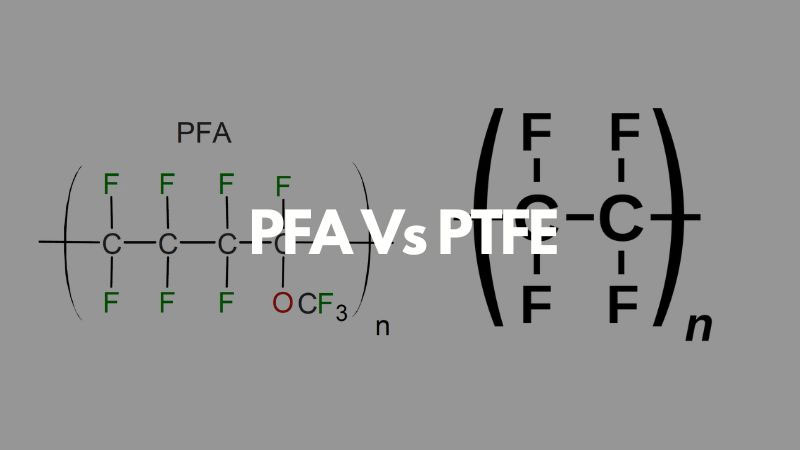
The first is the difference in chemical structure:
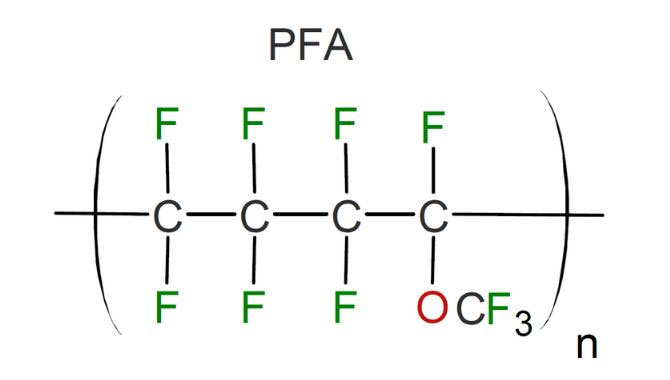
PFA incorporates a perfluoroalkoxy group, which is equivalent to replacing a fluorine atom in PTFE with a perfluoroalkoxy group. A carbon atom is directly linked to an oxygen atom, which in turn is linked to a group such as a perfluoromethyl or perfluoroethyl group. Compared to PTFE, this reduces melt viscosity, facilitating processing. Other properties are similar to those of PTFE.
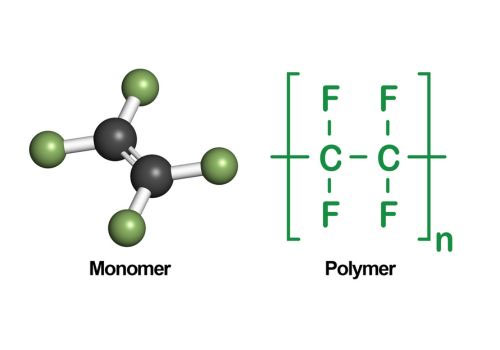
The second difference is the applications:
PFA—Has all the same excellent properties as polytetrafluoroethylene, but also exhibits excellent thermoplasticity and can be processed using conventional thermoplastic resin processing methods. It is produced by copolymerizing tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoropropyl vinyl ether in a certain ratio in an aqueous medium containing a perfluorocarboxylate dispersant and a persulfate initiator. It appears as white, translucent particles.

It not only has the same operating temperature as PTFE, but also exhibits greater mechanical strength (approximately 2-3 times greater) at 250°C and excellent stress crack resistance. Its wide processing range and excellent formability make it suitable for compression molding, extrusion molding, injection molding, and transfer molding. It can be used to manufacture insulation jackets for wires and cables, high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency insulation components, corrosion-resistant linings for chemical pipelines, valves, and pumps; special parts for the machinery industry; various anti-corrosion materials for the textile industry; and welding rods for PTFE anti-corrosion linings.

Produced by extruding fusible PTFE pellets, it has a translucent milky white appearance, a smooth surface, and a dense and uniform cross-section. It is specifically designed for welding PTFE sheets and tubes, allowing simple PTFE products to be welded into complex, larger pieces.
This aqueous dispersion is a copolymer obtained by copolymerizing tetrafluoroethylene and perfluoropropyl vinyl ether, added with an emulsifier and concentrated at a specific temperature. It has a solids content of 30% ± 1%. It is milky white or light yellow, translucent in appearance. It possesses the excellent properties of fusible polytetrafluoroethylene resin and can be used for extended periods at 260°C. Its excellent anti-sticking, anti-corrosion, and easy-to-process properties have been developed into advanced coatings for spraying and impregnation applications. It is widely used in copying technology and the food industry as an anti-stick and anti-corrosion material.
PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) is produced by the suspension or dispersion polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene monomer. Its molecular weight is 5.2-4.5 × 10⁷. It is a white powder, 75% of which is 400-mesh. It is odorless, non-toxic, and non-toxic. Its relative density is 2.1-2.3, its refractive index is 1.37, its glass transition temperature is 327°C, and its thermal decomposition temperature is 415°C. Above 400°C, it experiences a slight weight loss and releases toxic gases.

The operating temperature is -250-260°C, and it can last up to 10,000 hours at 210°C. It offers excellent chemical resistance, including resistance to strong acids (including aqua regia), strong bases, and grease. It is insoluble in all solvents, has an extremely low coefficient of friction, good wear resistance, and is self-lubricating. It also has excellent aging resistance. It also has excellent electrical properties and arc resistance. It is non-sticky, resisting almost all sticky substances and being completely non-flammable. It is known as the “King of Plastics.” Tensile strength (MPa) > 23 Elongation (%) > 250.
Again, the difference in processing methods:
The main difference in processing methods is that PFA can be processed by hot melt injection molding, while PTFE cannot be processed by hot melt injection molding.