Introduction
Before each new product is put on the market, a market benefit analysis will be conducted on the product, or it will be necessary to confirm whether there is a difference between the drawing and the actual product or whether the design is reasonable. Prototype production is an inevitable process for the company.
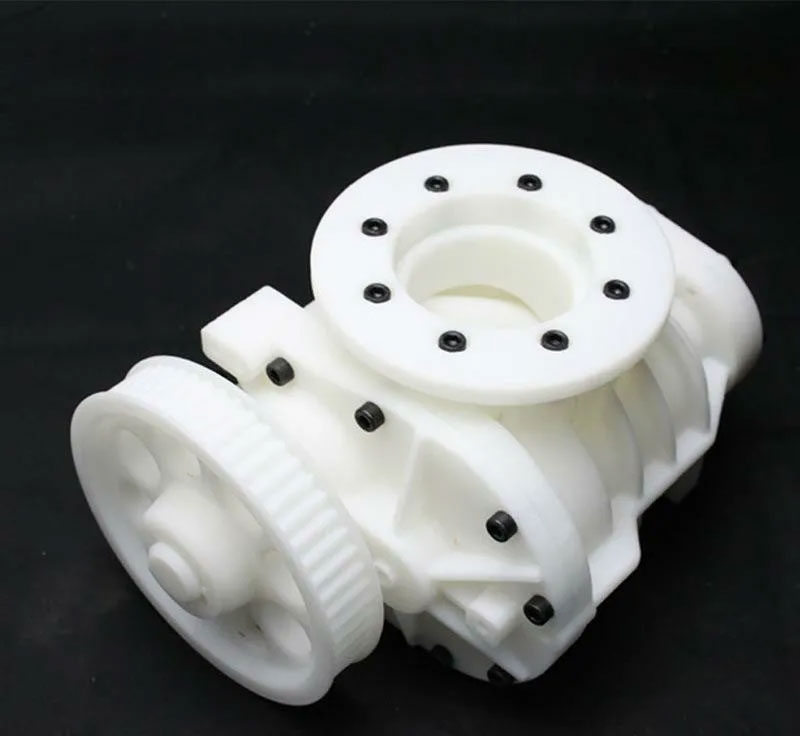

A prototype is a functional prototype that is made by making one or more models based on product design or structural drawings without making a mold to check the appearance or structural rationality. In fact, it is a prototype of a printed design product.
At present, there are three common processes for prototype production: CNC prototype processing, 3D printing prototype, and lamination. So, how to choose the most suitable process for your own prototype processing?
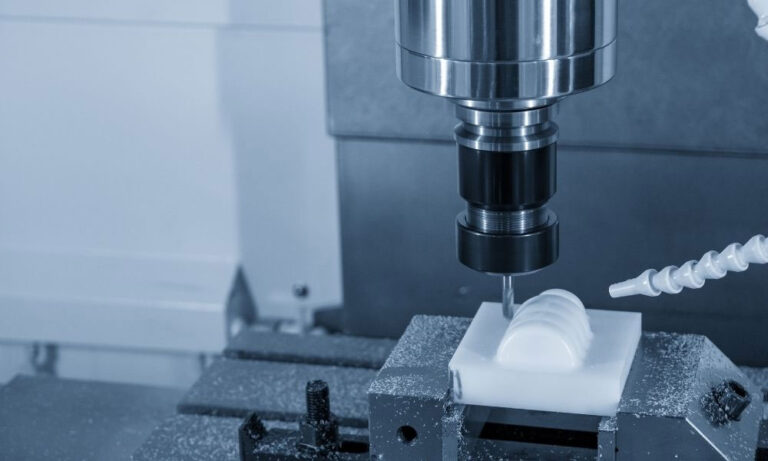
No.1 CNC prototype production
CNC machining uses the Mastercam system, which is mainly used to control CNC tool paths. CNC milling machines are specially used to process square and irregular objects, while lathes are used to process round objects.
CNC can process some relatively large workpieces. The maximum can reach 1800900600. It is cheaper than SLA and can meet many types of prototypes. It is currently the most widely used in China. The main materials are ABS, PC, PMMA, and the metals are mainly aluminum and copper.

CNC machining can produce relatively high-precision product samples. The main application materials are ABS, PC, PMMA, PP, aluminum, copper, etc. Bakelite and aluminum alloy are commonly used in the production of jigs and fixtures.
Advantages of CNC prototypes: good toughness, high tension, low cost, and a wide range of material options.
No.2 Composite molding (also known as vacuum infusion)
The replica mold is made by using the original sample, making a silicone mold under a vacuum state, and pouring PU material under a vacuum state, so as to clone a replica that is identical to the original, more resistant to high temperatures, and has better strength and hardness than the original sample.
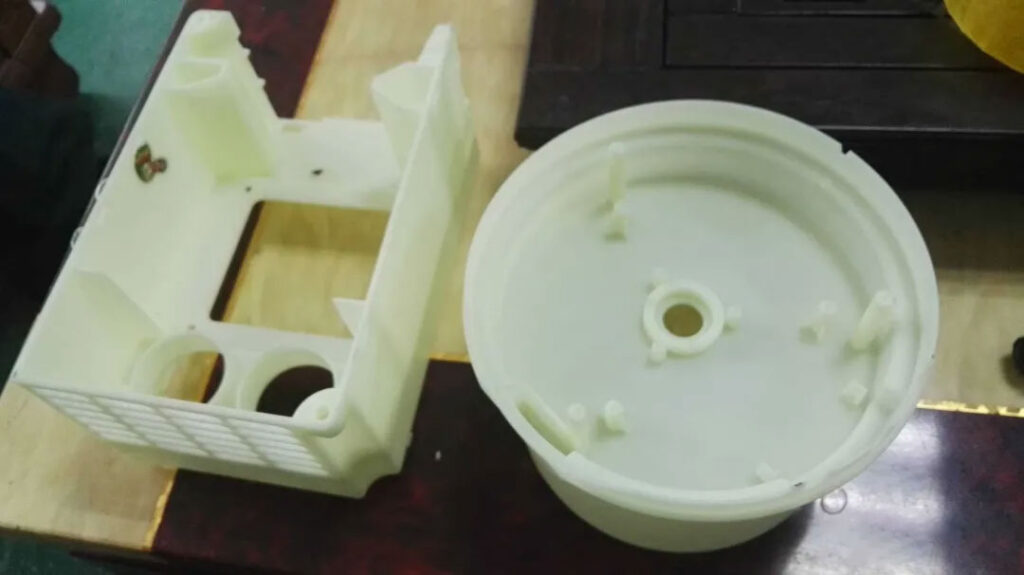

If the customer requires several or dozens of sets, this method is suitable, which greatly reduces the cost. The sample of the product that is vacuum-coated has a certain percentage of shrinkage. The cost of vacuum-coated product samples is generally lower than that of CNC, that is, the price of CNC processing multiple sets of samples is lower than the price of CNC processing one set and then vacuum-coating (except for special requirements for the material of the sample that is produced by the co-molding).
The mold materials are:
Ordinary PU: brittle and tough;
Transparent PU: The raw material is better, but the price is the most expensive;
Rubber-like PU: 8400 soft rubber.
The vacuum molding technology can be used in two ways:
- Produce small batches of product samples;
- Change the material: the sample carved by gypsum clay can be changed to PU or POLY material which is easy to process later through duplication, or the ABS material can be changed to a material with special requirements;
(For example: requiring transparency, high temperature resistance, high strength, or rubber properties, etc.).
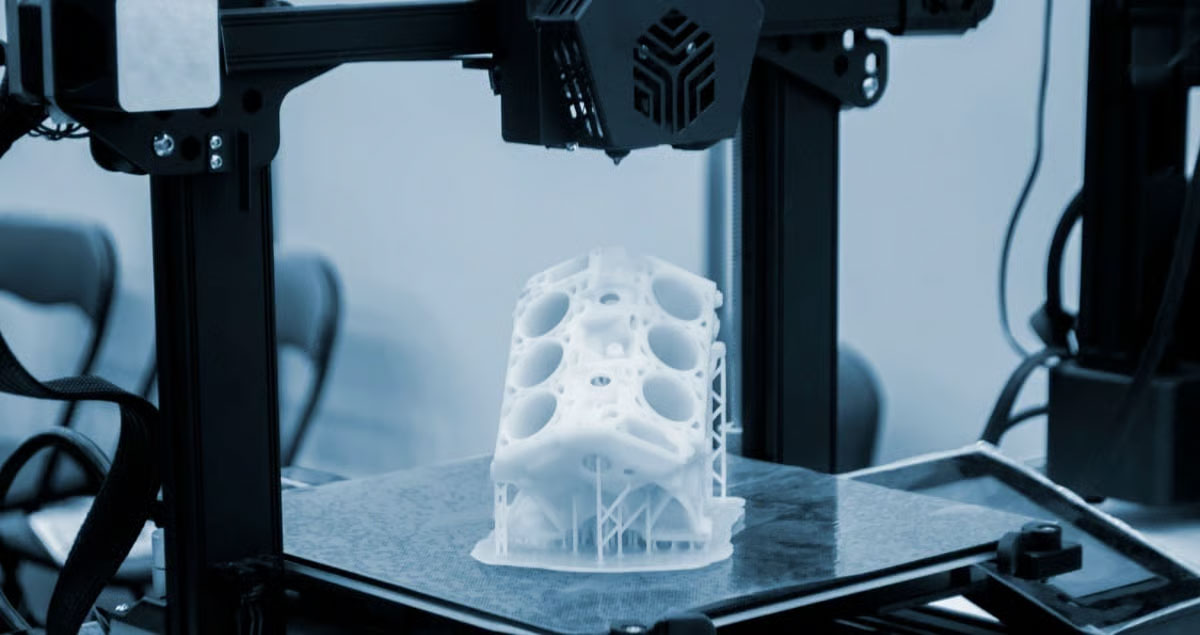
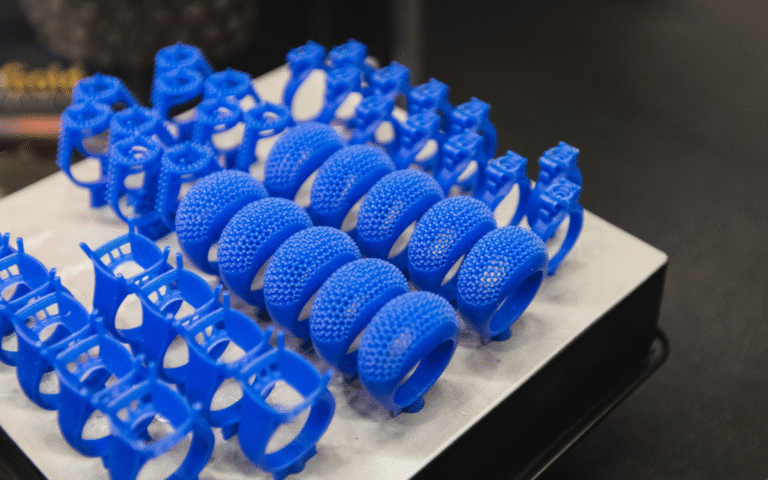
No.3 3D Printing Prototype
3D printing is a type of rapid prototyping technology. It is a technology that uses powder, linear plastic or liquid resin materials to construct objects by printing layer by layer based on digital model files.
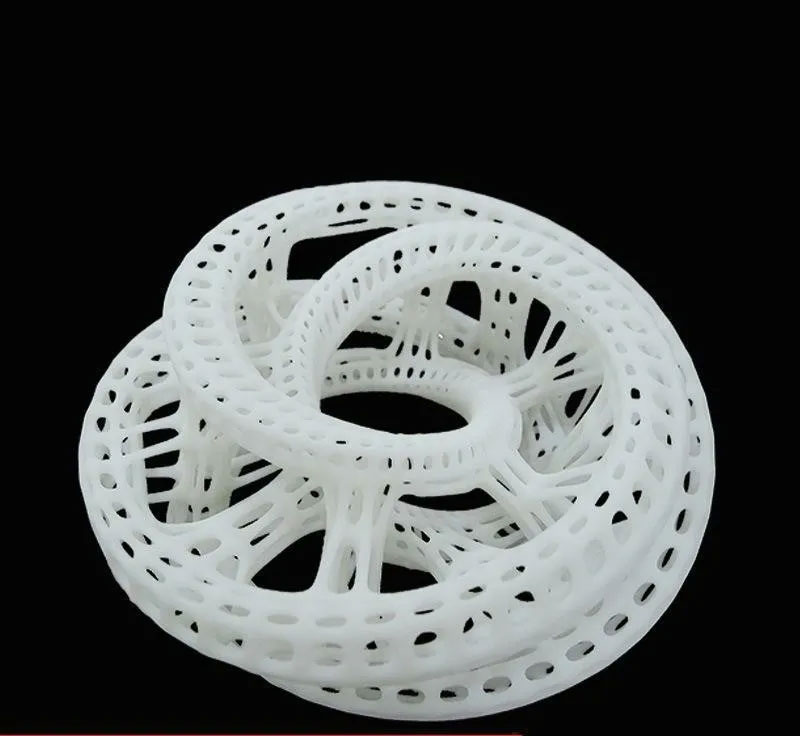

Compared with the above two processes, the main advantages are:
- The speed of making prototype samples is fast. Generally speaking, the speed of printing prototypes using SLA technology is three times that of CNC prototypes, so 3D printing is the first choice for small parts and small batch prototypes;
- The 3D printer is fully automated, with high precision in prototype production and small model error. The minimum error can be controlled within ±0.05mm. No human intervention is required during the entire process, which avoids errors caused by human factors. CNC prototype production is prone to prototype deformation.
- There are more optional materials for 3D printing prototypes.
However, 3D printing is not recommended in the following situations:
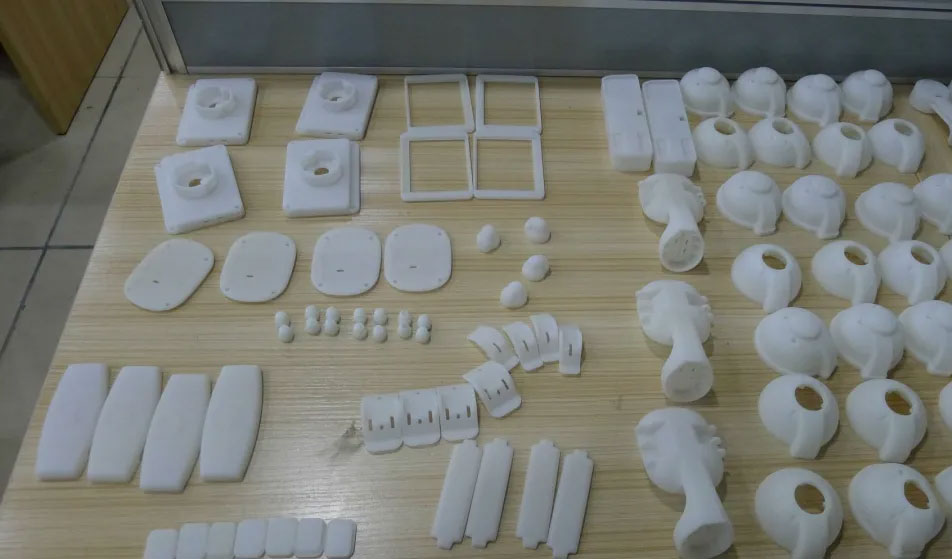

First, the prototype model is too large to be 3D printed. If 3D printing is required, it can only be split;
The second type is that the structure is special and cannot be processed or the processing fails to meet the requirements. For example, a square sealed box has a structure inside and needs support. 3D printing can print the seal, but there will be support, and the customer certainly does not want to have support. At this time, it is necessary to disassemble the parts for printing and remove the support.
The third option is that disassembly processing may be cheaper, and disassembly printing may be cheaper. At this time, customers can also disassemble and print.
Summary
The above is an introduction and application scenarios of the three prototype processing methods. You can match the most suitable process according to the actual processing needs. Of course, you must take into account multiple factors such as quotation, quality and efficiency!