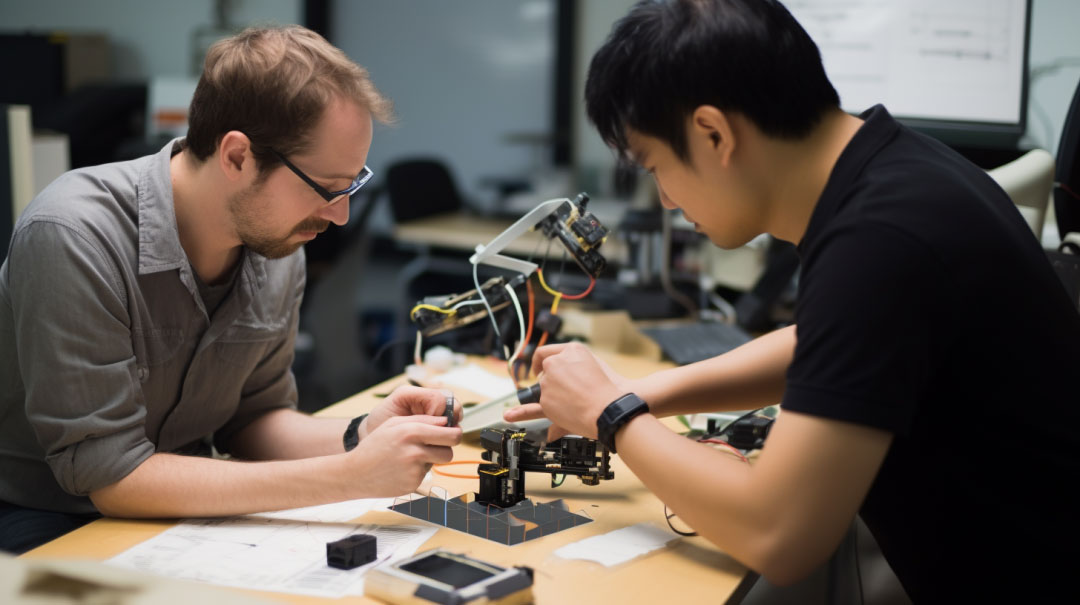
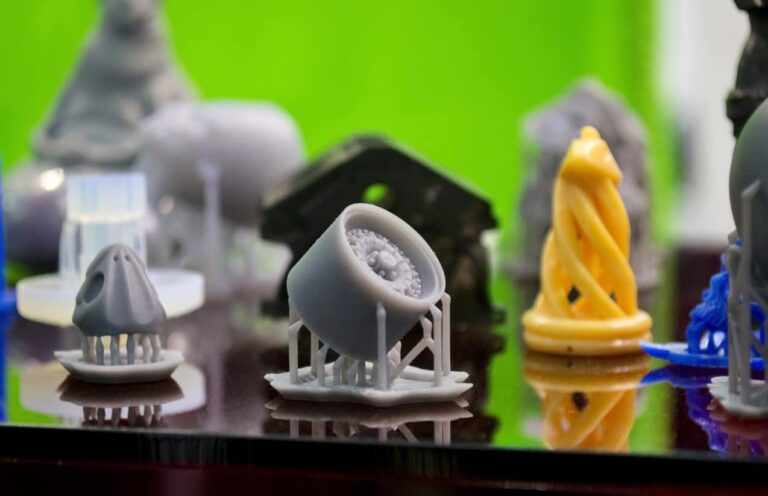
Prototyping is an essential step in the product development process, but high processing costs often put pressure on companies. As a professional team at Yingshuo Prototyping, we understand the importance of cost control to project budgets. This article will provide a detailed analysis of the cost structure of prototype processing and provide a series of proven cost-reduction solutions to help you significantly reduce prototype production costs while ensuring quality.

Prototype processing cost structure analysis
Understanding the composition of prototype proofing costs is the first step in controlling costs. As a professional prototype factory, Yingshuo divides the prototype processing costs into the following major parts:
Material costs
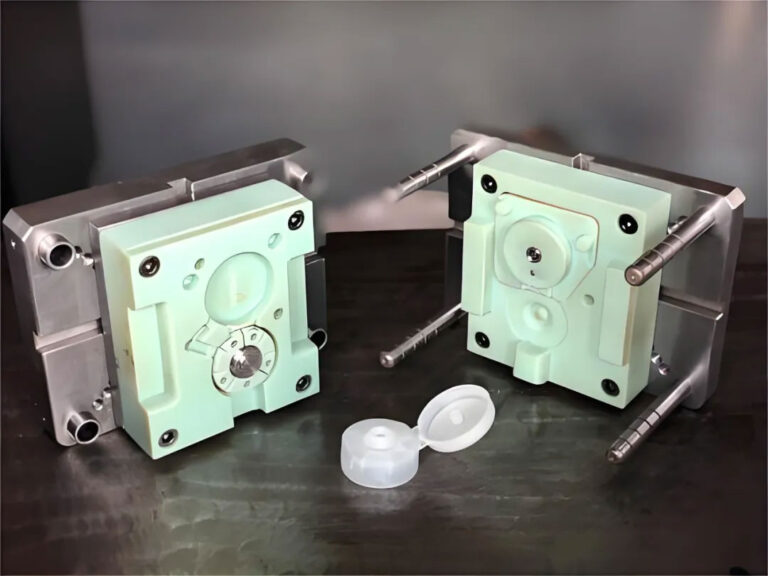
This is the foundation of the prototype cost. Prices vary significantly between different materials: Common engineering plastics (such as ABS and PC) cost approximately 10-100 yuan per piece; metals (such as aluminum alloy and stainless steel) cost 100-1000 yuan per piece; and special alloys (such as titanium alloy) can cost thousands of yuan per piece. Material selection directly impacts total cost, but more expensive isn’t always better. The key is to choose the most cost-effective material based on actual needs.
Processing costs
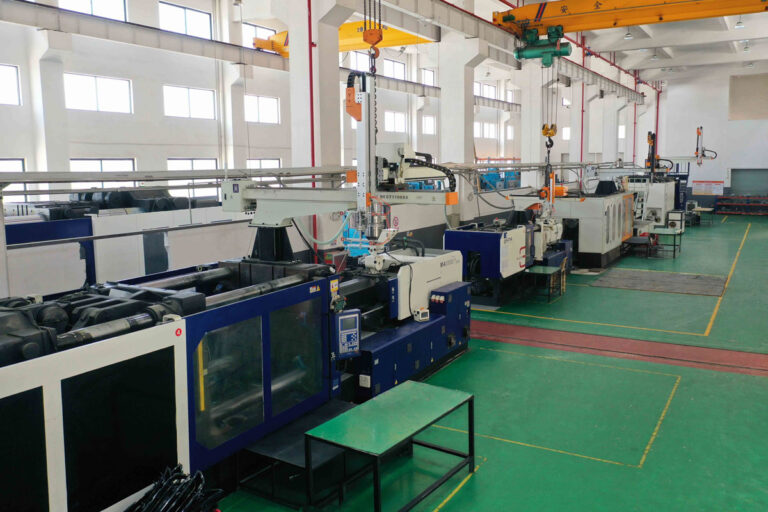
This typically accounts for the largest portion of the prototype cost. 3D printing (SLA/SLS) is charged by weight or time, with a unit price of approximately 50-500 yuan per piece. CNC machining, calculated based on labor hours and complexity, ranges from 300-3000 yuan per piece. The process choice should be determined by the prototype’s intended use (visual verification or functional testing) to avoid over-processing.
Surface treatment costs
These costs are often overlooked, but they can add up to significant costs. Basic finishing (such as grinding and sandblasting) adds 50-200 yuan per part, while advanced finishing (such as electroplating and anodizing) adds an additional 100-1000 yuan per part. In many cases, advanced surface treatments aren’t necessary in the early stages of product development, so there’s significant potential for savings here.
Other expenses
These include design optimization fees (if the manufacturer needs to provide design suggestions), assembly fees (multi-component assembly) and logistics fees. These usually account for a small proportion of the total cost, but they cannot be ignored.
Design optimization: control prototype costs from the source
Adopting cost-control strategies during the product design phase can significantly reduce prototype manufacturing costs from the source. Our team of engineers at Yingshuo Prototype Factory has developed the following design optimization solutions to help you reduce unnecessary expenses.
Simplify product structure
One of the most effective cost-reduction methods is to avoid overdesign and unnecessary complexity, such as small protrusions and decorative curves, which increase processing difficulty and time. Our experience shows that CNC processing time can be reduced by 15%-25% for each complex surface or internal structure removed. For example, one customer reduced the cost of processing a single piece by 30% by replacing the decorative relief on a product casing with a simple texture.
Reduce accuracy requirements
Another important strategy is to maintain a standard accuracy of ±0.1mm. While standard accuracy (±0.1mm) is sufficient for most testing needs, pursuing excessively high precision (e.g., ±0.01mm) can increase CNC machining costs by 30%-50%. Yingshuo Prototype Factory recommends that, unless precision-matched components are involved, a ±0.05-0.1mm accuracy is sufficient for most prototypes used for appearance and structural verification. This ensures functionality while significantly reducing costs.
Hollow design
This technology is particularly suitable for 3D printing prototypes. By converting a solid model into a hollow structure and maintaining wall thickness within the material safety range, material usage can be reduced by 30%-70%. We once helped a customer convert a completely solid component to a hollow design with a 3mm wall thickness, reducing material costs from 480 yuan to 150 yuan, while fully meeting testing requirements.
Integrated design
It can reduce the number of assembled parts. By combining multiple parts into a single, integrated structure, processing time can be reduced while avoiding subsequent assembly costs. For example, the original design of an electronic product housing was assembled from five components. After optimization, it was changed to a three-component integrated structure, reducing total processing costs by 40%.