Introduction
Each tool uses different processing parameters based on the material being processed. In the field of milling, tool manufacturers aim to improve processing efficiency by optimizing tool materials and developing more targeted coating technologies.
By combining various elements in the materials, we can see thousands of raw materials that can be processed. To process these materials, we must know the processing properties of the material and also know how to optimize the processing.
Material group to which the workpiece belongs

According to ISO 531:1966 international standard, machinable materials are divided into 6 categories, namely:
P represents steel material;
M represents stainless steel material;
K represents cast iron material;
N represents non-metallic materials;
S stands for high temperature materials;
H represents high hardness material;
Tool manufacturers further subdivide materials within these broad categories based on their tensile strength and hardness. If you are unable to find the performance parameters for the material you are working on within these subcategories, the best approach is to consult your tool supplier, who will be happy to help you resolve the issue.
Calculation formula
We often see the following formula in tool manuals
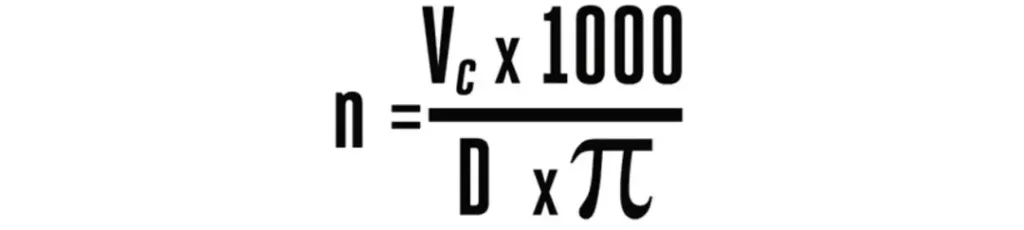
Before we talk about this formula, let’s recall the formula we learned about the circumference of a circle:
C (circumference) = π (pi) * d (diameter)
According to this formula, we can conclude that for a tool with a diameter of D, the distance traveled by the outermost point of the tool for each revolution is:
π *D
Then, when the tool rotates at a frequency of n revolutions per minute, the distance it travels is:
n*π *D
According to the formula time (T) × speed (V) = distance (S), the speed Vc of the outermost point of the tool at any time point during this period is:
Vc=(nπD)/1
The following formula is obtained by conversion:
n=Vc/(π *D)
Note! Our tool uses millimeters (mm) as the unit, so the unit of speed Vc in the previous formula is: mm/min
After length conversion (1m=1000mm), we have this common formula:
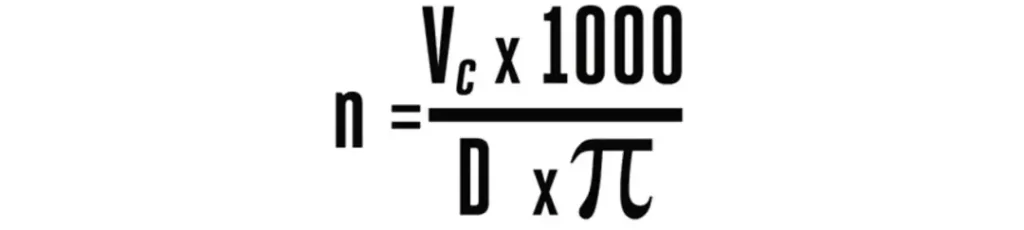
After simplifying the equation, we have our final formula:
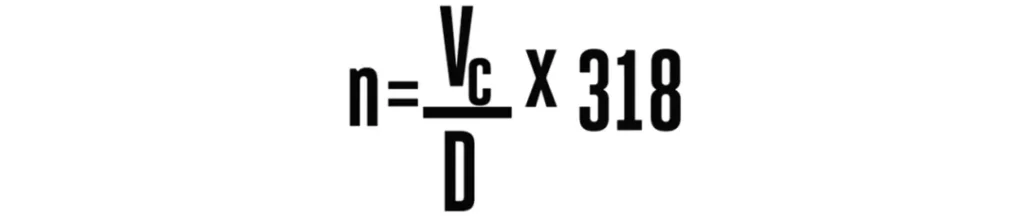
Notice:
Here the unit of D (tool diameter) is still mm (millimeter), while the unit of Vc (linear speed) has changed to: M/min (meters/minute)
This formula also applies to turning, except that D here represents the diameter of the blank.