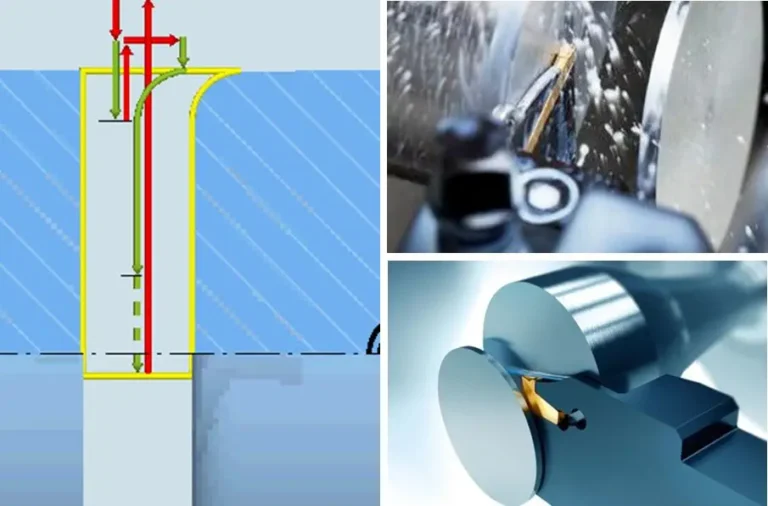
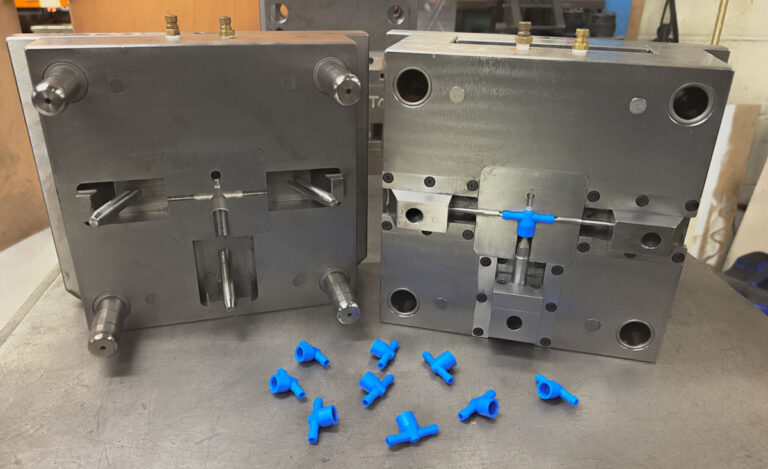
Introduction
In the plastic products industry, low volume manufacturing with an annual output of less than 10,000 pieces are more and more common. Such orders often come from new product trial sales, customized needs, or flexible production models with multiple varieties and small batches.
For mold companies, how to control development costs and shorten delivery cycles while ensuring mold quality has become a core issue in small-batch injection mold development.
Difficulties in developing small batch molds
The difficulty in developing molds for small batch products lies not in technology but in cost control.
Because traditional injection mold development usually follows the principle of “high precision and long life”, the lifespan starts at at least tens of thousands of molds, and the lifespan of high-quality molds can reach more than one million.
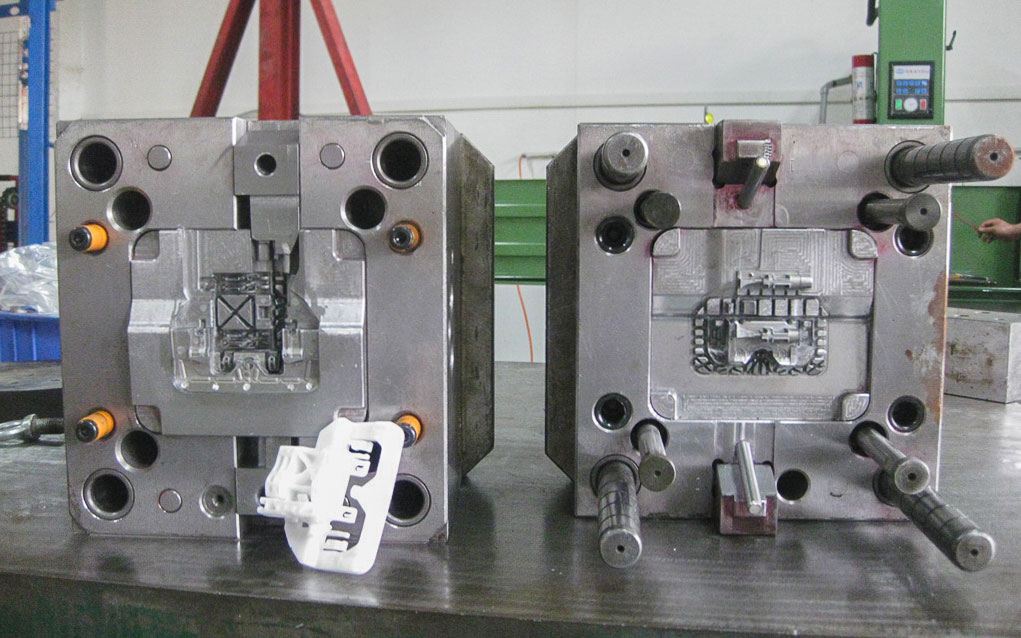
However, two major problems are prone to occur when used for small-batch production: mold fees account for too high a proportion of production costs and the development cycle is too long (conventional mold opening takes 45-60 days).
For example, a home appliance company developed a mold for an air conditioner panel with a trial production of 5,000 pieces. If it was designed according to conventional steel molds, the mold fee would be as high as 80,000 yuan, and the mold cost for a single product would be 16 yuan, far exceeding the value of the product itself.
To solve these two problems, the key is to accurately match the needs, give up “over-design” and focus on “just enough”. Three development intervals are divided according to production:
For ultra-small batches (<1000 pieces), fast prototyping is preferred, and low-cost alternatives are adopted;
Medium batch (1000-5000 pieces), balance precision and cost, optimize mold structure;
Close to mass production (5000-10000 pieces), with room for upgrades reserved to pave the way for subsequent mass production.
So, what should we do specifically?
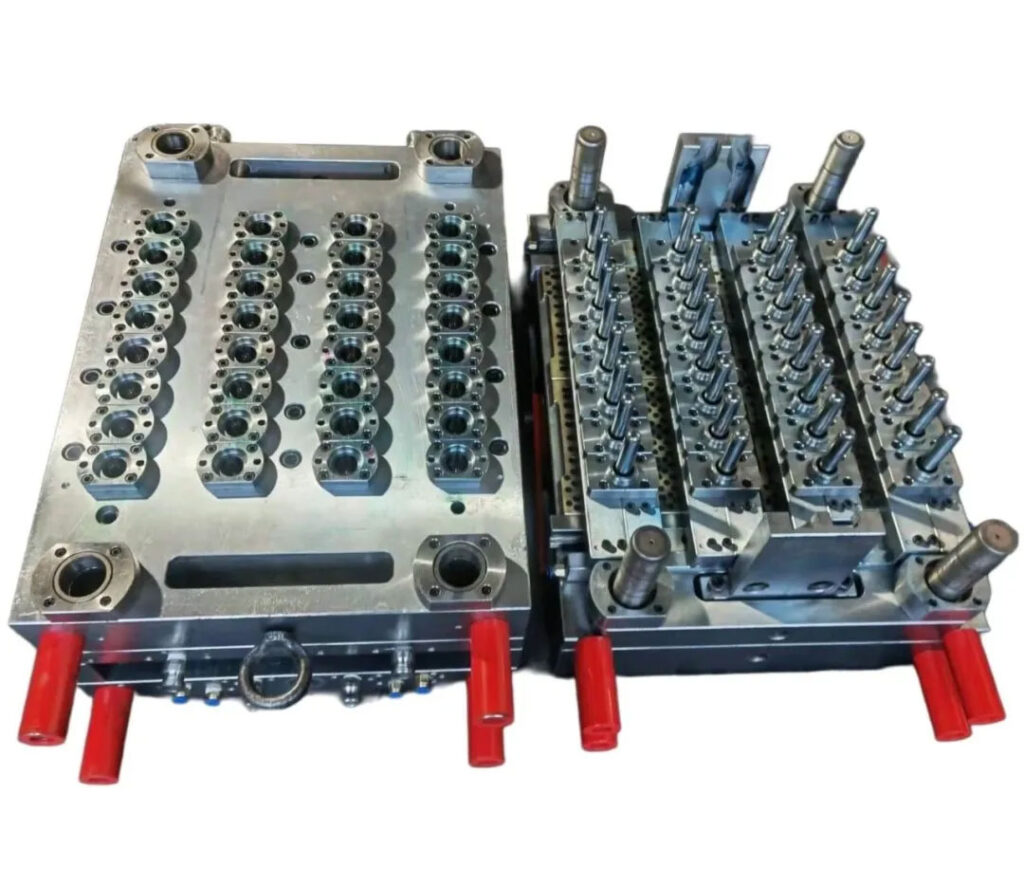

How to reduce mold opening costs and development cycle?
1.Simplify the cavity structure and reject “luxury configuration”.
Small batch molds do not need to pursue extreme automation, and costs can be reduced through manual design.
For example, by eliminating the complex core-pulling mechanism and changing the lateral undercut to manual demoulding, the processing fee can be reduced by 40%.
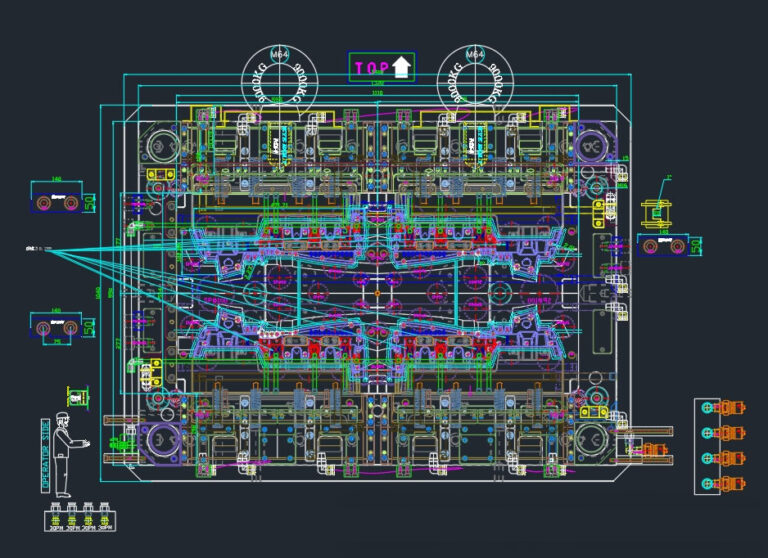
Merge parting surfaces and use flat parting instead of curved parting to reduce CNC processing time by more than 30%.
Simplify the cooling system, replace the conformal water channel with a straight-through water channel, and cooperate with the mold temperature controller to meet the needs of small batch production.
For example, when a medical device factory developed a 5,000-piece reagent bottle mold, it cancelled the hot runner system and automatic thread removal mechanism in the original design and used cold runner manual demoulding instead. The mold cost was reduced from 80,000 to 40,000, and the delivery cycle was shortened by 15 days.
2.Use standardized molds and low-cost materials.
80% of the mold cost is concentrated in the core and cavity, while the mold frame can be standardized to the maximum extent. Selecting a standard mold frame (such as LKM CI3030) has a short delivery time and a cost 50% lower than that of a customized mold frame.
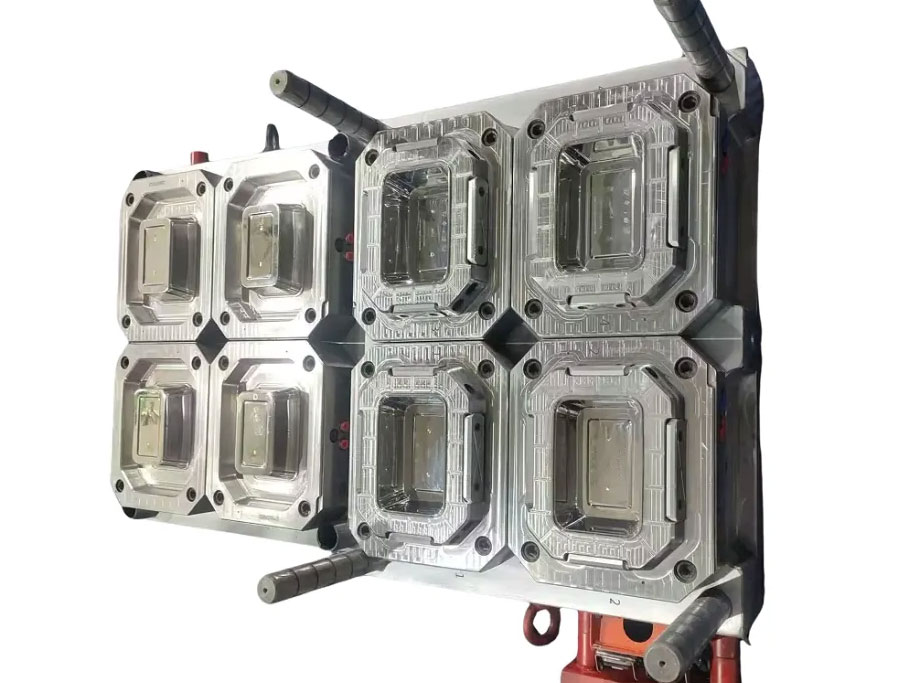

Core and cavity materials are graded . For products with a production volume of less than 5,000 pieces, 7075 aluminum alloy is used, which has a cost of only 1/3 of that of steel and a processing speed that is twice as fast. For products with a production volume of 5,000-10,000 pieces, P20 pre-hardened steel (hardness HRC30-35, lifespan of 100,000 molds) is used.
3.Cold runners should be used as the main flow channel as much as possible, and hot runners should be used with caution.
In small batch production, there is no need to pursue production efficiency too much. At this time, the cold runner system becomes the first choice due to its three major advantages: one is low processing cost; one is simple maintenance, no temperature control system is required, and it is suitable for non-professional injection molding factories to operate; and the other is flexible mold modification. If the product needs to be adjusted later, the cost of modifying the cold runner mold is only 50% of that of the hot runner.
However, if it is a thin-walled product (wall thickness <1.5mm) or a transparent part, you need to consider using a hot runner, because the cold runner is prone to insufficient filling and gate marks that affect the appearance.
4.Precise control of the mold trial process
The problem of “over-mold repair” often occurs in small batch mold trials. To control costs and shorten time, the mold trials should be controlled within three times as much as possible:
The first mold verifies the basic functions of the mold, allowing 10% dimensional deviation;
Adjust the cooling system of the second mold to control the deformation to less than 0.3%;
The third mold finally confirmed that the surface quality roughness Ra≤1.6μm.
An auto parts factory used this method to reduce the number of mold trials from an average of 5 to 3 times, and shortened the mold trial time by 8 hours each time.
5.Finding the right supplier is more important than lowering the price
Precise matching of three types of suppliers:
Small batch professional factory, 10 days fast proofing, confirm whether there is aluminum mold processing capability;
Regional integrated factory, cost control, requiring reuse of stock standard parts;
Foreign-funded precision factory, high-precision requirements, clear priority for small batch orders.
Risk control of contract terms:
Payment in stages: 30% deposit (design confirmation + 50% progress payment (qualified mold trial) + 20% final payment (delivery and use);
Ownership of molds: clearly define “customers own the molds after paying off the money” to avoid being tied to suppliers during subsequent mass production;
Warehousing terms require free storage for 6 months (if a second order is possible).
However, although the above optimization methods can save costs and mold opening time, an injection mold has a fixed cost from design to delivery, and it is impossible to blindly meet customers’ low-cost demands.
If you still feel that making a mold is not cost-effective after optimization, you can only consider other alternatives, such as 3D printing and silicone mold making.