Introduction
“Prototype” is a common industry term, and the professional terminology is: sample, verification piece, sample, proportional model, etc. Generally it is a verification sample manufactured in small quantities before the product is finalized.

Products that have just been designed are usually not perfect or even unusable. If they are directly produced and have defects, they will all be scrapped, which greatly wastes manpower, material resources and time.

Therefore, usually products that have just been developed or designed need to be prototyped. For products that need to be produced by molds, one or more functional samples are usually made first based on the product appearance drawings or structure drawings to check the rationality of the appearance or structure.

Prototype is to verify the feasibility of the product without making a mold. Prototype is generally a small number of samples, with a short production cycle, less loss of manpower and material resources, and can quickly find out the shortcomings of product design and improve them, providing sufficient basis for product finalization and mass production.
There are many ways to make prototypes, and different processes have their own advantages and disadvantages.
1.Clay Sculpture
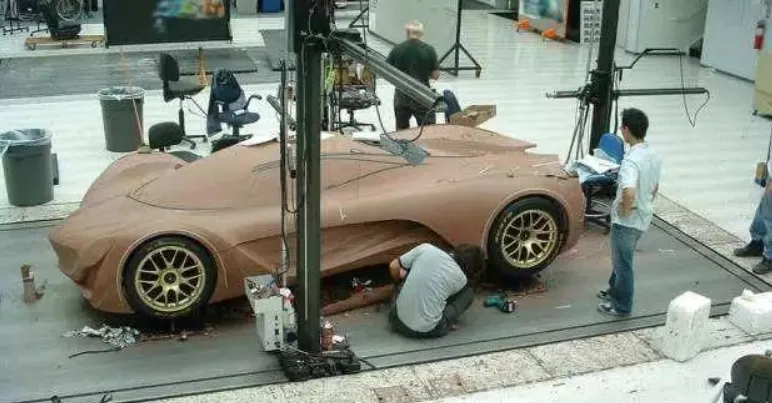

Hand-carving a three-dimensional product out of oil clay is called clay sculpture. In the early days of industrial manufacturing when there was no automated equipment, prototypes were all shaped by carving clay.
The material used for clay sculpture is hard oil clay, which is generally carved manually. The sculptor piles and carves the oil clay according to the design concept of the product or refers to the design picture, and finally obtains the oil clay model of the product appearance.

To obtain a high-quality appearance model, the sculptor’s aesthetic sense and artistic touch are required to be relatively high, so the cost is relatively higher.
2.CNC engraving machining
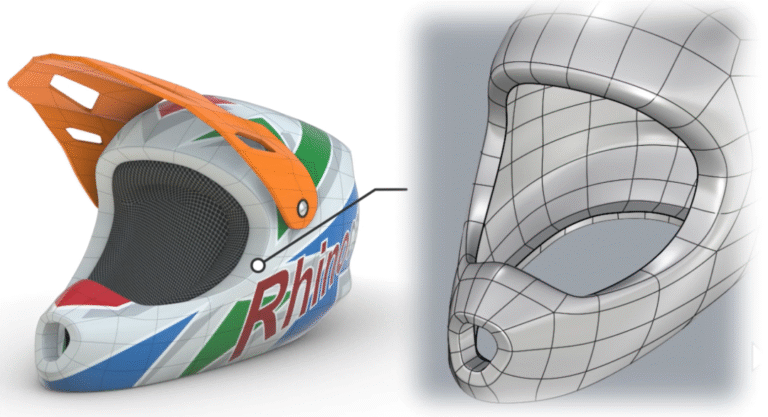
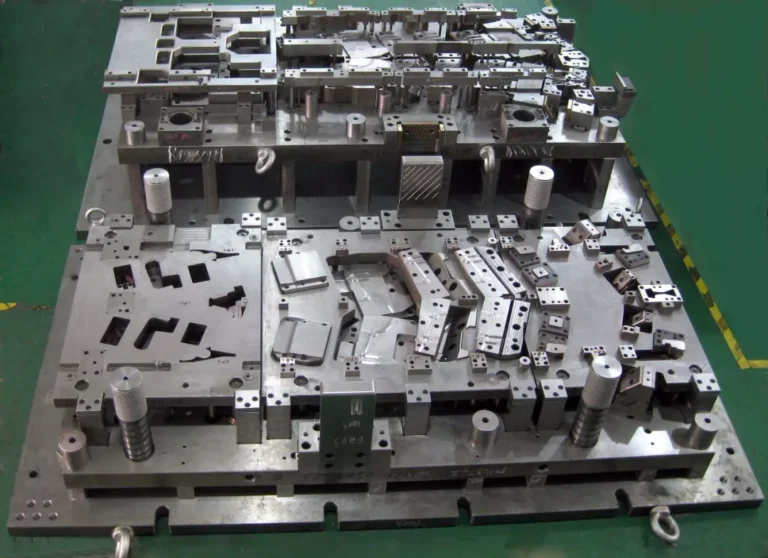
CNC engraving machine processing is a more traditional prototype production process. It is good at small tool finishing and has the ability of milling, grinding, drilling and high-speed tapping. It is widely used in 3C industry, mold industry, medical industry and other fields.

The prototypes produced by CNC engraving machine processing technology can accurately reflect the information expressed in the drawings, and the surface quality of the prototypes is high, especially after the surface is sprayed and silk-screened, it is even more dazzling than the products produced after the mold is opened.
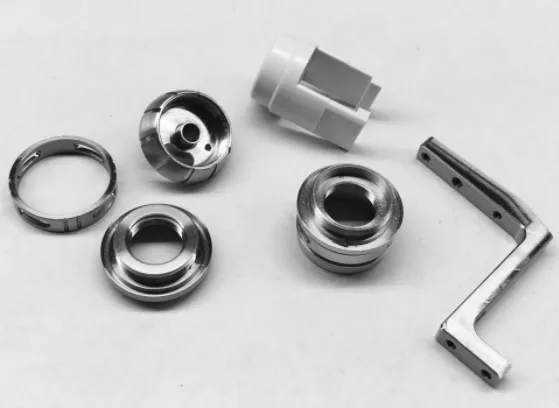

CNC processing is suitable for products with high material toughness requirements, large products, and high precision. Suitable materials include organic glass, resin, wood, metal (including copper, aluminum, and soft steel with a hardness less than HRC40), etc.
Most CNC equipment used to make prototypes are 3-axis machines. Some workpieces with complex structures need to be disassembled and processed and then manually assembled, because 3-axis machines can only process one surface at a time.
3.3D printing
3D printing is usually achieved by using digital technology material printers. It is often used to make models in the fields of mold manufacturing, industrial design, etc., and then gradually used for the direct manufacturing of some products. There are already parts printed using this technology. This technology is used in jewelry, footwear, industrial design, architecture, engineering and construction (AEC), automobiles, aerospace, dental and medical industries, education, geographic information systems, civil engineering, firearms and other fields.
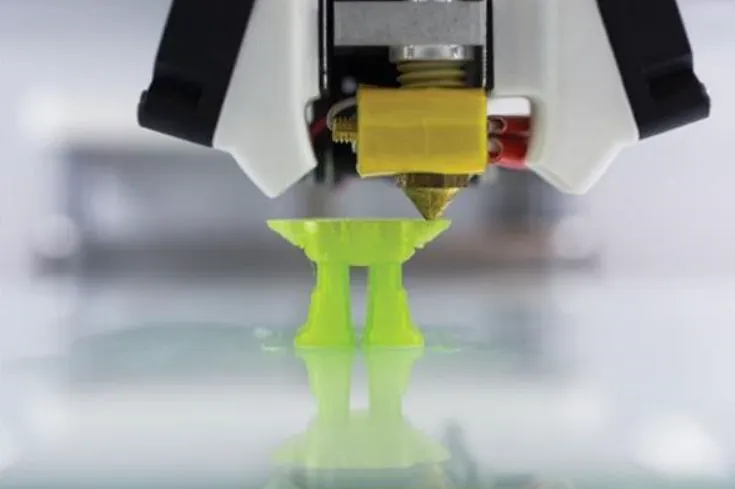

There are many different 3D printing technologies that differ in the way they use the materials available and in the way they build up the parts in layers.
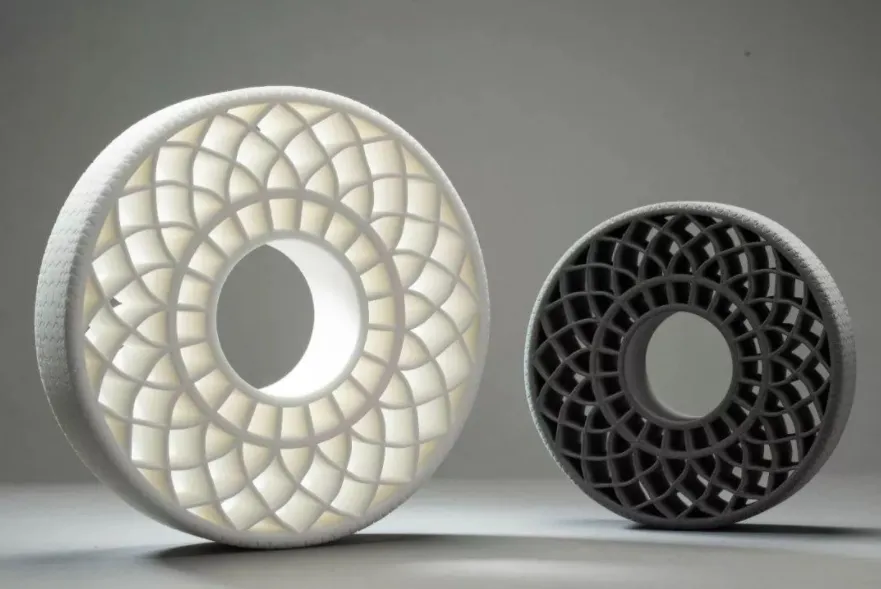
Commonly used materials for 3D printing include resin, nylon glass fiber, durable nylon material, stainless steel, aluminum material, titanium alloy, silver plating, gold plating, gypsum material, rubber material, etc.
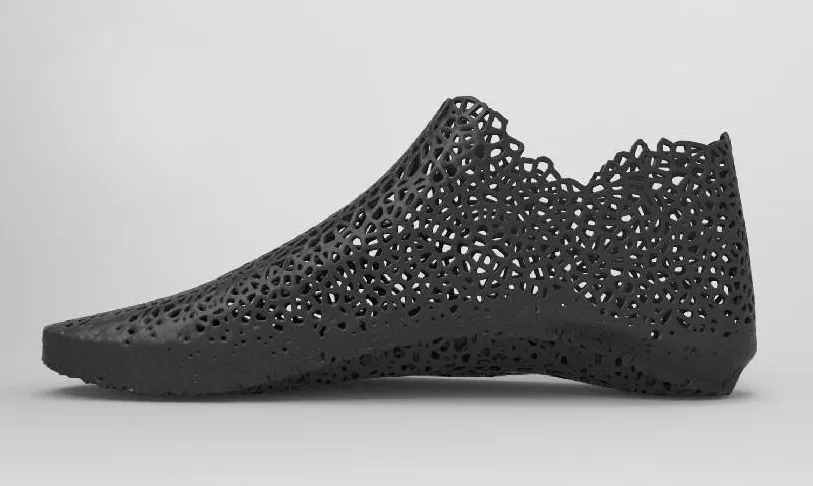

3D printing has low cost (high material utilization), fast cycle, simple operation, high precision, and can be integrated into one piece regardless of the complexity of the product structure. This molding method is the most popular, and it is an important supplement to traditional processing methods rather than a substitute.
4.Silicone compound molding
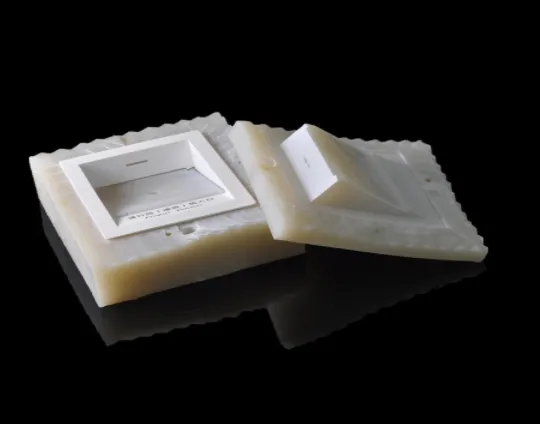
The silicone compound molding process refers to the process of degassing, mixing, preheating, and injection molding the castable under vacuum conditions, and then performing secondary curing molding in a constant temperature box at 60℃-80℃ for 2-3 hours.
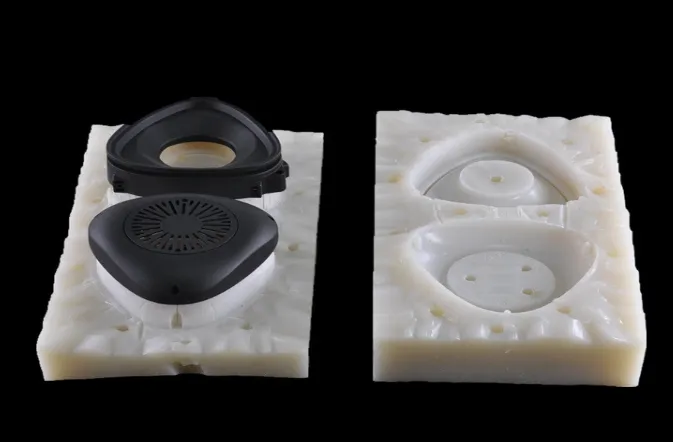

The imitation products made by silicone mold can reach the strength and hardness of ABS and other materials. More than 20 identical products can be made using one silicone mold, which greatly reduces the development cost, cycle and risk of products.

For small batch samples with complex structures, uniform wall thickness, and certain functional and appearance requirements, the cost of making iron molds is high and the cycle is long. Silicone molds can be selected for molding.
The materials that can be made of silicone molds include ABS, PC, PP, soft rubber, PMMA, nylon, PVC and so on.

Disadvantages of silicone mold: the mold is not resistant to acid and alkali, not resistant to aging, short life, and the mold surface is prone to marks, stripes, and roughness. Because the mold is a soft mold, the tolerance is in the range of 0.1-0.2mm, so the product precision is not high.