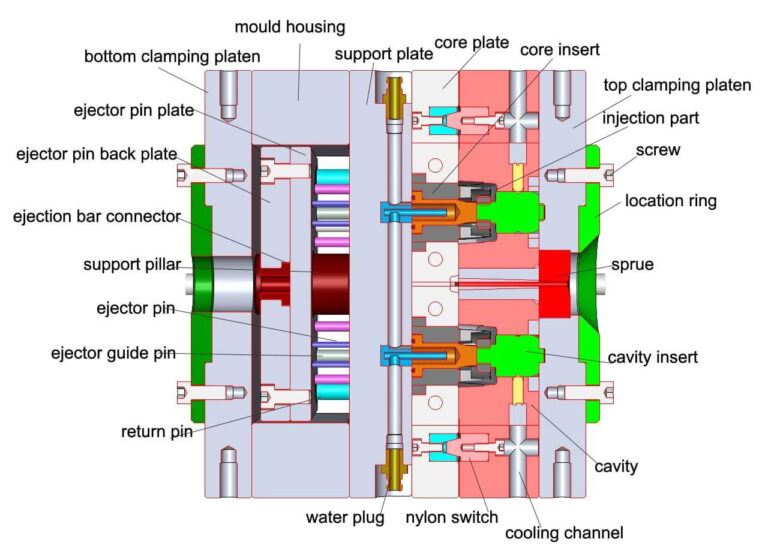
Intro
In injection molding production, mold costs directly affect product profits, but blindly reducing costs may lead to reduced quality, shortened life, and frequent maintenance, which in turn increases long-term expenses.

So, how do we find the best balance between quality, efficiency and budget?
Mold cost structure
Before optimization, first understand the composition of mold costs:
- Material costs, accounting for 30% to 40%. Choose materials appropriately and avoid excessive specifications.
- Processing fee, accounting for 30% to 50% . Optimize design and reduce complex processing.
- Design fee, accounting for 10%-20%. Standardized design, clear requirements, and reduced trial and error.
- Mold trial and modification fees, accounting for 5% to 15%. Simulation analysis in advance can reduce the number of mold trials.
Key principles:
Don’t just look at the initial price; evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), including maintenance, lifespan, productivity, etc.
Avoid “false savings”: low-quality molds may lead to frequent repairs, downtime, and increased scrap rates, which will actually cost more!
6 major mold cost optimization strategies
1.Reasonable material selection: match the needs, do not blindly use high-end steel
General needs (such as daily necessities, packaging):
The use of low- and medium-end mold steels such as P20 and 718H can reduce costs by 30% to 50%.
High precision/wear-resistant requirements (such as electronic parts, medical):
Use S136 and H13 (quenching treatment) to increase service life by 3 to 5 times.
Small batch/trial production:
Use aluminum molds (cost savings of 50%+) or experimental molds (quick verification).
Case: A home appliance company changed its shell mold from S136 to P20, saving RMB 20,000 per set while still meeting the requirement of 100,000 molds.
2.Design optimization: reduce complex structures and improve manufacturability
Simplify parting surface: avoid multi-slider structure and reduce processing difficulty.
Standardized formwork: Using standard formwork is 20% to 30% cheaper than custom formwork.
Insert design: Inserts are used in vulnerable parts, so only part needs to be replaced during maintenance, reducing long-term costs.
Moldflow analysis: Predict filling problems in advance and reduce the number of mold trials (each mold trial costs about 500 to 3,000 yuan).
Key questions:
“Can I reduce runner scrap by adjusting the gate location?”
“Can symmetrical design reduce machining time?”
Process Optimization: Balancing Precision and Efficiency
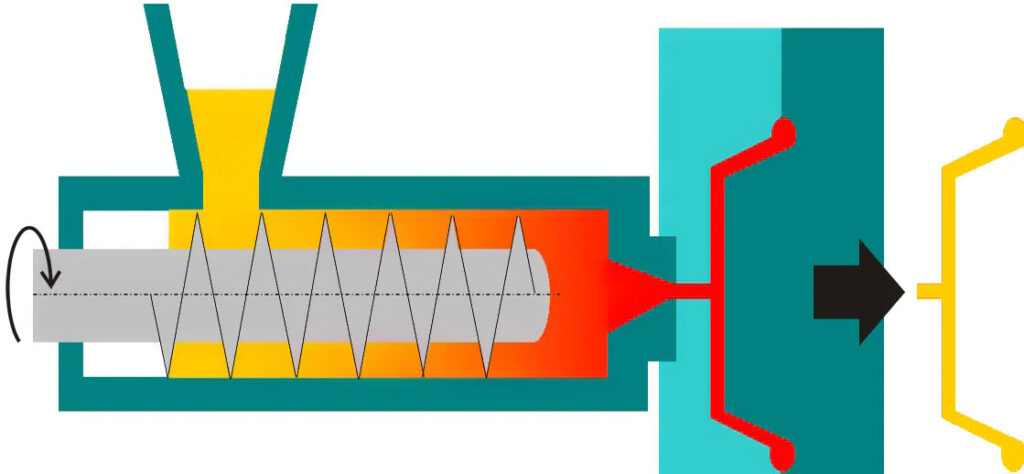
Processing method:
Ordinary parts: CNC rough machining + EDM finishing to reduce costs.
High gloss surface: Mirror EDM (reduces manual polishing costs).
Cooling system design:
Adopting conformal water channels (3D printing or drilling optimization) can shorten cooling time by more than 20% and improve efficiency.
Batch and production mode selection
Small batch (<10,000 pieces): Aluminum molds or modular molds are preferred to avoid the high amortization of steel molds.
Medium to large batches (>100,000 pieces): Invest in high-life steel molds (such as H13 quenching) for lower unit costs.
Multiple varieties and small batches:
The quick mold change system (QMC) is used to reduce mold change time from 2 hours to 10 minutes.
Case: An auto parts factory uses modular molds, with 10 products sharing the same mold base, reducing total mold costs by 40%.
Supply Chain Optimization: Select Cost-Effective Manufacturers
Local vs. out-of-town: Local manufacturers are convenient to communicate with and suitable for frequent modifications; out-of-town manufacturers may have prices that are 20%~30% lower.
Evaluation criteria: Don’t just look at the quotation, but also pay attention to the accuracy of the processing equipment (such as ±0.01mm) and the speed of after-sales response.

Tips for avoiding pitfalls:
❌ Be wary of “super cheap molds” – they may be second-hand steel or cut-edge materials.
✅ Material report (such as DIN standard) and processing accuracy test data are required.
Maintenance and life management
Regular maintenance: Clean and lubricate the guide posts to prevent rust.
Stock up on wearing parts: Stock up on ejectors, springs, etc. in advance to reduce downtime.
Surface treatment: Chrome plating or nitriding of core components can extend service life by 30%+.
???? Cost comparison:
Strategy 1: No maintenance, use until the mold breaks down, and the mold is scrapped prematurely, resulting in a loss of more than 50,000 yuan.
Strategy 2: Invest 2,000 yuan per year in maintenance: Spend 2,000 yuan per year, extend the lifespan by 2 to 3 years, and save more than 30,000 yuan.
Summary
- Clarify requirements: First determine product accuracy, batch size, and lifespan requirements to avoid over-design.
- Design stage optimization: Reduce trial and error costs through DFM and mold flow analysis.
- Full life cycle management: From material selection and processing to maintenance, systematic cost control.
remember:
The cheapest mold does not equal the most cost-effective one. Low-quality molds may lead to increased scrap rate and downtime losses.
Collaborate closely with manufacturers to enable them to provide cost optimization suggestions (such as gate design and cooling solutions).
Through the above strategies, you can reduce mold costs by 20%~50% while ensuring quality, truly achieving cost reduction and efficiency improvement!