Do you know what precision tolerance levels can be achieved by turning, milling, planing, grinding, drilling and boring?
Tolerance grade refers to the grade that determines the degree of dimensional accuracy. The national standard stipulates that it is divided into 20 grades, from IT01, IT0, IT1, IT2 to IT18. The larger the number, the lower the tolerance grade (processing accuracy), the larger the allowable range of dimensional variation (tolerance value), and the easier the processing difficulty.
The processing accuracy required for product parts varies according to their functions, and the selected processing methods and processing technologies are also different. This article introduces the processing accuracy that can be achieved by several common processing methods such as turning, milling, planing, grinding, drilling, and boring.
ISO Tolerance Grades (IT) Table
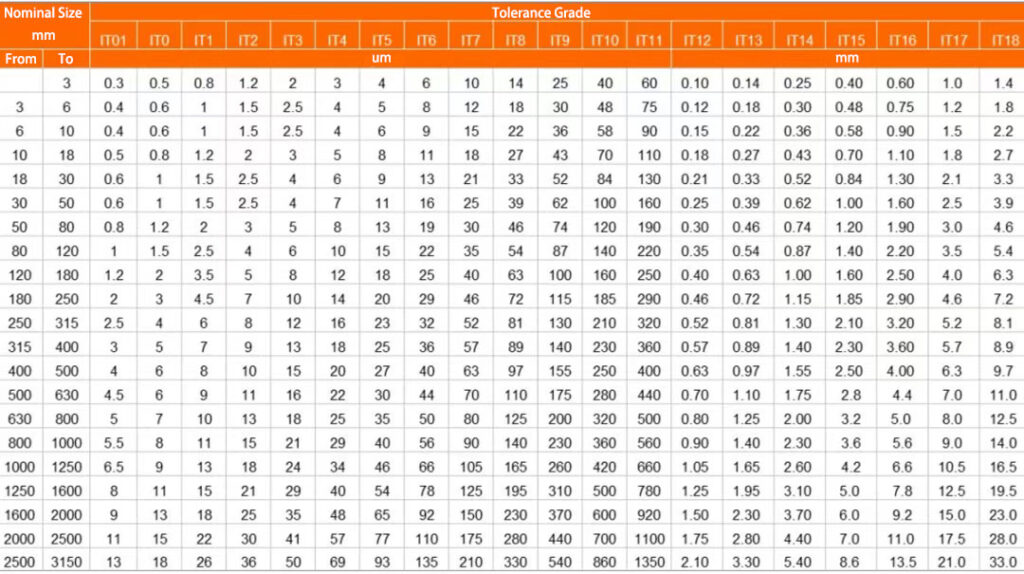
Note: When the basic size is less than 1mm, there is no IT14 to IT18
01-Turning
The workpiece rotates and the turning tool moves in a straight line or curve in the plane for cutting. Turning is generally performed on a lathe to process the inner and outer cylindrical surfaces, end faces, conical surfaces, forming surfaces and threads of the workpiece.
The turning accuracy is generally IT8~IT7, and the surface roughness is 1.6~0.8μm.
1) Rough turning strives to improve turning efficiency by using large cutting depth and large feed rate without reducing cutting speed, but the machining accuracy can only reach IT11, and the surface roughness is Rα20~10μm.
2) For semi-finishing and finishing turning, high speed and small feed rate and cutting depth should be used as much as possible. The machining accuracy can reach IT10~IT7, and the surface roughness is Rα10~0.16μm.
3) Using a finely polished diamond turning tool on a high-precision lathe to high-speed precision turn non-ferrous metal parts can achieve a machining accuracy of IT7~IT5 and a surface roughness of Rα0.04~0.01μm. This type of turning is called “mirror turning”.
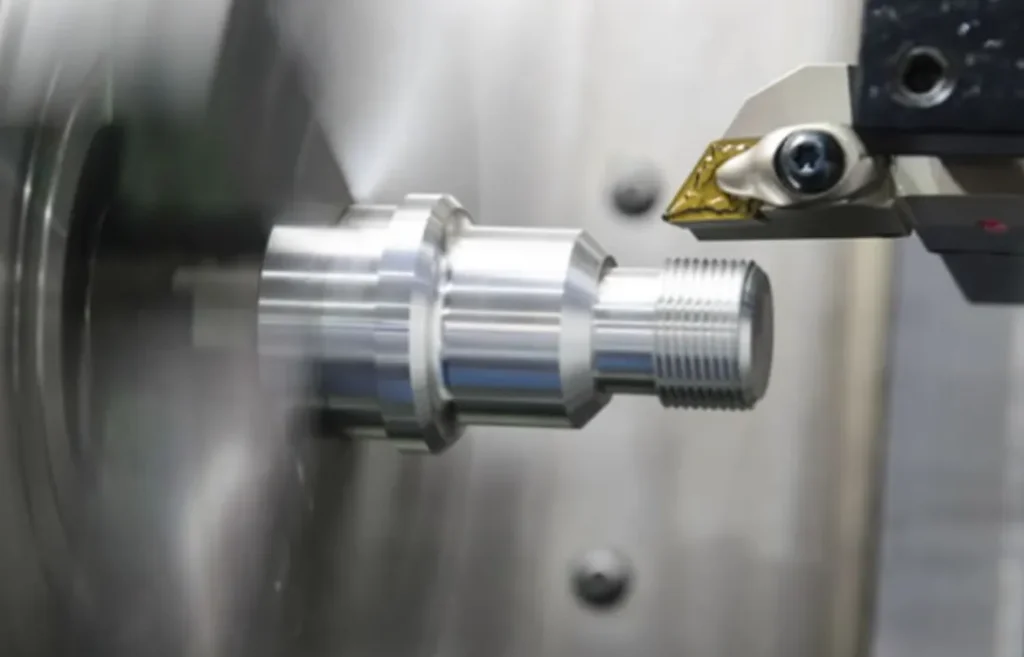

02-Milling
Milling is a highly efficient machining method that uses a rotating multi-edged tool to cut workpieces. It is suitable for machining planes, grooves, various forming surfaces (such as splines, gears and threads) and special surfaces of molds. According to whether the main motion speed direction during milling is the same or opposite to the workpiece feed direction, it is divided into forward milling and reverse milling.
The milling processing accuracy can generally reach IT8~IT7, and the surface roughness is 6.3~1.6μm.
1) The machining accuracy during rough milling is IT11~IT13, and the surface roughness is 5~20μm.
2) The machining accuracy during semi-finishing milling is IT8~IT11, and the surface roughness is 2.5~10μm.
3) The machining accuracy during fine milling is IT16~IT8, and the surface roughness is 0.63~5μm.

03-Planing
Planing is a cutting method that uses a planer to make horizontal relative linear reciprocating motion on the workpiece, and is mainly used for the shape processing of parts.
The planing processing accuracy can generally reach IT9~IT7, and the surface roughness is Ra6.3~1.6μm.
1) The rough planing accuracy can reach IT12~IT11, and the surface roughness is 25~12.5μm.
2) The semi-precision planing accuracy can reach IT10~IT9, and the surface roughness is 6.2~3.2μm.
3) The precision of fine planing can reach IT8~IT7, and the surface roughness is 3.2~1.6μm.
04-Grinding
Grinding refers to a processing method that uses abrasives and grinding tools to remove excess material from a workpiece. It is a finishing method widely used in the machinery manufacturing industry.
Grinding is usually used for semi-finishing and finishing, with an accuracy of IT8~IT5 or even higher, and the surface roughness is generally ground to 1.25~0.16μm.
1) The surface roughness of precision grinding is 0.16~0.04μm.
2) The surface roughness of ultra-precision grinding is 0.04~0.01μm.
3) The surface roughness of mirror grinding can reach below 0.01μm.

05-Drilling
Drilling is a basic method of hole processing. Drilling is often performed on drilling machines and lathes, but can also be performed on boring machines or milling machines.

The machining accuracy of drilling is low, generally only reaching IT10, and the surface roughness is generally 12.5~6.3μm. After drilling, expansion and reaming are often used for semi-finishing and finishing.
06-Boring
Boring is a cutting process that uses a tool to enlarge the inner diameter of a hole or other circular contour. Its application range generally ranges from semi-roughing to finishing. The tool used is usually a single-edged boring tool (called a boring bar).
1) The boring accuracy of steel materials can generally reach IT9~IT7, and the surface roughness is 2.5~0.16μm.
2) The machining accuracy of precision boring can reach IT7~IT6, and the surface roughness is 0.63~0.08μm.
The following table is more intuitive!
Machining Methods and Achievable Tolerance Grades (IT)
| Machining Method | Achievable Tolerance Grade (IT) |
| Grinding | IT01 – IT5 |
| Cylindrical Grinding | IT01 – IT5 |
| Surface Grinding | IT01 – IT5 |
| Diamond Grinding | IT01 – IT5 |
| Diamond Filing | IT01 – IT5 |
| Broaching | IT5 – IT7 |
| Reaming | IT6 – IT8 |
| Turning | IT7 – IT10 |
| Filing | IT8 – IT10 |
| Milling | IT8 – IT10 |
| Planing & Shaping | IT9 – IT11 |
| Drilling | IT10 – IT12 |
| Rolling & Extrusion | IT10 – IT12 |
| Stamping | IT11 – IT13 |
| Die Casting | IT12 – IT14 |
| Powder Metallurgy (Forming) | IT12 – IT14 |
| Powder Metallurgy (Sintering) | IT13 – IT15 |
| Sand Casting & Gas Cutting | IT14 – IT16 |
| Forging | IT15 – IT16 |