Introduction
Many customers may think that developing an injection mold is a simple task and wonder why the price is so high. In fact, injection mold development is a complex system engineering project involving multiple disciplines and multiple links. From product concept to mass production mold, it requires rigorous processes and professional collaboration.

Next, let’s take a look at the entire process of an injection mold from the proposal of requirements to the delivery of products.
Product Definition and Preliminary Analysis
1.Product demand confirmation
Clarify the product’s function, appearance, dimensional accuracy, material requirements, operating environment, lifespan requirements, regulatory standards, etc. Obtain the final confirmed 3D model (usually in STEP, IGES, X_T format) and 2D drawings.
2.Mold feasibility analysis
Structural analysis: Evaluate the product structure’s suitability for injection molding (wall thickness uniformity, draft angle, ribs, snap fit, assembly relationships, etc.).
DFM analysis. Optimize the design for manufacturability for the injection molding process. This is one of the most critical steps, aiming to:
Optimize the draft angle to ensure smooth demoulding;
Optimize wall thickness to reduce defects such as shrinkage, deformation, and air entrapment;
Optimize fillet transition to improve flow and stress concentration;
Optimize the design of features such as stiffeners, struts, and clips;
Analyze whether the parting line position is reasonable, beautiful and easy to process;
Evaluate the need for side core pulling mechanisms such as sliders and inclined lifts and their complexity;
Initial assessment of gate location and type;
Communicate closely with product designers to propose modifications and reach consensus.
3.Material selection
Select appropriate plastic raw materials according to product performance requirements, as their shrinkage rate directly affects mold size design.
4.Preliminary planning of mold solution
Determine the number of cavities (how many cavities in one mold).
Initial design of parting surface, core/cavity structure, and side core pulling mechanism scheme.
Preliminary assessment of mold size, tonnage requirements, and injection molding machine specifications.
Preliminary quotation and project plan: Based on the above analysis, the mold factory provides a preliminary quotation and development cycle plan.
Mold Design
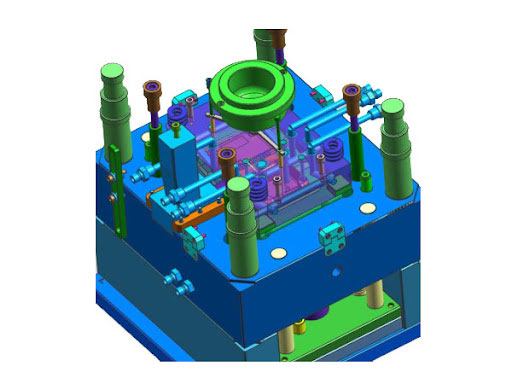
1.Detailed mold design
It is carried out by professional mold designers using CAD software, and generally includes the following tasks:
Parting design: precise design of main parting surface, insertion surface and collision surface.
Mould frame design/selection, choose standard mould frame or design non-standard mould frame (size, plate thickness, guide pins and sleeves, reset mechanism, etc.).
Core/cavity design: Based on the product 3D model, split the design of the core and cavity inserts (considering materials, heat treatment, processing technology, and exhaust).
Gating system design, design of main runner, branch runner, gate (type, position, size), balanced runner design.
Cooling system design, designing the water circuit (layout, aperture, spacing) to ensure efficient and uniform cooling, is the key to production efficiency and product quality.
Ejector system design: design the position, size and stroke of the ejector, sleeve, push plate, inclined ejector, air ejector and other mechanisms to ensure smooth product ejection without deformation.
Design of lateral core pulling mechanism, design of slider, inclined ejector (inner position) and its driving mechanism (inclined guide column, oil cylinder, bending pin, etc.).
Exhaust system design, reasonable design of exhaust grooves, insert gaps, ejector pin gaps, etc. to avoid trapped air and burning.
Other auxiliary systems, hot runner system (if used), sequential valve control, mold heating/cooling interface, lifting holes, positioning blocks, support columns, etc.
2.Design Review
Conduct design reviews within the organization or with customers to check the rationality, processability, assemblability, and safety of the design.
3.Produce engineering drawings
Generate detailed part processing drawings (dimensions, tolerances, materials, heat treatment, surface treatment requirements) and mold assembly drawings.
4.Mold CAE analysis (optional but highly recommended)
Mold flow analysis predicts the filling behavior, pressure, temperature distribution, shear force, weld line location, cavitation location, warpage deformation trend, etc. of the plastic melt in the mold cavity, and optimizes the design of the casting and cooling systems.
Structural stress analysis evaluates the strength and stiffness of key mold components (such as core, cavity, slide, and lifter) under injection pressure.
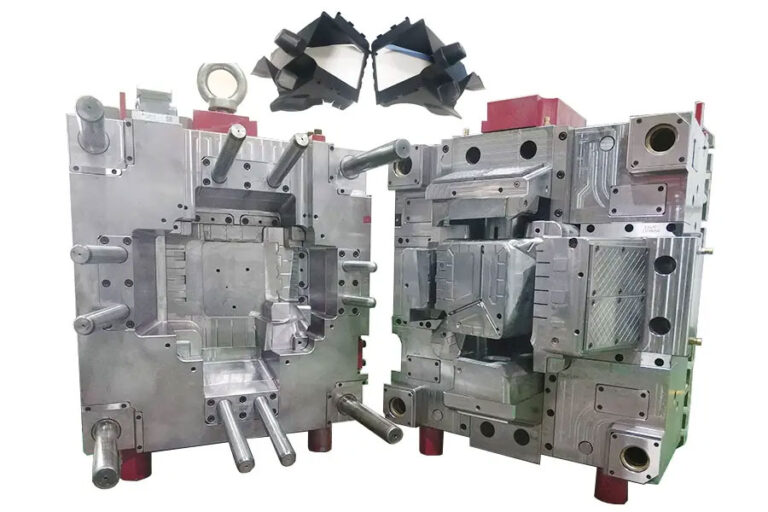
Mold processing and manufacturing
1.Material procurement
Purchase mold bases, mold steel (such as P20, H13, S136, NAK80, etc.), standard parts (ejectors, sleeves, guide pins and sleeves, springs, screws, etc.), hot runner systems, etc.
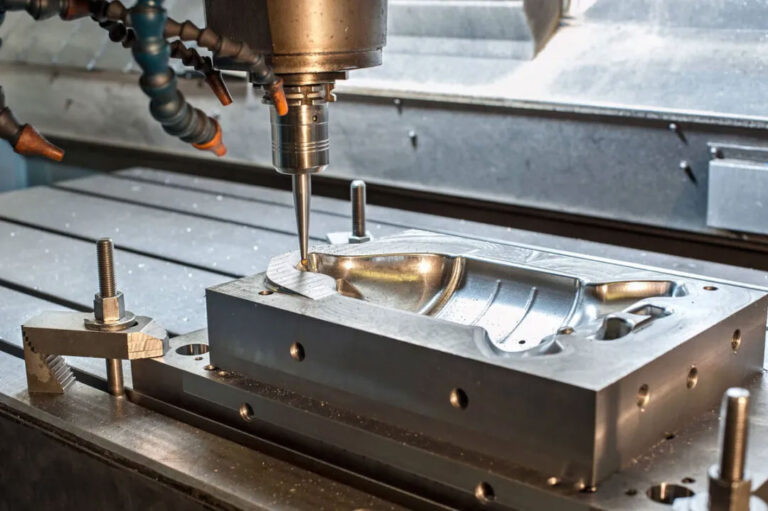
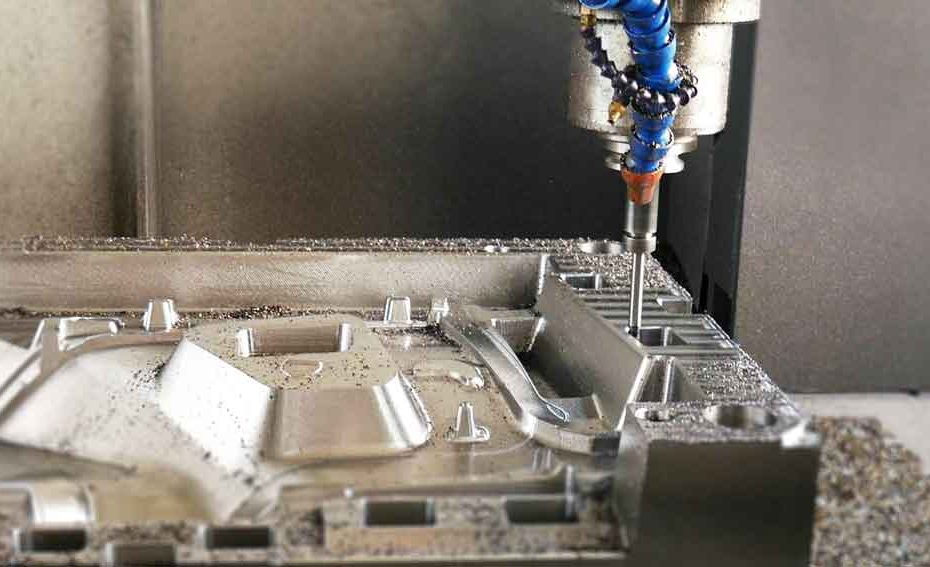
2.Precision machining
Rough machining: Milling, turning, etc. to remove most of the allowance.
Heat treatment: Quenching and tempering are performed on key components (core, cavity, slider, lifter, etc.) that require high hardness and wear resistance.
Semi-finishing/finishing:
CNC milling, processing complex surfaces and structures;
EDM (Electro-Discharge Machining) processes deep grooves, narrow slits, sharp corners, and complex shapes of high-hardness materials (using copper/graphite electrodes);
Wire cutting, processing precision inserts, ejector holes, and straight body parts;
Deep hole drilling, processing cooling water channels;
Grinding to ensure the flatness, parallelism, verticality and precise dimensions of the template;
Engraving/texture processing, processing leather grain, sun grain, etc. on the product surface.
3.Precision measurement
Use three-coordinate measuring machines, height gauges, projectors and other equipment to strictly inspect the processed parts to ensure that they meet the requirements of the drawings.

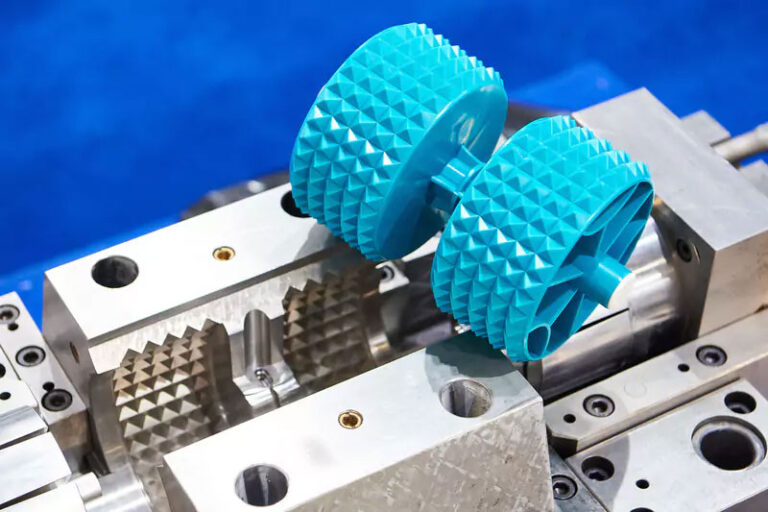
4.Mold assembly
Clean all parts; assemble mold base and insert core into cavity.
Install the slider and tilting mechanism.
Install the gating system (cold runner or hot runner) and cooling system.
Install the ejection system.
Install all standard parts, pipe interfaces, etc.
Ensure that all moving parts are smooth and without interference.
Mould trial and acceptance
1.Preparation of trial mold
Install the mold on a suitable injection molding machine.
Connect cooling water pipes, hydraulic oil pipes (if there is an oil cylinder), hot runner temperature controller, gas line, etc.
Set the preliminary injection molding process parameters (temperature, pressure, speed, time).
2.First mold trial
Injection plastic (usually with pure resin or cheaper material first).
Observe the filling process (short shot).
Check the molded sample (“first sample”).
3.Sample evaluation and problem analysis
Measure critical dimensions.
Check for appearance defects (flash, shrinkage, weld lines, air marks, burning, glue deficiency, deformation, white top, etc.).
Analyze the causes of defects (design problem? processing problem? assembly problem? process problem?).
4.Mold modification and optimization
Based on the mold trial results, make necessary modifications to the mold (such as surface modification, polishing, gate/runner size modification, ejector pin position adjustment, water channel optimization, vent repair, etc.). This process may be repeated multiple times; adjust and optimize the injection molding process parameters.
5.PPAP/small batch trial production
Under the optimized mold and stable process, a certain number of samples are produced continuously.
Conduct more comprehensive dimensional inspection, appearance inspection, functional testing and reliability testing.
Confirm whether the product fully meets the design requirements.
6.Final mold acceptance
The customer or project team makes the final confirmation on the sample and mold status.
Sign the mold acceptance report.
Hand over mold related documents (drawings, modification records, mold trial reports, process parameters, etc.).
Mold delivery and mass production
1.Mould transfer
The qualified molds will be delivered to the production department or the injection molding factory designated by the customer.
2.Preparation for mass production
Install and debug the mold on the mass production injection molding machine.
Set and solidify process parameters for mass production.
Train operators.
Prepare relevant operating instructions and inspection standards.
3.Formal mass production
The mold is put into continuous production.
4.Mold maintenance and care
Establish a regular maintenance plan (cleaning, lubrication, rust prevention, inspection of wearing parts).
Monitor mold status during production (such as whether ejection is smooth, abnormal wear, cooling effect, etc.).
Carry out preventive maintenance and corrective repairs in a timely manner to extend the life of the mold and ensure production stability and product quality.
Conclusion
It can be seen that the development of injection molds is a complex and meticulous process, with each link being closely linked. Problems in any link may lead to the failure of mold development. After reading the entire process of injection mold development, do you still think that developing an injection mold is easy?