Selection and application of flame retardants for PBT and PET engineering plastics
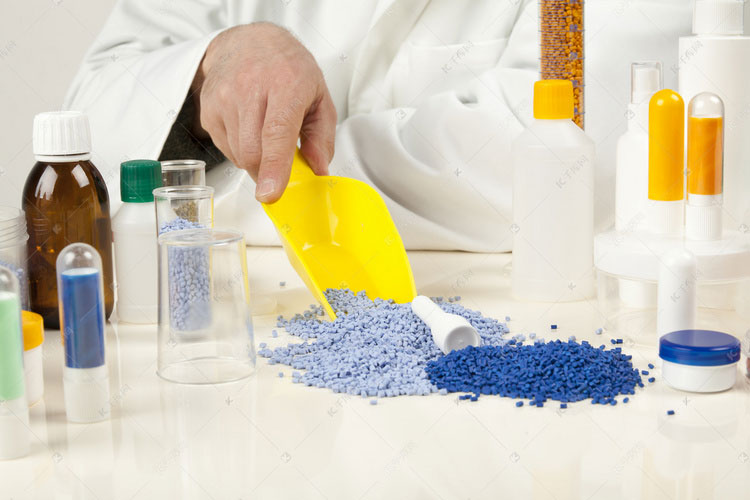
Flame retardant PBT and PET (linear polyester) PBT and PET are two important engineering plastics, widely used in electronics, instrumentation and automotive industries. Its flame retardant products are used in components with high flame retardancy requirements. Their flame retardant treatment is as follows:

(1) Adding brominated flame retardants
Commonly used ones include decabromodiphenyl ether, brominated polystyrene (BPS), brominated epoxy resin (BER), bis(tribromophenoxy)ethane, etc.
For example, adding 10%-15% bromine flame retardant and 3%-5% antimony trioxide can achieve a UL94 V-0 rating and an oxygen index of 27%-29% for PBT containing 30% glass fiber. When using additive flame retardants, it’s important to consider their dispersibility in PBT and PET, their exudation potential, and their impact on the polyester’s gloss and mechanical strength.
(2) Adding bromophosphate
Tris(dibromophenyl) phosphate (TDBPPE) is commonly used. Because it contains Br and P elements in the same molecule, it has a halogen-phosphorus synergistic effect and is highly flame-retardant in PBT and PET.
It’s important to note that antimony trioxide is often added to flame-retardant treatments for synergistic effects. If oxygen index testing is performed, the limiting oxygen index will increase. However, in an oxygen-rich test environment, Sb and P appear to have an antagonistic effect. Therefore, the UL94 vertical combustion method is the most appropriate method for evaluating the flame retardancy of the system.
(3) Flame retardant PET is used as flame retardant fibers and fabrics.
There are two common methods. One is to post-treat PET fabric with hexabromocyclododecane for flame retardancy. This fabric can be used for interior decoration, such as curtains, screens, and wall coverings. However, due to this post-treatment, the flame retardant is prone to seepage, resulting in a less durable fabric feel and flame retardancy.
The second method is flame-retardant modification using copolymers. These reactive flame-retardant monomers primarily include bromine-containing aromatic compounds, aromatic phosphine oxide compounds, and brominated aromatic phosphine oxide compounds. Because the flame-retardant elements become part of the core of the oligomer molecule, they offer long-lasting flame retardancy, good hand feel, and light resistance. This is the primary flame-retardant method used for PET flame-retardant fibers and fabrics in my country today.