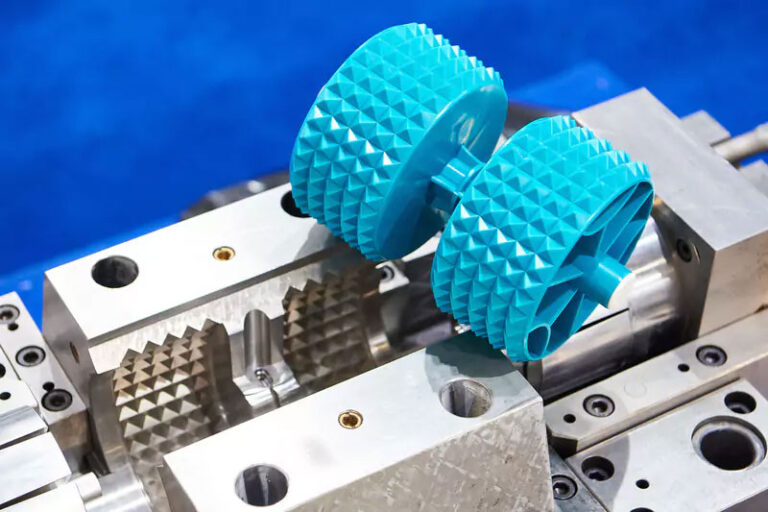
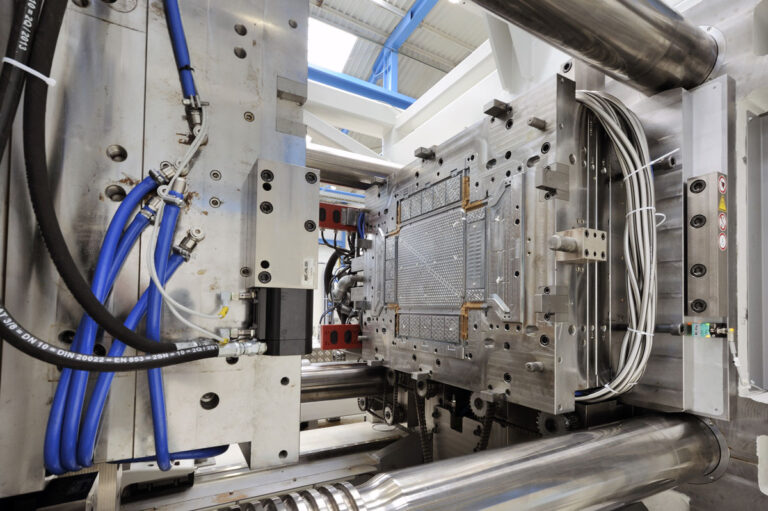
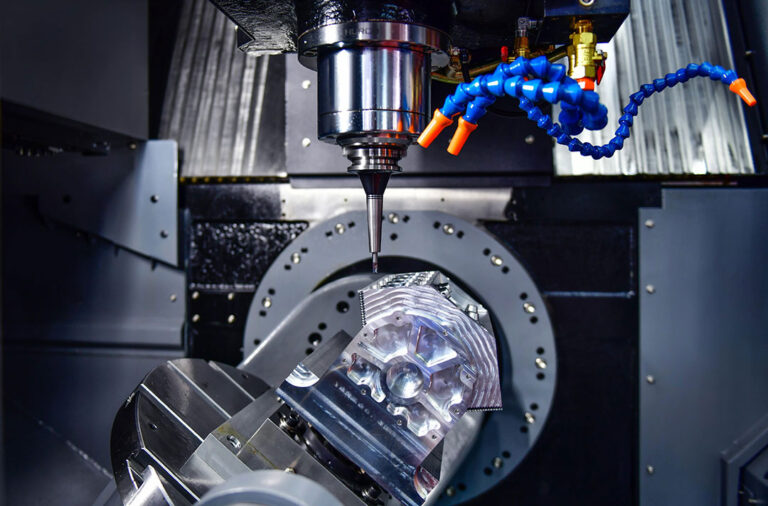
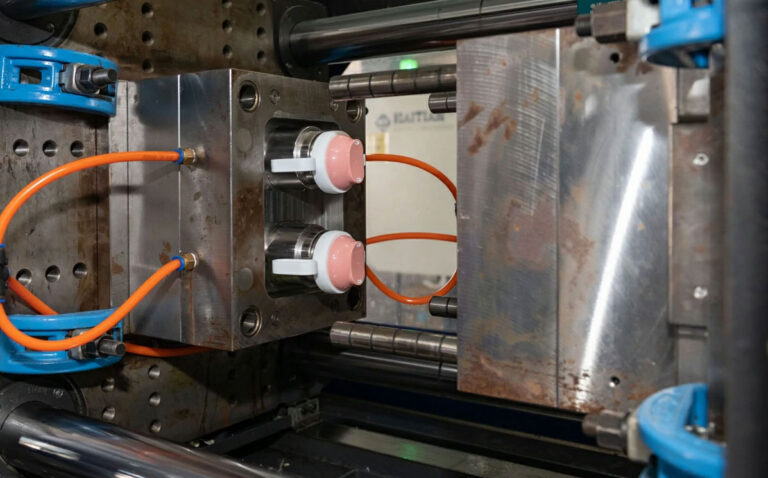
Intro
In recent years, processing technology has become increasingly advanced, and the machining industry has entered a new stage of higher precision and faster efficiency. Today, we have brought you the latest machining processes and quotations. Take a look and see if your factory’s prices are similar.
1, Different machining equipment
In machining, different equipment has different capabilities and is responsible for specific tasks. Selecting the right equipment and using it effectively is key to improving efficiency and product quality.
1) Ordinary lathe
Lathes are a common tool in machining, primarily used to process shafts, discs, sleeves, and other workpieces with rotating surfaces. By synchronizing workpiece rotation with tool movement, they can precisely machine external diameters, internal holes, and tapered surfaces. Common lathes are versatile and can meet most parts machining needs, achieving accuracy of 0.01mm. They are an essential tool in any factory.
2) Ordinary milling machine
Conventional milling machines are primarily used for machining flat surfaces and grooves, using a rotating spindle to drive the tool to cut the workpiece. They offer high flexibility and are suitable for machining small and medium-sized parts. With an accuracy of approximately 0.05mm, they are often used for initial machining or where moderate precision is required.
3) Grinder
A grinder is a device specifically designed for precision surface processing. Using a high-speed rotating grinding wheel, it grinds workpieces to achieve an exceptionally smooth surface finish. Grinding machines typically achieve a precision of 0.005mm, and for small parts, even 0.001mm, making them crucial for ensuring workpiece surface quality.
4) Fitter
Benchwork is a traditional manual processing method, including filing, sawing, drilling, and tapping. It is suitable for small-batch production or the detailed finishing of parts. Although CNC equipment is now popular, it is still an irreplaceable part of the factory when it comes to finishing complex parts and assembling.
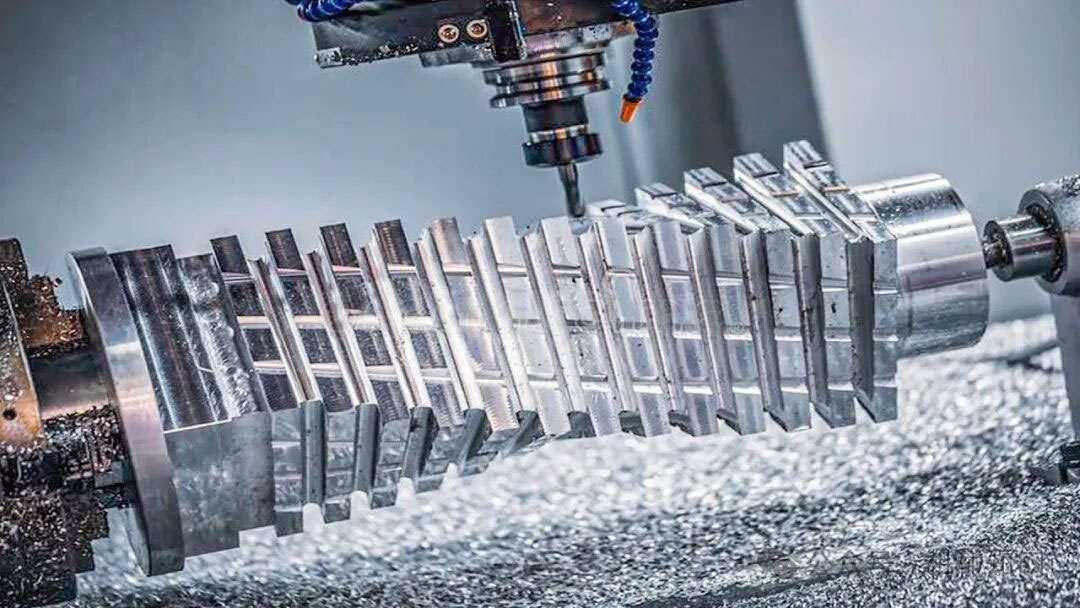
5) CNC lathe
CNC lathes are the “efficiency kings” of modern production. Combining the functionality of traditional lathes with the precision control of CNC technology, they are particularly well-suited for machining high-precision parts. They operate through programmed automation, resulting in high efficiency and stable machining accuracy within 0.01mm, making them ideal tools for machining complex parts and high-volume production.
6) CNC milling machine
CNC milling machines can handle products with complex shapes. Through multi-axis linkage, they can not only complete general milling, but also process three-dimensional surfaces and mold parts. Its accuracy can reach within 0.01mm.
7) Wire cutting
Wire EDM is specifically designed for machining high-precision through-holes, slots, and other shapes. Slow-speed wire cutting can achieve accuracies up to 0.002mm, making it suitable for high-precision machining in the mold and die industry. Medium-speed wire cutting, on the other hand, is suitable for applications requiring slightly lower precision, with an accuracy of around 0.02mm.
8) Spark machine
Spark machines are specialized for processing complex, high-hardness materials, such as grooves, small holes, and special-shaped holes in molds. Because the process involves no cutting force, no burrs or tool marks are generated, ensuring quality and achieving precision of 0.005mm, they are experts in mold manufacturing and processing high-hardness materials.
2, Process Flow
The machining process specification is one of the process documents that stipulates the machining process and operating methods of parts. It is a process document that writes the more reasonable process and operating methods in the prescribed form under specific production conditions to guide production.

The machining process of parts is composed of many processes, and each process can be divided into several installations, workstations, steps and tool paths.
The processes that a process needs to include are determined by the structural complexity of the parts being processed, the processing accuracy requirements and the production type.
Different production quantities require different processing techniques.
3, Some common process knowledge:
1) Holes with an accuracy of less than 0.05 cannot be processed by milling and require CNC processing; if it is a through hole, wire cutting can also be used.
2) Finish holes (through holes) after quenching require wire cutting; blind holes require rough machining before quenching and finish machining after quenching. Non-finished holes can be finished before quenching (with a quenching allowance of 0.2 on each side).
3) Grooves with a width of less than 2mm require wire cutting, and grooves with a depth of 3~4mm also require wire cutting.
4) The minimum allowance for rough machining of quenched parts is 0.4, and the minimum allowance for rough machining of non-quenched parts is 0.2.
5) The coating thickness is generally 0.005~0.008mm, and the processing should be based on the pre-plating dimensions.
4, Processing hours
The time quota is the time required to complete a process and serves as an indicator of labor productivity. Based on the time quota, production schedules can be arranged, cost accounting can be performed, equipment quantity and staffing can be determined, and production area can be planned. Therefore, the time quota is an important component of process specifications.
The time quota should be determined based on the production and technical conditions of the enterprise, so that most workers can achieve it through hard work, some advanced workers can exceed it, and a few workers can reach or approach the average advanced level through hard work.
As the production and technical conditions of the enterprise continue to improve, the time quotas are revised regularly to maintain the average advanced level of the quotas.
Time quotas are typically determined by direct estimates by process engineers and workers, drawing upon past experience and relevant technical documentation. They can also be derived through comparative analysis of time quotas for similar workpieces or processes, or by measuring and analyzing actual operating times.
Process time = preparation time + basic time
Preparation time refers to the time workers spend familiarizing themselves with process documents, receiving blanks, installing fixtures, adjusting machine tools, and disassembling fixtures.
Calculation method: Estimate based on experience. The basic time is the time it takes to cut away the metal.

5, Quotation cost calculation method
Machining quotes are directly related to a company’s survival. In such a competitive market, if machining shops can’t earn reasonable profits, machining quality will inevitably suffer. Therefore, everyone in the industry should focus on win-win cooperation, jointly promoting the machining industry towards high-quality, sustainable development, and forming a virtuous cycle.
Processing cost = (material cost + processing fee) * 1.2
[The coefficient of 1.2 includes management fees]
Equipment cost = (material cost of processed parts + processing fee + purchase cost + assembly and debugging fee + design fee) * 1.2
[The coefficient of 1.2 includes management fees]
Material cost = weight (density * volume) * unit price (yuan/kg)
Processing fee = process hours * unit price (yuan/hour)
Design fee = working hours * unit price (yuan/hour)
Japanese purchase cost (yuan) = purchase price (yen) / exchange rate
The cost of domestically purchased products shall be based on the supplier’s quotation
6, Quotation Details
Lathe: ¥60/hour (~$8.22/hour)
Milling Machine: ¥60/hour (~$8.22/hour)
Grinding Machine: ¥60/hour (~$8.22/hour)
Fitter: ¥80/hour (~$10.96/hour)
Machining Center: ¥60-120/hour (~$8.22-$16.44/hour)
CNC Lathe: ¥60-120/hour (~$8.22-$16.44/hour)
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machine): ¥80-150/hour (~$10.96-$20.55/hour)
Wire Cutting : ¥60-150/hour (~$8.22-$20.55/hour); Small parts from ¥80 (~$10.96), large parts based on area: ¥0.06-0.08/mm² (~$0.008-$0.011/mm²).
Small Hole EDM: Carbon steel, tungsten steel:
Φ0.3mm and above: ¥1/mm (~$0.14/mm)
Φ0.3mm and below: ¥2-3/mm (~$0.27-$0.41/mm)
Φ0.3mm and above (tungsten steel): ¥1.8-2/mm (~$0.25-$0.27/mm)
Management Fee: 20% of cost price
Note: The exchange rate used here is based on 1 USD = 7.3 CNY. Please verify the current exchange rate, as it can fluctuate.