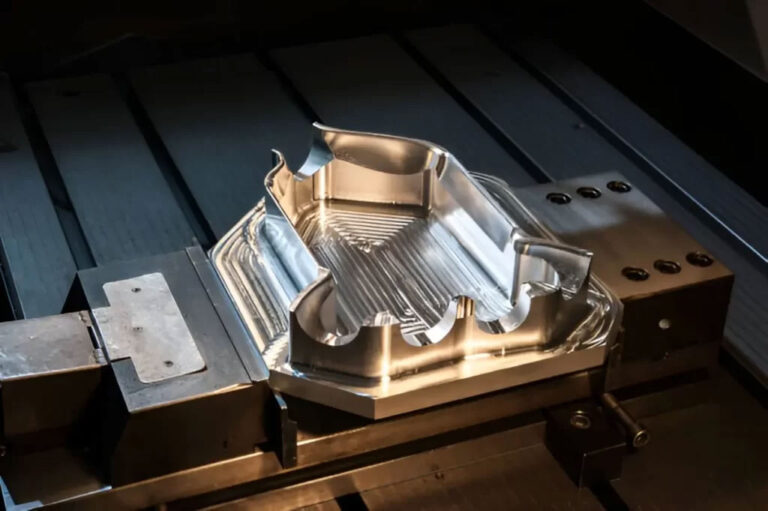
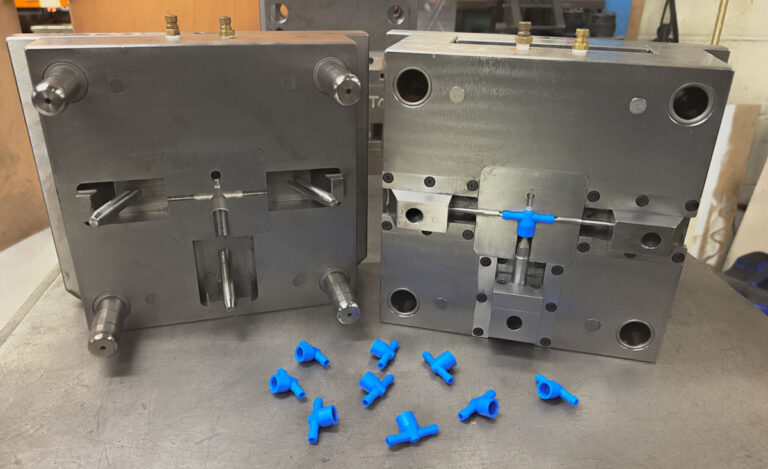
Silicone mold technology and steel mold technology are two different mold manufacturing and product molding technologies. The main differences are reflected in materials, costs, production cycles, precision, application scenarios , etc.
Let’s take a look at the characteristics and differences between the two with Gaofeng.
Materials and mold making
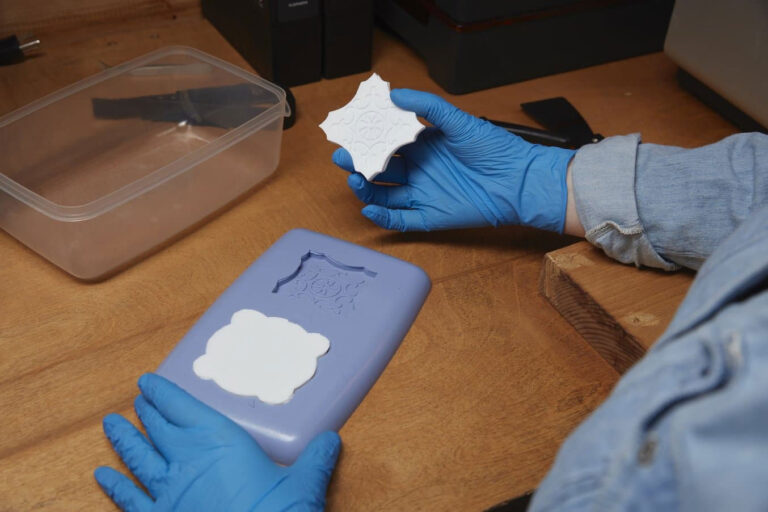
Silicone molding process
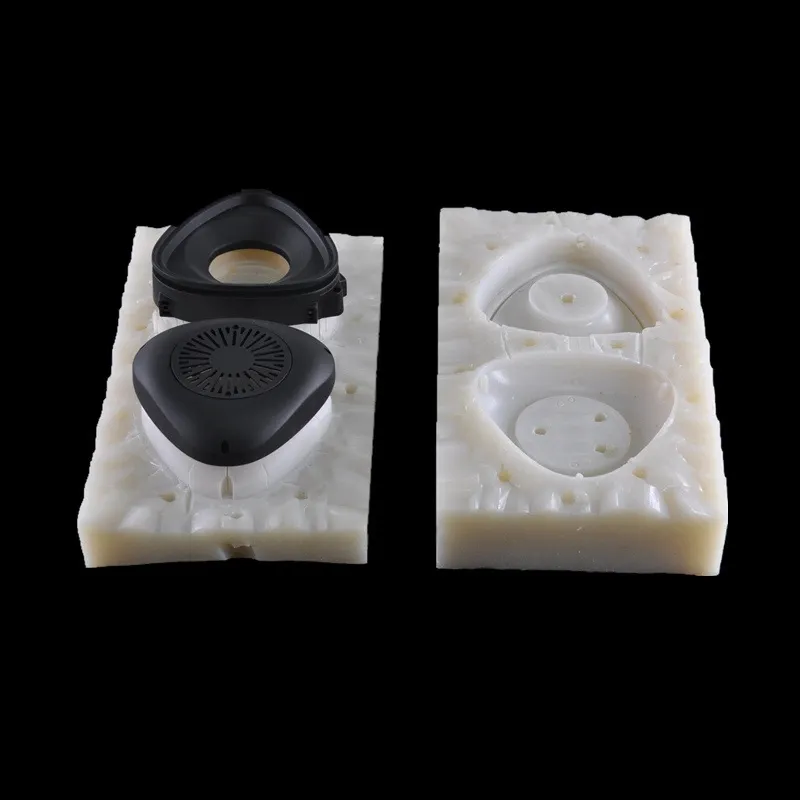
① Mold material: Flexible mold made of liquid silicone.
② Production method: The silicone mold is made by remolding the prototype (such as 3D printing or CNC model). The process is simple and does not require high temperature and high pressure.
③ Mold characteristics: soft, elastic, adaptable to complex shapes, but short lifespan (usually dozens of times).

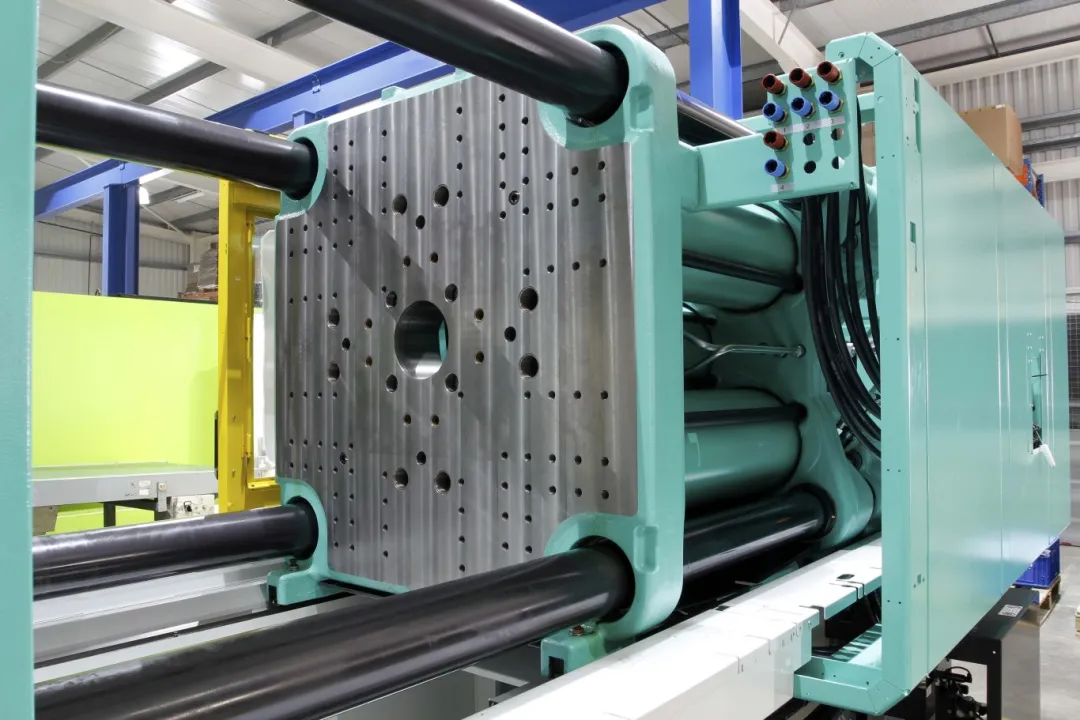
Steel mold process
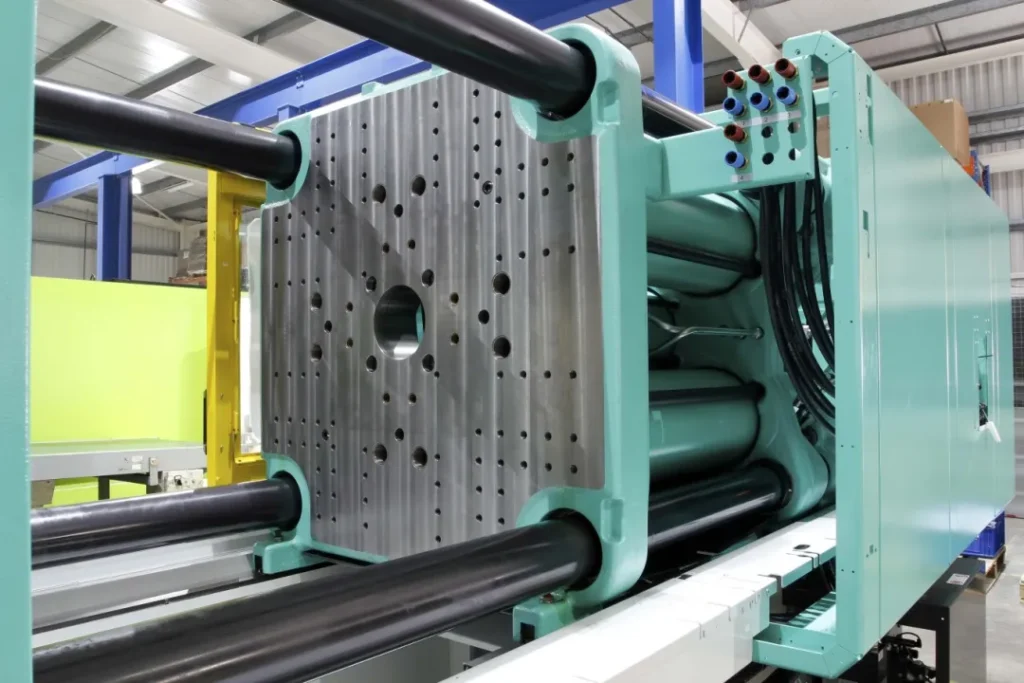

① Mould material: Made of steel.
② Manufacturing method: It is manufactured through precision processes such as CNC machining and electric discharge machining (EDM), which requires high temperature and high pressure treatment.
③ Mould features: high rigidity, wear resistance, long life (up to hundreds of thousands of times), but high cost and long processing cycle.
Cost Comparison
Silicone mold
① Low initial cost: The cost of making silicone molds is much lower than that of steel molds (maybe only 1/10 of that of steel molds).
② Suitable for small batches: The cost of each piece is higher after amortization, but the total cost is low, which is suitable for small batch prototype trial production (such as dozens to hundreds of pieces).

Steel mold process
① High initial cost: mold processing costs are high (possibly tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of yuan).
② Suitable for large quantities: The cost per piece is extremely low, suitable for large-scale production (such as more than 10,000 pieces).

Production cycle
Silicone mold
① Fast mold making: Usually the mold making can be completed in 1-3 days.
② Flexible production: suitable for rapid iteration or urgent delivery.
Steel mold process
① Slow mold production: It takes weeks or even months (involving complex processing and debugging).
② Long production cycle: suitable for long-term and stable mass production needs.

Precision and surface quality
Silicone mold
① Low precision: Due to the shrinkage rate (about 0.1%-0.5%) and deformation of silicone, details may be lost.
②Surface quality: depends on the quality of the prototype, slight defects may occur.
Steel mold process
① High precision: The mold tolerance can be controlled within ±0.01mm, which is suitable for high-precision parts.
② Excellent surface quality: Mirror or texture can be processed directly, and the product surface is highly smooth.
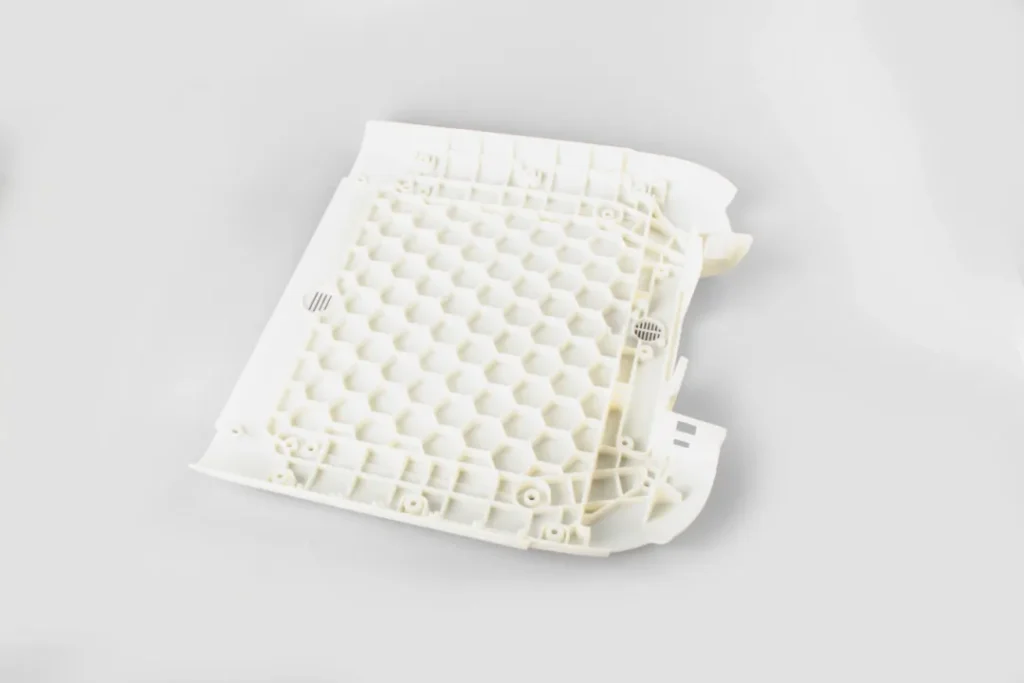

Applicable Scenarios
Silicone mold
① Prototype verification: quickly make prototype samples to test functions or appearance.
② Small batch production: prototypes, customized products, and low-melting-point materials.
③ Complex structure: suitable for parts with undercuts or deep cavities.
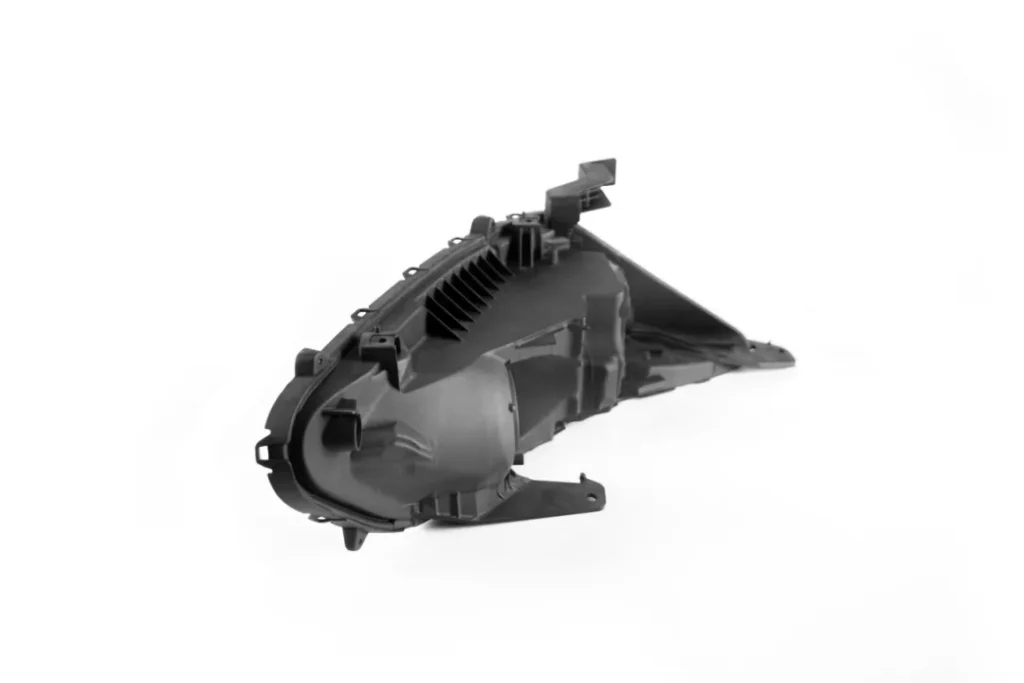

Steel mold process
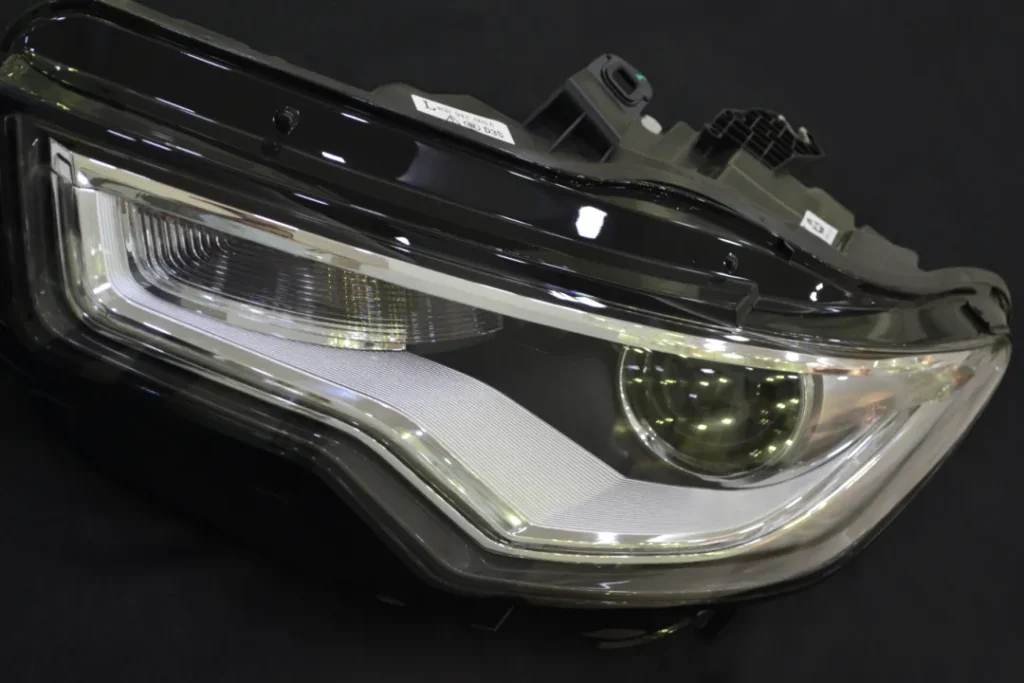
① Large-scale mass production: industrial production such as injection molding (plastic parts) and die casting (metal parts).
② High-precision requirements: automotive parts, electronic housings, medical equipment, etc.
③ Long-term orders: The mold has a long life and is suitable for stable products.
Other Differences
① Modification flexibility:
Silicone molds are easy to adjust (just re-mold), while steel molds are expensive to modify (need to be re-processed).
②Material compatibility:
Silicone molds are only suitable for low-temperature and low-pressure materials, while steel molds can withstand high temperature and high pressure (such as engineering plastics and metals).

③Environmental protection:
Silicone molds are easy to handle after being discarded, while steel mold materials are recyclable but have high energy consumption.
Summary:
Silicone mold technology: small batch, fast verification, low cost, complex structure.
Steel mold technology: large batch, high precision, long-term production, high temperature and high pressure materials.
In practice, the two processes can be used in combination: first use silicone molds to quickly verify the design, and then use steel molds for mass production.