Introduction
The manufacturing industry loves acronyms, and they work well. MP, FA, EPM, ODM, OPM, PRD, DRP, BOM, DFX, DFM, and so on—some of these acronyms stand for process, others for documentation—all refer to industrialization. These acronyms have become a kind of industry jargon.
Today we will mainly introduce EVT, DVT, PVT, and MP which are related to the product development process.
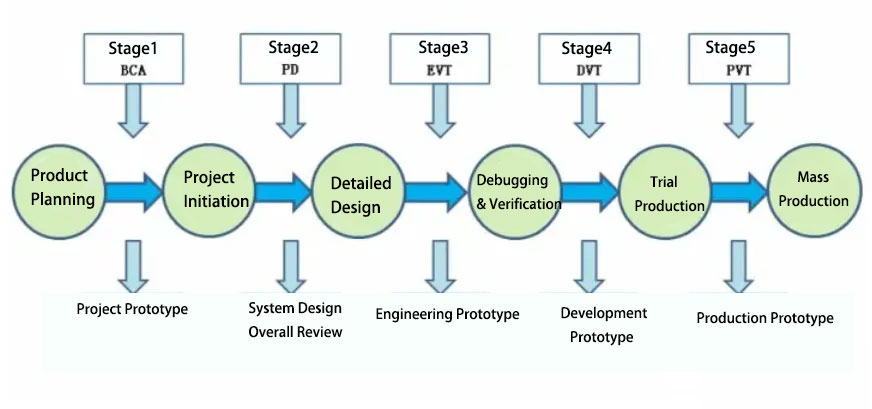
The product development process can be roughly divided into five stages:
Planning (product conception stage);
EVT (Engineering Verification and Testing Phase);
DVT (Design Verification and Testing Phase);
PVT (Production Verification and Testing Phase);
MP (mass production stage).
EVT
EVT (Engineering Verification Test) Engineering Verification Test Phase.

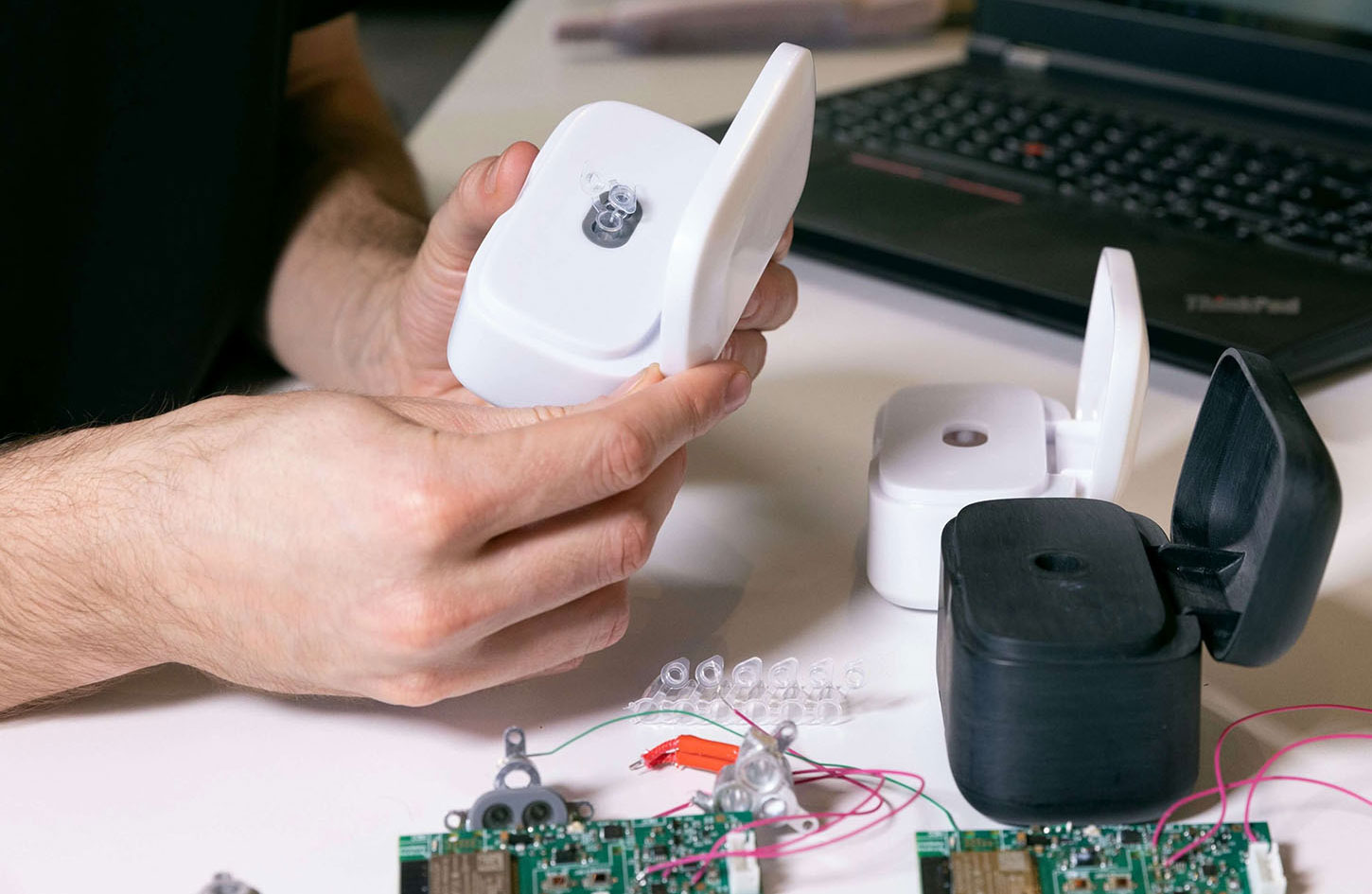
Design verification is performed during the early stages of product development. Many products are initially designed as engineering prototypes, potentially subject to numerous issues. These issues must be addressed one by one, with a focus on design completeness and ensuring that no specifications are missed. This includes functional and safety testing, and is typically performed by the RD. Because these prototypes are likely to contain numerous issues, multiple tests may be required.
1, Design verification in the early stages of product development generally verifies the integrity of the product design and confirms whether there are any remaining requirements or specifications.
2, Test basic functions, safety regulations, and of course, performance and reliability;
3, Generally, 3D printed prototypes are used instead of molded shell materials;
4, This stage is generally not assembled on the production line;
5, This stage generally has many problems and requires multiple revisions and verifications. There may be EVT1, EVT2, and other stages .
6, Often, a preliminary test for certification can be conducted at this time;
7, Quantity: The number of prototypes produced during the EVT phase is usually one or more, and the quantity will not be large.
8, Prototyping methods: rapid prototyping, 3D printing, CNC, etc.
9, Appearance: Generally speaking, prototypes have no surface condition, surface finish, color… but it all depends on how important appearance is in your product.
10, Simplification: For rapid verification and cost considerations, the prototype at this stage may lack some minor functions.
DVT
DVT (Design Verification Test) Design Verification Test Phase
This is the second stage of R&D. All designs are complete, and the focus is on identifying design issues and ensuring that all designs meet specifications. This is verified by RD and DQA (Design Quality Assurance). At this point, the product is essentially finalized.
1, The product design has been completed, and the verification is for the compliance of all designs, considering DFX;
2, Verification items include all test verification requirements such as function, performance, and reliability, because the product has been basically finalized at this time;
3, Usually, the assembly line is used to verify manufacturability. At the same time, the number of tests is increased to further identify design problems.
4, Arrange third-party certification, as certification takes a long time;
5, During DVT, the design is tested using real parts that are close in size and material to what we want to obtain.
6, Quantity: Typically between 10 and 100 units. This depends entirely on the number of MPs (mass production) and the cost of the prototypes. Certification requires a certain number of prototypes, with verification testing alone requiring at least 20 to 30 units. Not to mention the additional requirements for marketing.
7, Prototype production methods: 3D printing, CNC, silicone mold lamination, simple mold, etc.
8, The prototypes at this stage should be free of major defects. Some prototypes can be distributed to “special testers” or shown to future customers.
9, Appearance: The appearance at this stage should be as close to the mass production state as possible, and some defects are allowed.
PVT
PVT (Production/Process Verification Test) Production/Process Verification Test Phase
At this stage, product design must be completed and all design verification must be completed. Finally, only pre-production verification is required to ensure that the factory is able to produce the originally designed product according to the standard operating procedures.

Before entering into large-scale production, it is important to conduct a trial run of the production line to evaluate quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC). PVT is to optimize your production process and ensure that the product is produced at the right quantity, cost and quality, thereby testing the entire production speed.
Products produced during these tests, if they meet all requirements, can be planned for sale to customers and will be considered part of your first production run. If faults are discovered, this will be your last chance to adjust the tooling before full-scale production.
1, All designs and design verifications have been completed, and mass production verification has been completed before mass production;
2, Carry out small batch production according to the tooling equipment, production process and operating methods of mass production;
3, Verify the production process;
4, Verify the stability and reliability of the product;
5, Sometimes, because the conditions of PVT are consistent with those of mass production, there is a possibility of PVT product shipment;
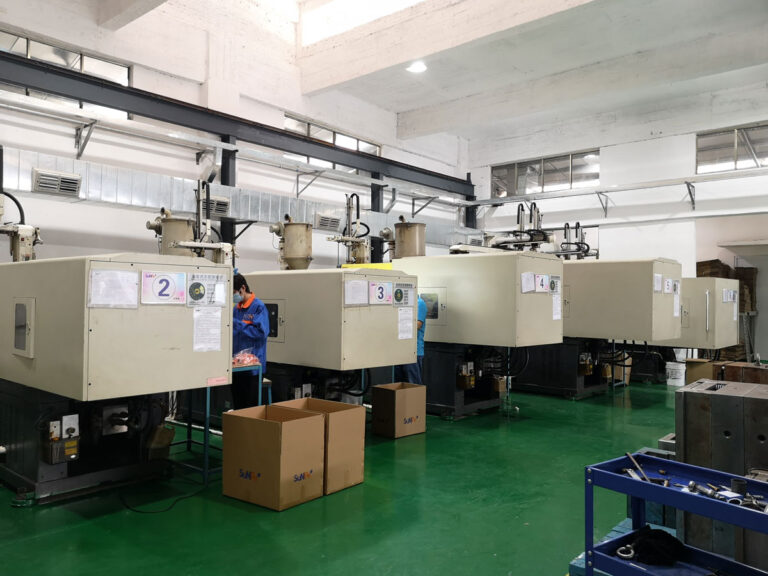
6, Quantity: Between 50 and 200 or more, depending on the specific product. The large quantity is mainly to verify the manufacturability (including the product itself and the production line production process).
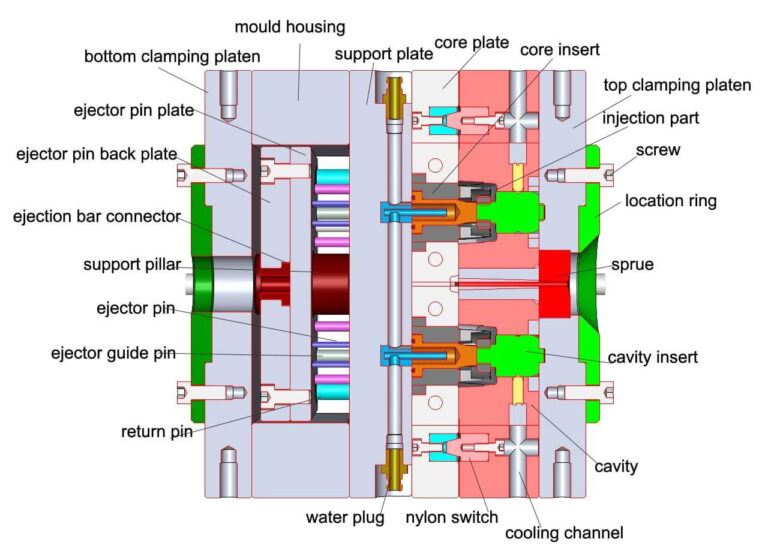
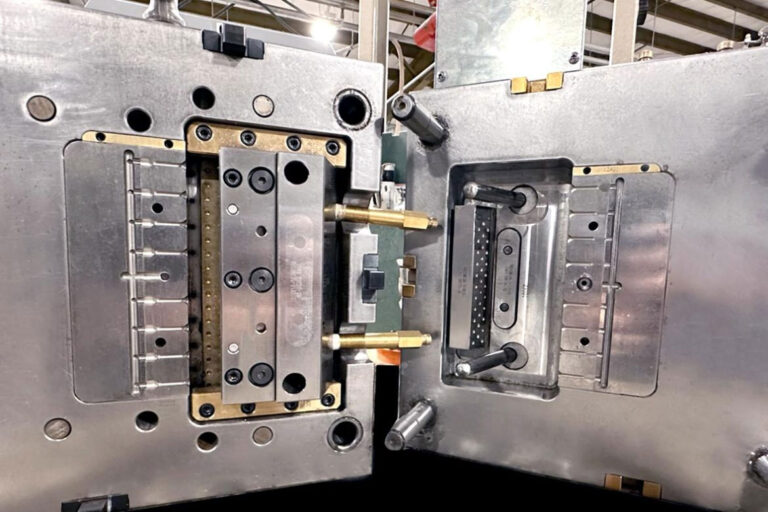
7, Prototype production method: formal mold production;
8, Appearance: consistent with the final mass-produced product;
MP
MP (Mass Production) large-scale production stage
After all the above testing stages, the factory can mass-produce the design. In theory, to enter the mass production stage, all designs and production should be free of omissions and errors, and become a formally launched product.

1, MP stage Customers usually monitor and follow up, but the factory controls production and should ensure high output and lowest cost.
2, The final stage of product maturity evolution is the move toward mass production, where quantities can range from a few thousand units to millions of units (the sky’s the limit!).
3, At this stage, once the line is stable, it can be replicated to other lines and run in parallel to achieve higher yields. Failure and yield analysis on a small number of units ensures consistent quality (this is constantly monitored by the line manager).
4, During this phase, design effort is minimal and continuous process improvement becomes the primary driver for cost reduction (along with any cost restructuring due to higher and/or more regular parts sourcing with suppliers).
Summary
In the product life cycle, how to distinguish which period requires EVT\DVT\PVT?
Project establishment: The stage before project approval is the project establishment stage;
Design: Before the design review is passed, it is the design stage, which mainly converts the requirements into drawings;
EVT: After the design review is passed, the engineering prototype review is passed. This stage mainly converts the drawings into physical objects;
DVT: After the engineering prototype passes the DVT review and approval stage, this stage mainly involves all test verifications to ensure that the design is complete and has passed the verification;
PVT: Before the DVT review is passed to MP, this stage is mainly to verify the production process, yield, whether there are any design problems, and product consistency and stability.