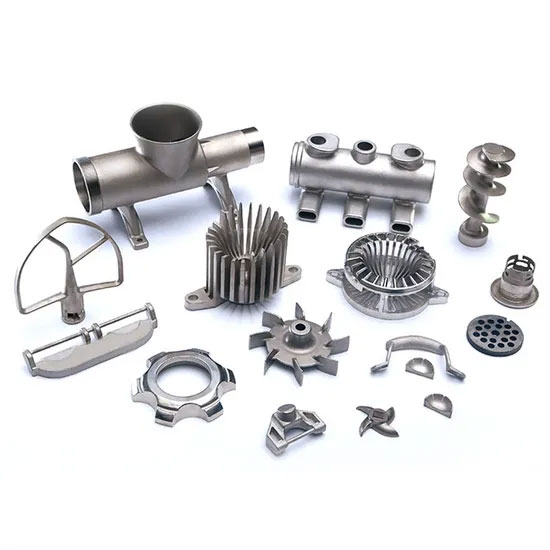

Hardware tools: wrenches, screwdriver handles (zinc alloy die-casting and surface treated), lamp bases, etc.
Household items: faucet housings (copper alloy die-casting), door lock panels (zinc alloy), furniture connectors, etc.
Summary
The core difference between the three is that injection molding is for plastics, stamping is for plastic deformation/separation of metal sheets, and die casting is for high-pressure forming of molten metal, so there are clear applicable boundaries in product materials and structures.