Introduction
I have read many articles about injection molding machines, hot runner molds and systems recently. I feel that they all talk about a certain part separately, which is not complete and systematic. Although they are described in detail, it is still difficult for novices to understand what they do, how to use them, and which link they belong to.
Therefore, here I will take the entire injection molding machine as an example to talk about its concept, composition, operating principle, and its position in production.
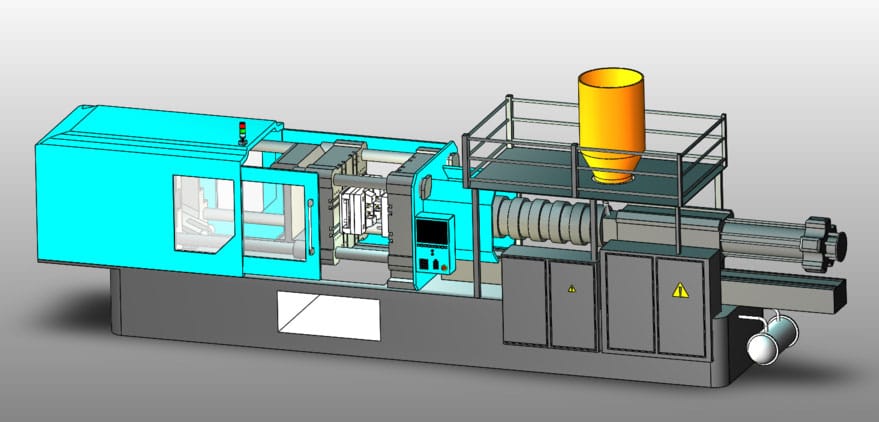
Concept of Injection Molding Machine
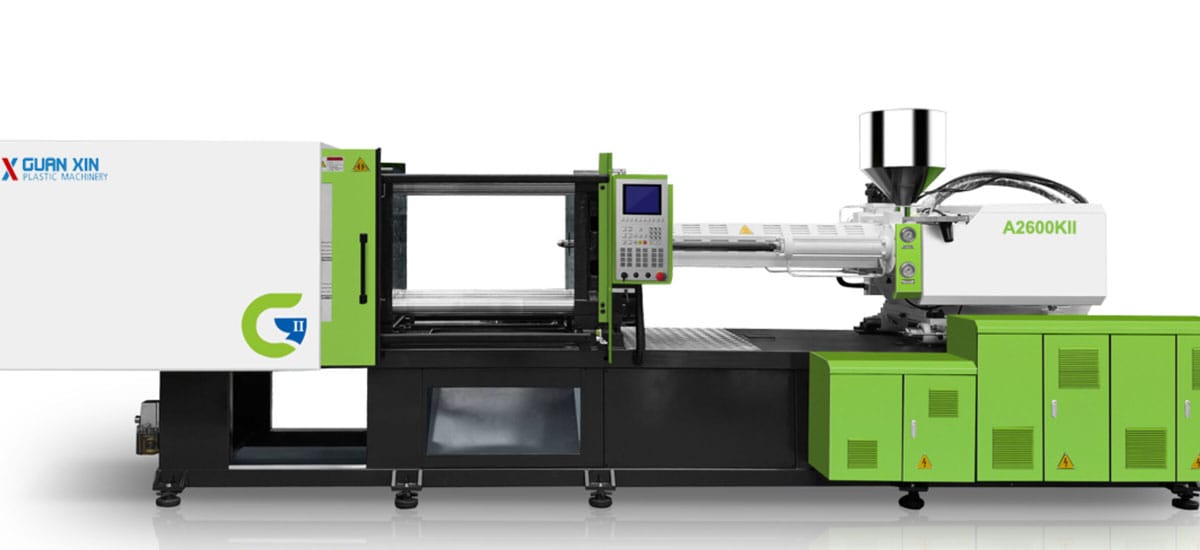
Injection molding machines are the main molding equipment that uses plastic molding molds to make plastic products of various shapes from thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics . This is the term given in the encyclopedia and is relatively easy to understand.
An injection molding machine is a specialized piece of equipment that combines the thermal processing properties of plastics with the melt die-casting principles of metals. This is what a Zhihu article says, and it might be a little hard to understand, so let’s break it down.
The thermal processing characteristics of plastics: in fact, they are its thermosetting and thermoplastic properties. The main difference between them is that thermosetting is a chemical change that cannot be restored after the change, that is, the process is irreversible; while thermoplastic is a physical change, and it remains the same after processing, and all the most basic components remain unchanged.

Melting: The process of a substance changing from a crystalline phase to a liquid phase, that is, from a crystalline state to a liquid state.
Die casting: It is a metal casting process characterized by the use of the mold cavity to apply high pressure to the molten metal. It is a precision casting method that uses high pressure to force the molten metal into a complex-shaped metal mold. In other words, die casting requires the use of molds and thermal processing to apply high pressure to the molten metal to cause it to deform.
After decomposition, we can see that this concept coincides with the statement in the encyclopedia, that is, the injection molding machine is a machine that uses tools (plastic molding molds) and means (melt die casting) combined with the thermal processing characteristics of plastics to die-cast the original crystalline plastic into the shape we need.
Injection molding machine type
Vertical, horizontal, all-electric—this is how it’s described in the encyclopedia. A note: While vertical and horizontal injection molding machines are easily distinguishable from each other in appearance, that doesn’t necessarily mean their primary difference lies in their appearance. The primary difference lies in their clamping method . Vertical injection molding machines inject from top to bottom, with their center of gravity downward, while horizontal injection molding machines inject horizontally or transversely, resulting in a larger footprint.
What is a vertical injection molding machine? Actually, it is an injection molding machine that is erected, like this, long and slender.

Similarly, a horizontal injection molding machine is an inverted injection molding machine, like this:

So what is an all-electric injection molding machine? It’s pretty straightforward: it’s powered entirely by electricity. Vertical and horizontal injection molding machines, on the other hand, are collectively referred to as fully hydraulic, powered by hydraulic oil. Therefore, all-electric injection molding machines offer high precision and are relatively energy-efficient, but they also come at a relatively high price.

Comparison Between All-Electric Injection Molding Machines and Traditional Hydraulic Injection Molding Machines
| Machine Type | Traditional Variable Displacement Pump Hydraulic Injection Molding Machine | Traditional Variable Displacement Pump Hydraulic Injection Molding Machine |
| Energy Consumption | Uses hydraulic oil; energy loss as high as 36% to 68% | Uses servo motors and drives; energy saving efficiency typically 50% to 70% (varies by product) |
| Cleanliness & Noise | High noise from hydraulic pumps and pressure release; oil leakage issues, poor workshop environment; low production efficiency for cleanliness-sensitive products | No hydraulic pump noise; noise reduced by 10-15 dB; no oil leakage, clean workshop, easy maintenance |
| Response | Mature hydraulic technology with relatively short response time | Faster response with servo motors and drives; wider control range, especially suitable for short-stroke injection |
| Precision & Repeatability | Electronic ruler control; precision generally above 0.3mm; high-speed precision machines can reach 0.2mm | Servo motor with full closed-loop control; high precision up to 0.02mm; suitable for high-precision products with high repeatability |
| Molding Efficiency | Relatively low injection speed; generally around 100mm/s for hydraulic machines; some modified high-speed machines can reach 150–200mm/s | High injection speed, generally above 300mm/s; high molding efficiency |
| Initial Investment | Low price | Relatively high price; imported all-electric machines are about 4–5 times more expensive than hydraulic ones; domestic prices vary by manufacturer |
| Maintenance | Relatively simple maintenance; many technicians can service, but the market is disorganized with no fixed rules for parts and maintenance costs | More complex maintenance; requires support from specific control systems and high-power servo motor/drive suppliers |
Injection molding machine composition
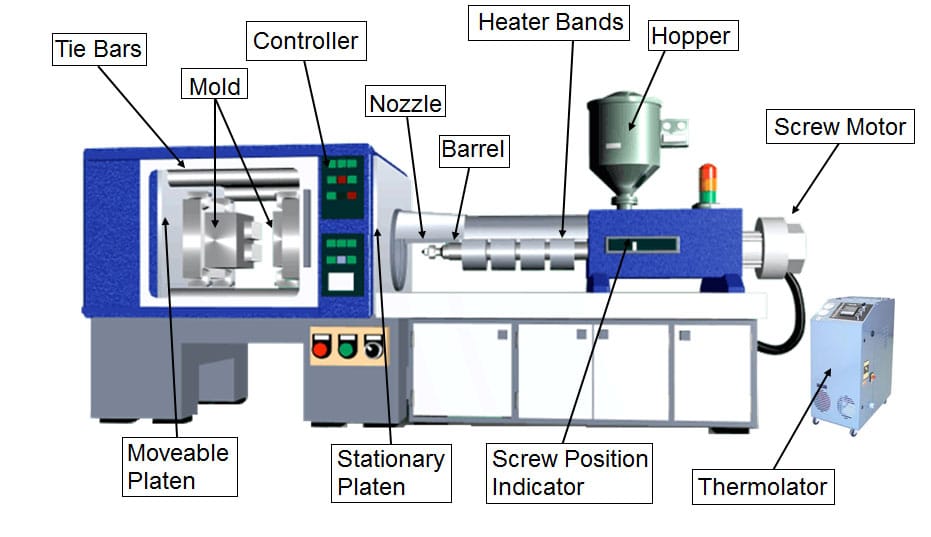
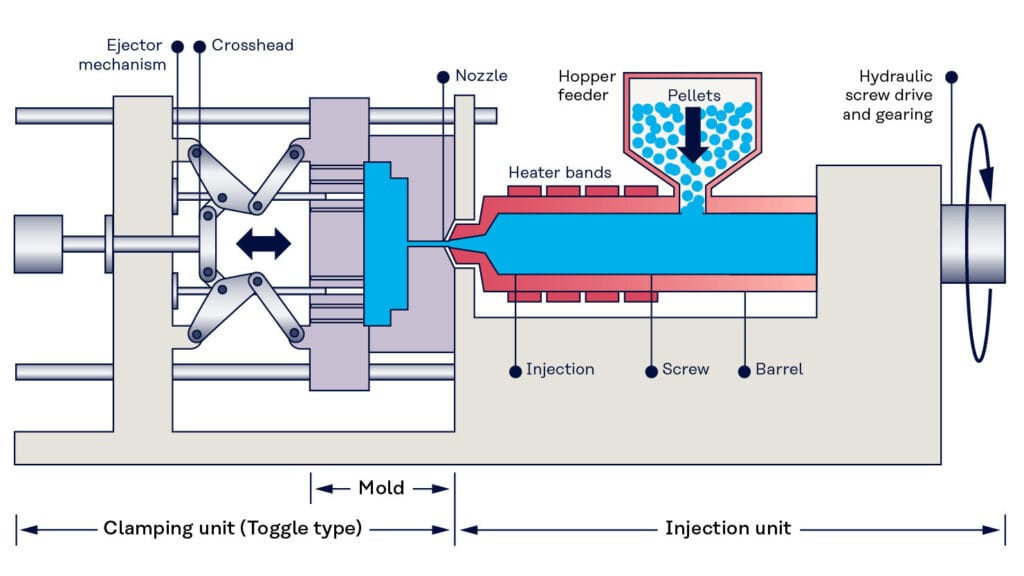
Although there are so many types of injection molding machines, their structures are actually similar. They are usually composed of an injection system, a mold clamping system, a hydraulic transmission system, an electrical control system, a lubrication system, a heating and cooling system, a safety monitoring system, etc. This is what the encyclopedia says, and we will break it down one by one.
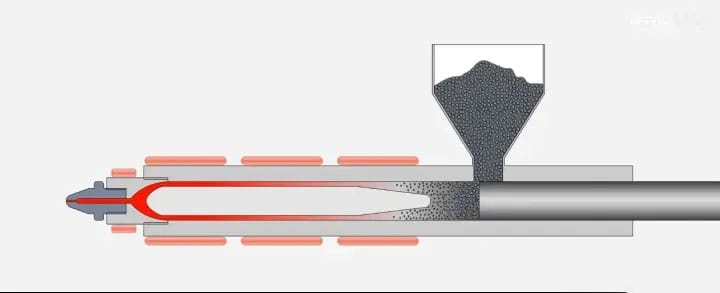
Injection systems are classified into three main types: plunger , screw , and screw-pre-plasticized plunger injection (I’m not entirely sure about this type; I haven’t found any relevant information yet). Their function is to heat and plasticize a certain amount of plastic, then inject the molten plastic into the mold cavity via a screw at a specific pressure and speed . After injection, the molten material in the mold cavity is held in place.

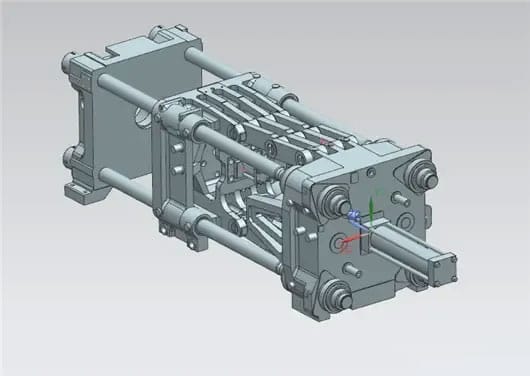
Clamping system: The clamping system primarily consists of a movable platen, a fixed platen, tie rods, a clamping mechanism, a product ejection mechanism, and safety mechanisms. Its function is to ensure the flexible, accurate, rapid, reliable, and safe opening and closing of the mold. During injection, the plastic melt injected into the mold cavity by the injection system exerts very high pressure, requiring the clamping system to generate sufficient clamping force (locking force) to ensure a tight closure of the mold cavity and prevent the plastic melt from overflowing.
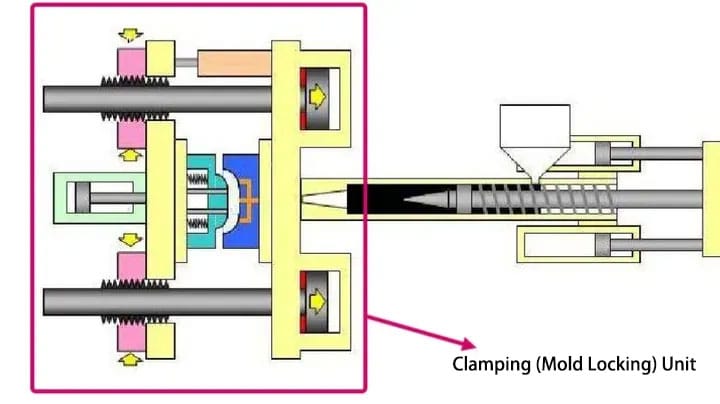
The hydraulic transmission system is the machine’s power unit, so it’s not necessary to elaborate on this. Its function is to provide power for the various movements required by the injection molding machine’s process and meet the pressure, speed, and temperature requirements of each component.
The electrical control system works effectively with the hydraulic transmission system to achieve the injection molding machine’s process requirements (pressure, temperature, speed, time) and various programmed actions.
The lubrication system provides lubrication for the machine’s moving platen, mold adjustment mechanism, connecting rod hinge, and shooting platform, among other parts that experience relative motion, thereby reducing energy consumption and increasing component life. Lubrication can be performed manually or automatically.
The heating and cooling system heats the barrel and injection nozzle. Heat is transferred through the barrel wall, providing a heat source for plasticizing the material.
The cooling system primarily cools the oil. Excessive oil temperature can cause various malfunctions, so oil temperature must be controlled.
Another location requiring cooling is near the feed pipe outlet to prevent material from melting there, which could disrupt proper feed delivery. It is worth mentioning that the heating system is actually the hot runner part of the hot runner mold .

Safety monitoring system:
This device is primarily used to protect personnel and machines. It consists of safety doors, safety baffles, hydraulic valves, limit switches, and photoelectric detection elements, providing electrical, mechanical, and hydraulic interlocking protection.
The monitoring system primarily monitors the injection molding machine’s oil temperature, material temperature, system overload, and process and equipment failures, providing indications or alarms when abnormal conditions are detected.
Working Principle of Injection Molding Machine
The working principle of the injection molding machine is similar to that of a syringe used for injections. It uses the thrust of the screw (or plunger) to inject plasticized molten plastic (i.e., viscous flow state) into a closed mold cavity, and then obtains the finished product after solidification and shaping.
Injection molding is a cyclic process. Each cycle mainly includes: quantitative feeding – melting and plasticization – pressure injection – mold filling and cooling – mold opening and part removal. After the plastic part is removed, the mold is closed again and the next cycle begins.
The general molding process of a screw injection molding machine is: first, granular or powdered plastic is added to the barrel, and the plastic is molten through the rotation of the screw and the heating of the outer wall of the barrel. Then the machine closes the mold and moves the injection seat forward so that the nozzle is close to the gate of the mold. Then, pressurized oil is introduced into the injection cylinder to push the screw forward, thereby injecting the molten material into the closed mold with a lower temperature at a very high pressure and a relatively fast speed. After a certain period of time and pressure maintenance (also called pressure holding) and cooling, it is solidified and formed, and then the mold can be opened to take out the product (the purpose of pressure holding is to prevent the backflow of the molten material in the mold cavity, to add material to the mold cavity, and to ensure that the product has a certain density and dimensional tolerance).