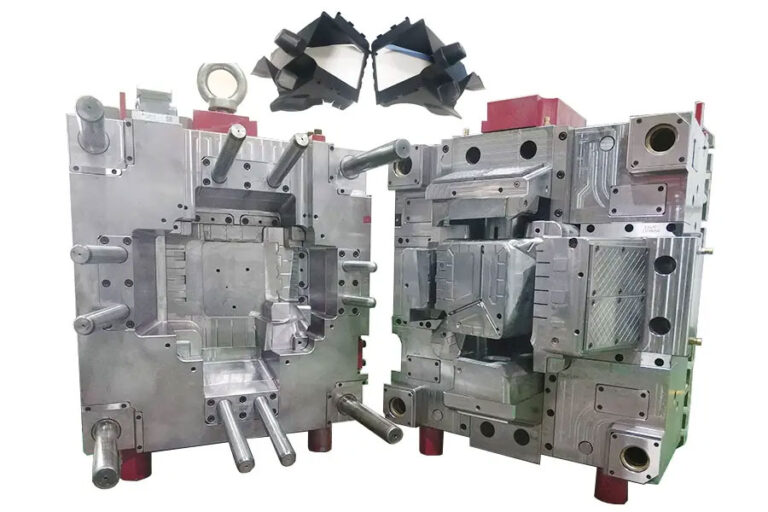
Many CNC processing manufacturers have been seeking ways to control processing costs as much as possible. Many users have also found that different companies offer very different quotations for the same product. What is the main reason?
Putting aside many factors such as factory size and factory location, how can we better control the cost of CNC machining?
Next, we will share with you what factors will affect the CNC machining cost. Let’s learn about it together.
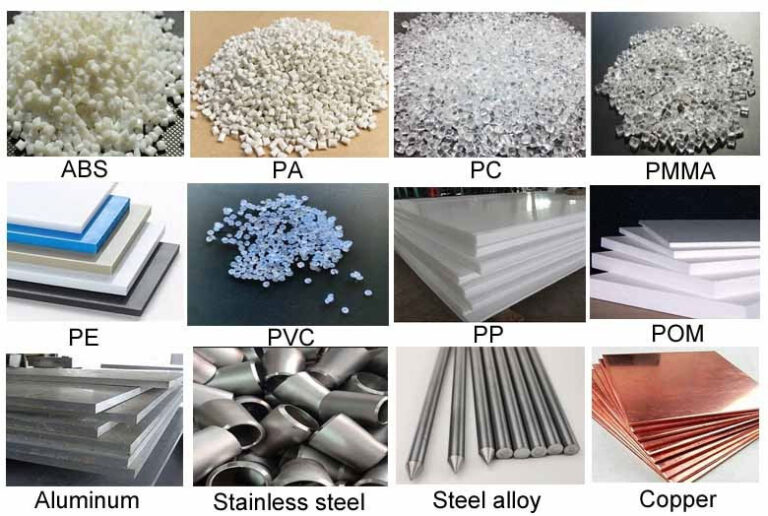
1.Materials
The cost will depend on:
Raw Materials: Includes the cost of the raw materials themselves. The availability of raw materials is also a factor that affects the cost. Materials that are difficult to find will be more expensive than materials that are easily available. Machinists purchase materials by the block, and they will charge for the use of the entire block. Customers must try to fit as many parts as possible in one block. Using fewer blocks can save money in the long run.

Machinability: Materials with low machinability will require more time and effort to machine. In addition to time and effort, these materials also consume cutting fluids, electricity, and cutting tools. Materials with high machinability can be machined faster.
Additional measures: If the material poses certain hazards, additional measures will be taken. An example is the processing of composite materials. During processing, a lot of dust is generated. The dust is a health hazard and can damage machine controls and equipment. To control this dust, a suitable cartridge dust collector is installed. Such additional measures will increase costs.
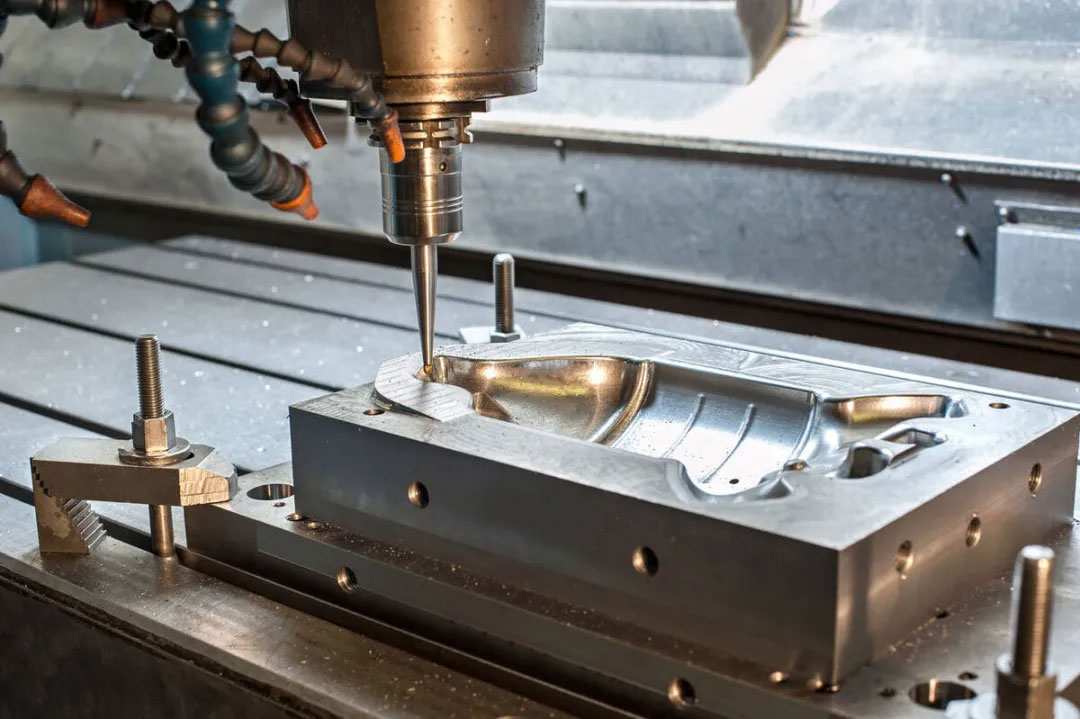
2.Manufacturing equipment
The shop sets an hourly rate for running the machine. This rate depends on:

Number of axes.
The operation to be performed. For example: drilling, milling, etc.
The number of machines used, i.e. one or more than one.
The capacity and size of the equipment.
Tool cost.
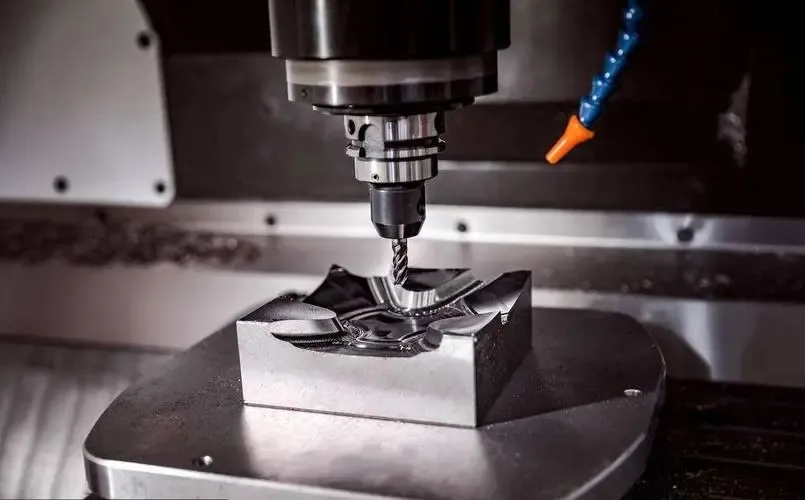

3.Tolerance
Tighter tolerances increase the cost of CNC machining. Tighter tolerances require more time and more effort to produce a part. It also requires better quality control equipment for inspection. Tighter tolerances will dictate the tools, machines, and cutting techniques used to make the part.
Tolerances must be provided only for appropriate features. For example: mating areas. If tolerances are provided for every dimension, costs will increase due to increased setup time, modifications to computer programs, and scrap and rework.
4.Parts

It takes time for an operator to set up the machine used to make a part. This setup cost is fixed regardless of quantity. The same setup cost can be assigned to single and batch quantities. If we order in bulk, the overall cost will increase, but the cost per piece will decrease. In addition, the machine shop can purchase bulk raw materials at a better price if we order in bulk.
5.Labor
Although CNC is automated, the following tasks require manual intervention.
Design: If we outsource the task of preparing the 3D model or CAD file of the part, there is a labor cost involved. This cost can be eliminated by preparing the CAD file ourselves.

Programming: Manufacturing engineers review the design and make suggestions. Programmers then prepare the computer program.
Setup: The operator must load the tool into the tool changer and set up the machine and workpiece.
Post-processing: It involves cleaning, bracket removal and assembly of parts.
6.Design
Complex features such as non-standard hole sizes, lettering, and thin walls increase the cost of CNC machining. Complex features require more programming time, specialized tools, and multiple setups to make the part. Increased run times increase costs.
By eliminating unnecessary features, we can simplify the design. Where possible, we can choose recessed text over raised text. For thin walls, a good rule of thumb is a 3:1 aspect ratio. Walls can be machined more easily by adding draft at angles of 1, 2, and 3 degrees.