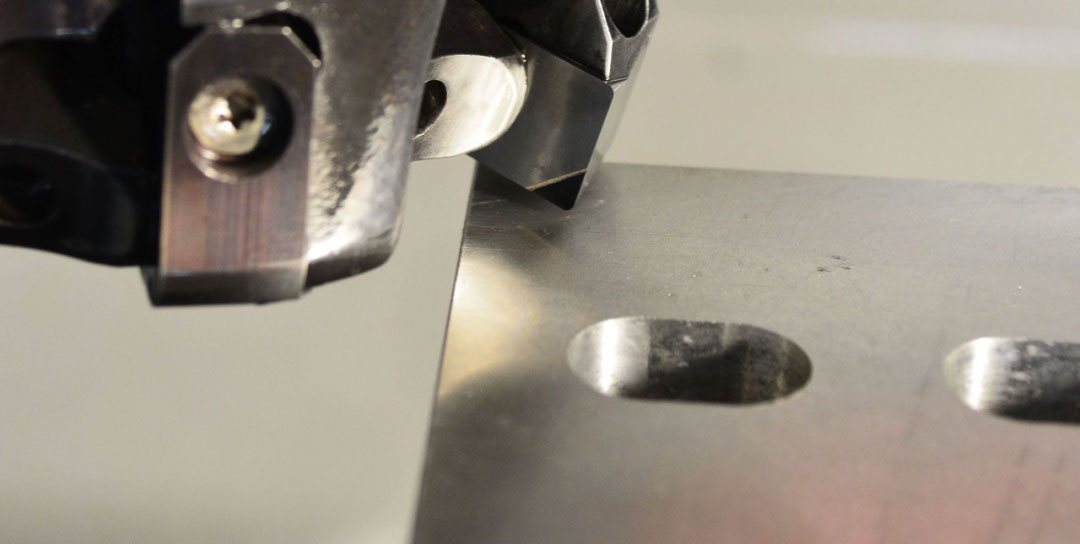
Polycrystalline diamond tools are a type of high-end tools that use natural or synthetic diamond particles as the core material of the cutting edge. Its manufacturing process is quite technical, and the blades are made by combining diamond particles (usually polycrystalline diamond, PCD for short) with a cemented carbide matrix and sintering them at high temperature and high pressure. This composite structure retains the superhardness of diamond and enhances the overall strength of the tool with the help of the cemented carbide matrix.
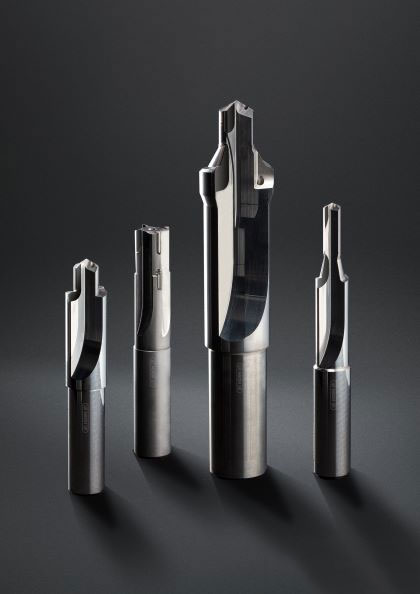

The outstanding advantages of this type of tool are derived from the inherent characteristics of diamond – Mohs hardness is as high as 10, which is the hardest material in nature. Therefore, polycrystalline diamond tools have excellent wear resistance. When processing non-ferrous metals such as high-silicon aluminum alloys and copper alloys, the service life can reach 10-50 times that of traditional carbide tools. At the same time, diamond has a low friction coefficient and is not prone to built-up edge during cutting. It can achieve extremely high surface processing quality and is often used in precision parts processing that require mirror effects.

However, polycrystalline diamond tools also have obvious limitations. They have poor impact resistance and high brittleness, and are difficult to withstand large cutting vibrations and impact loads, so they are not suitable for intermittent cutting or processing materials containing hard particles. In addition, diamonds are prone to chemical reactions with iron elements at high temperatures, and have low heat resistance. Usually, the cutting temperature needs to be controlled below 600°C, which makes it impossible to use it for processing ferrous metals.
In terms of structural design, polycrystalline diamond tools usually adopt a “local strengthening” solution, distributing diamond particles only in the working part of the blade (i.e., the cutting edge area), which not only ensures cutting performance but also reduces manufacturing costs.
In order to expand the scope of application, diamond-like carbon coating (DLC) technology came into being. By coating an amorphous carbon coating on the surface of ordinary tools, the cutting edge can obtain hardness and wear resistance close to that of diamond, while retaining the toughness of the base material. This type of coated tool costs less than pure polycrystalline diamond tools and is suitable for general occasions with high requirements for processing accuracy, becoming an alternative solution with outstanding cost performance.