1.Analyze the client’s information. After receiving a prototype production order, we first analyze the client’s information to determine the materials required, the desired prototype effect, quantity, delivery time, and packaging. If the client does not provide a 3D drawing, we will determine whether to create a 3D drawing based on the specific situation.

2.Issue programming tasks to the CNC team, who will compile programs based on 3D drawings and arrange CNC processing.
3.Assign manual production tasks to the manual group. Because product parts vary in difficulty, some simpler parts can meet the requirements by manual production alone, without the need for CNC production.
4.Drawing measurement: After all parts have been manufactured, they should be measured and verified according to the customer’s information or drawings.
5.Assembly: Once parts have been verified as problem-free, assembly can begin. This critical step is essential for verifying the rationality of the product design and whether it achieves the intended functionality. Parts that do not affect functionality can be omitted and proceed directly to the next step. If problems are discovered during assembly, there are two options: manual modification or redesign of the problematic part and starting over from step 1.
6.Grinding or Polishing: After all the previous steps are complete, the parts can be ground or polished. Grinding and polishing prepare for the next surface treatment step. For parts that are not visible after the final product is assembled, grinding or polishing may be omitted or treated with minimal polishing. Before proceeding with this step, it may be necessary to disassemble the parts assembled in step 5.
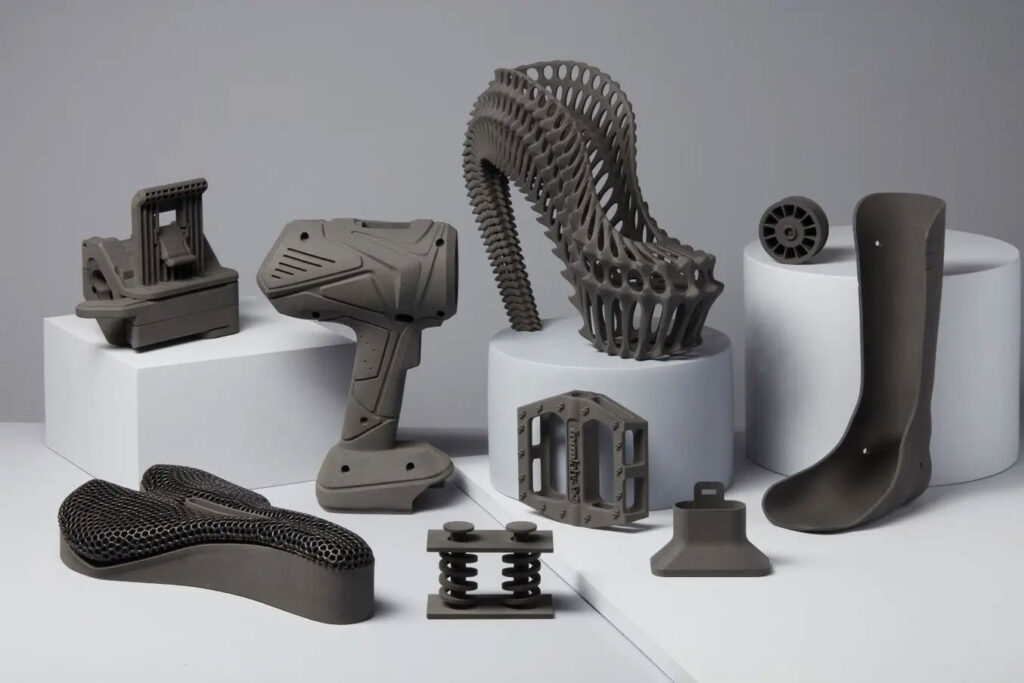

7.Surface treatment: Surface treatment refers to painting or electroplating. Similarly, with the customer’s consent, parts that are not visible after the final product is assembled can be left untreated, but only with the customer’s consent.
8.The final embellishment and decoration mentioned here are silk screen printing, pad printing, hot stamping, etc., which are mainly aimed at the processing of logos or specific texts. Sometimes customers often use these methods to surface their company logos on the prototype in order to increase their company’s awareness in the market. This is also a relatively common practice.
- Assembly: Different from the previous assembly, this time it refers to the assembly of all parts.
10.Packing and shipment.