Introduction
In injection mold manufacturing, the choice of steel is crucial and needs to be considered comprehensively based on the characteristics of the plastic, product batch, precision requirements, and surface quality. So, which different mold steels are suitable for making molds for plastic products?
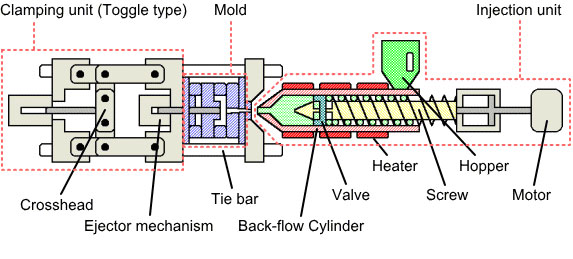
1.Pre-hardened mold steel
Pre-hardened mold steel is a type of steel that has been pre-heat treated (quenching + tempering) to reach the hardness for use before leaving the factory. It does not require further quenching or other heat treatment after processing and can be directly used in mold manufacturing. Common types include P20, 718H, NAK80, etc.
P20 steel has a hardness of 28-36 HRC and is a mold steel with good overall performance, low cost, easy cutting, and medium polishability. It is commonly used in the manufacture of molds for daily necessities, toys, home appliance housings, and automotive interiors.
Applicable plastics: PE, PP, PS, ABS, PA (non-reinforced), and common engineering plastics.
718H steel is an improved mold steel of P20 steel with a hardness of 33-38 HRC. It is stronger than P20 and has good polishing and toughness. It can be used for complex structure molds such as optical lenses, transparent containers, mobile phone housings, and car lights.
Applicable plastics: PE, PP, PS, ABS, PA (non-reinforced), common engineering plastics, etc., also suitable for PC, PMMA, PET, transparent plastics, and high-gloss products.
The hardness of NAK80 steel is 37-43 HRC. This mold steel has excellent mirror polishing performance and good surface quality after discharge machining, without the need for secondary polishing. It can be used to manufacture injection molds for products such as optical lenses, light guide plates, and transparent parts of medical equipment.
Applicable plastics: PC, PMMA (highly transparent plastic)
2.Corrosion-resistant mold steel
Corrosion-resistant mold steel is a special type of steel used to manufacture molds working in corrosive environments. Its corrosion resistance is improved mainly by adding alloying elements such as chromium (Cr), nickel (Ni), and molybdenum (Mo). Common examples include S136 steel and 4Cr13 (420 stainless) steel .
S136 steel has a pre-hardened hardness of 29-33 HRC and can reach a hardness of 50-52 HRC after quenching. It is a martensitic stainless steel that is corrosion-resistant and rust-proof, and has a high surface finish after polishing. It is suitable for mold manufacturing of products such as medical devices, food packaging, cosmetic containers, and sanitary products.
Applicable plastics: PVC, POM, flame retardant plastics, food contact plastics, etc.
4Cr13 steel has a hardness of up to 52-56 HRC after quenching. It is also a martensitic stainless steel and a type of corrosion-resistant mold steel, corresponding to the 420 stainless steel (American ASTM) in the international standard .
It is characterized by high carbon and chromium content, and has both corrosion resistance and wear resistance. It is widely used in the manufacture of molds that require hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance, such as water pipe joints, chemical containers, and long-term corrosion-resistant molds.
Applicable plastics: PVC, reinforced plastics (including glass fiber), plastics with highly corrosive additives, etc.
3.Hot working die steel
Hot work die steel is a type of steel specifically designed for manufacturing molds operating in high-temperature environments. This type of steel must possess high-temperature resistance, thermal fatigue resistance, wear resistance, and high strength to withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles. Common examples include H13 steel and SKD61 steel .
H13 steel has a hardness of 48-52 HRC after quenching. It is a high-toughness hot-work die steel with good high-temperature and thermal fatigue resistance and can be nitrided. It can be used to manufacture injection molds for automotive engine parts, electronic connectors, high-temperature products, thin-walled products, etc.
Applicable plastics: high temperature processing plastics (such as PEEK, LCP, PPS), glass fiber reinforced plastics.
The hardness of SKD61 steel after quenching is 48-52 HRC. Its performance is similar to H13, but its thermal fatigue resistance is better. It is suitable for high-speed injection molding, such as fast food box molds.
Applicable plastics: Same as H13, especially suitable for rapid prototyping process.
4.Rapid prototyping mold materials
Rapid prototyping molds are molds created quickly using rapid prototyping technology, primarily used for small-batch part production or prototype verification. Compared to traditional mold steels, rapid prototyping mold materials prioritize rapid manufacturability, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for small-batch production. They also must meet certain strength, wear resistance, and temperature resistance requirements. Common materials include 7075 and 6061 .
The hardness of this mold material is about 150-200 HB. It has the characteristics of fast processing speed, low cost and good heat dissipation, but it has a short lifespan and is only suitable for mold manufacturing for product prototypes, trial molds and short-term production.
Applicable plastics: small batch production of low-viscosity plastics such as PE, PP, PS, and soft rubber.
In short, when opening an injection mold, you need to choose the appropriate mold material based on the characteristics of the product material.