Material properties
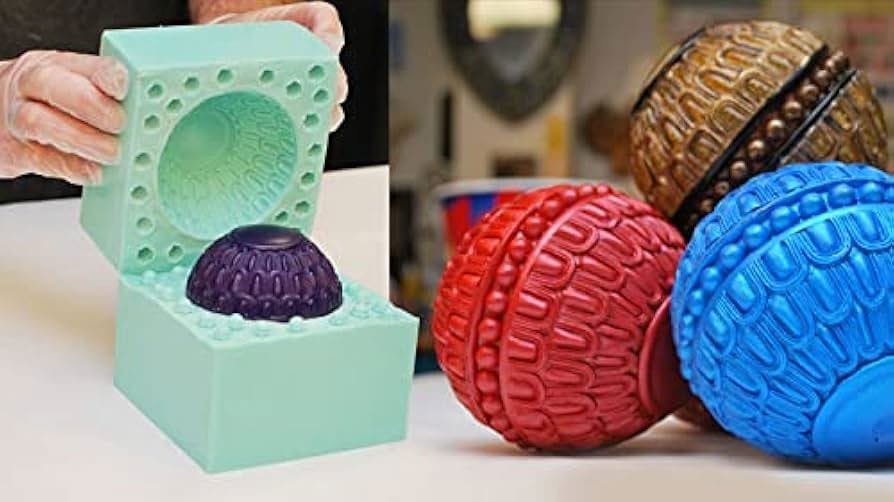

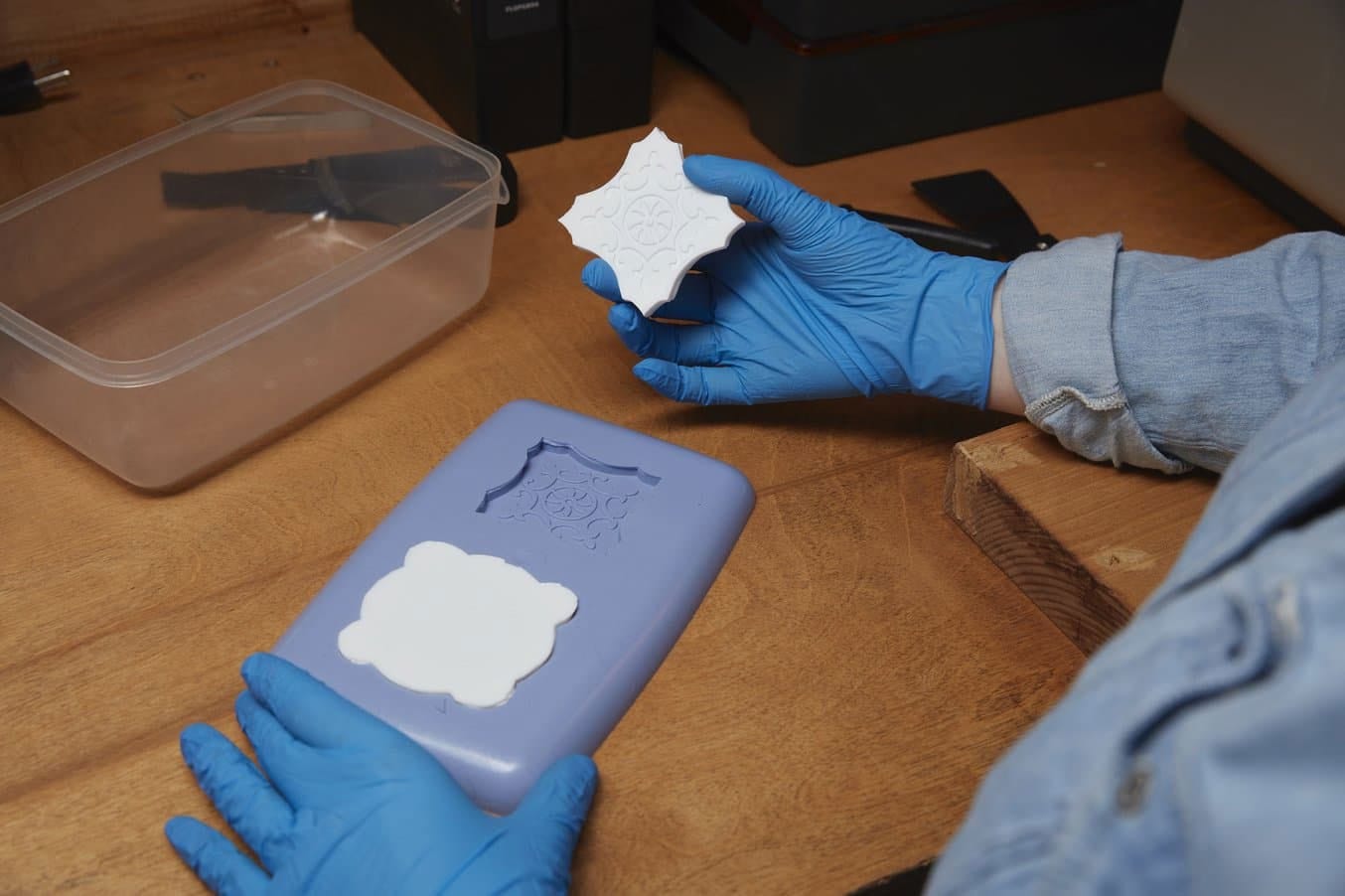
Silicone mold
Material: Mainly liquid silicone rubber (thermosetting), containing cross-linking agent and filler, with soft texture and high elasticity.
Features: Wide temperature resistance range (-40~230℃), strong resistance to chemical corrosion, but low hardness and easy to deform and age after long-term use .
Safety: Food-grade silicone is non-toxic and suitable for kitchenware and maternal and child products .
Plastic mold
Material: mostly mold steel (such as H13) or aluminum alloy (rigid thermoplastic material) .
Characteristics: High hardness, good wear resistance, and excellent dimensional stability; but it is easy to become brittle at low temperatures and may release harmful substances at high temperatures .
Manufacturing process and structure
Silicone mold
Process characteristics:
Injection molding (room temperature/heat curing), no runner system required
Structural complexity: simple, relying on shell support
Plastic mold
Process characteristics:
Injection molding/extrusion precision machining (CNC, EDM) required
Structural complexity: complex (including cavity, ejector, etc.)
Cost and applicable scenarios
| index | Silicone mold | Plastic mold |
|---|---|---|
| Mold cost | Low (about 50% of plastic mold) | High (high steel cost) |
| life | Short (suitable for small batches) | Long (up to millions of times) |
| Typical Applications | Handicrafts, food molds, medical products | Electronic parts, auto parts, home appliance casings |
Accuracy and post- processing
Precision requirements: Plastic molds have higher requirements (surface finish Ra<0.8μm), while silicone molds usually only need to meet Ra0.8~1.6μm.

Polishing Difficulty: Plastic molds are more difficult to polish due to their high material hardness; silicone molds are easy to polish .
???? Summary
Silicone molds are suitable for trial production of smaller batches (20-30 pieces), especially in the new product development stage. The molds are made of soft silicone and have good toughness. They can produce parts with complex structures, fine patterns, no draft angles or even reverse draft. The production cycle is short and the product quality is high.
Before mass production of products, many manufacturers need to produce some products in small batches for market feedback testing. At this time, if mass production processes such as injection molding are used, the production cycle is long and the mold opening cost is high. If the structure needs to be adjusted later, the cost of changing the mold is high or even impossible. Therefore, the silicone mold-replacing process is a very good choice in the early stage.
Injection molding is one of the most widely used molding processes for mass production of plastic products. Its biggest features are wide material selection, high production efficiency, and rapid mass production after the mold is completed.
Silicone Molding vs. Injection Molding Comparison
| Category | Silicone Molding | Injection Molding |
| Equipment | Vacuum Casting Equipment | Injection Molding Machine |
| Mold Material | Silicone | Various Types of Steel |
| Mold Production Cycle | About 1 Week | 1-2 Months |
| Product Material | PU (ABS-like, PC-like, PP-like, PMMA-like, PA-like, etc.) | ABS, PC, PMMA, PA, PP, PEEK, PETE, etc. (Various Engineering Plastics) |
| Material Properties | Good anti-aging and corrosion resistance | Wide selection with diverse properties |
| Mold Lifespan | 20-30 parts | 10,000+ (varies by mold material) |
| Surface Characteristics | Usually requires coating for desired effects; can also use color masterbatch | Typically ready for appearance use without coating |