Introduction
Because of its unparalleled efficiency and accuracy, CNC machining is an indispensable part of modern manufacturing. The processed components find application in almost every industry. Nevertheless, there exist certain limitations with regard to the scope and capabilities of CNC machining, and not every component is appropriate for CNC machining. Today, we will discuss the ways to ascertain if a component can be CNC machined.
1. Turning accuracy
Turning refers to the cutting process in which the workpiece rotates and the turning tool moves in a straight line or curve in a plane. It is used to process the workpiece’s internal and external cylindrical surfaces, end faces, conical surfaces, forming surfaces and threads, etc.
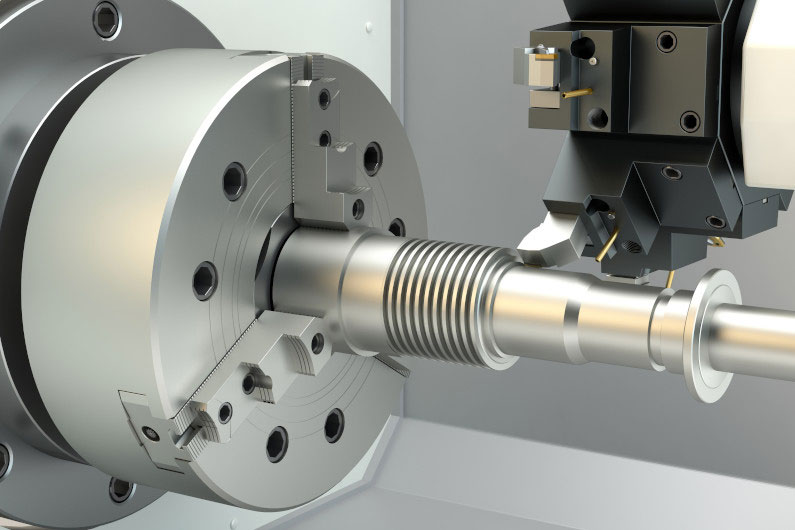
The surface roughness of turning processing is 1.6-0.8μm.
Rough turning requires the use of large cutting depth and large feed rate to improve turning efficiency without reducing the cutting speed, and the surface roughness requirement is 20-10um.
For semi-finishing and finishing turning, high speed and small feed rate and cutting depth should be used as much as possible, and the surface roughness should be 10-0.16um.
Using a finely ground diamond turning tool on a high-precision lathe, non-ferrous metal workpieces can be turned at high speed with a surface roughness of 0.04-0.01um. This type of turning is also called “mirror turning”.
2. Milling accuracy
Milling is a highly efficient machining method that uses a rotating multi-edged tool to cut workpieces. It is suitable for machining planes, grooves, and special surfaces such as splines, gears, and threaded molds.
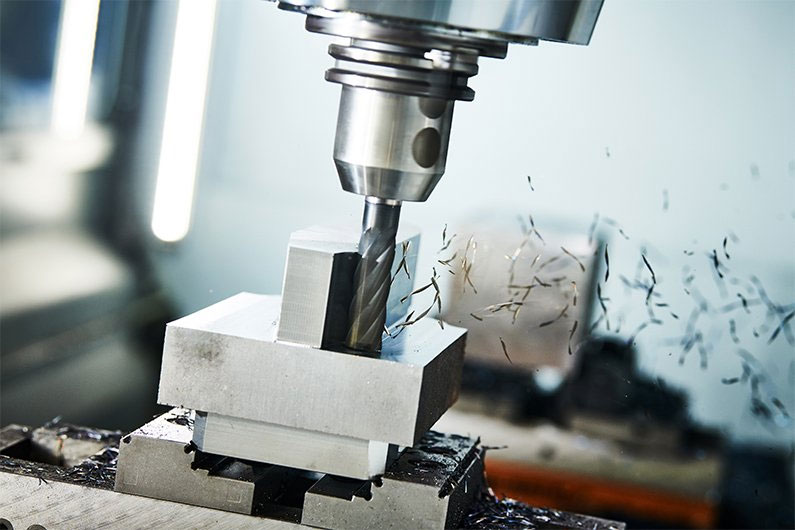

The milling processing accuracy is generally 6.3-1.6μm.
The surface roughness during rough milling is 5-20μm.
The surface roughness during semi-finishing milling is 2.5-10μm.
The surface roughness during fine milling is 0.63-5μm.
3.Planing accuracy
Planing is a cutting method that uses a planer to make horizontal relative linear reciprocating motion on the workpiece, and is mainly used for the shape processing of parts.
The surface roughness of the planing process is Ra6.3-1.6μm.
The surface roughness of rough planing is 25-12.5μm.
The surface roughness of semi-fine planing is 6.2-3.2μm.
The surface roughness of the fine planing process is 3.2-1.6μm.
4.Grinding accuracy
Grinding refers to a processing method that uses abrasives and grinding tools to remove excess material from a workpiece. It is a finishing method widely used in the machinery manufacturing industry.
Grinding is usually used for semi-finishing and finishing, and the surface roughness is generally 1.25-0.16μm. The surface roughness of precision grinding is 0.16-0.04μm.
The surface roughness of ultra-precision grinding is 0.04-0.01μm.
The surface roughness of mirror grinding can reach below 0.01μm.
5.Boring
It is a cutting process that uses a tool to enlarge the internal diameter of a hole or other circular contour. Its application range generally ranges from semi-roughing to finishing. The tool used is usually a single-edged boring tool (called a boring bar).
The boring accuracy of steel materials can generally reach 2.5-0.16μm.
The machining accuracy of precision boring can reach 0.63-0.08μm.