Intro
3D printing prototypes are becoming more and more popular among manufacturers. So what special advantages do 3D printing prototypes have compared to CNC prototypes? Today, the editor will take you to learn more about 3D printing prototypes.
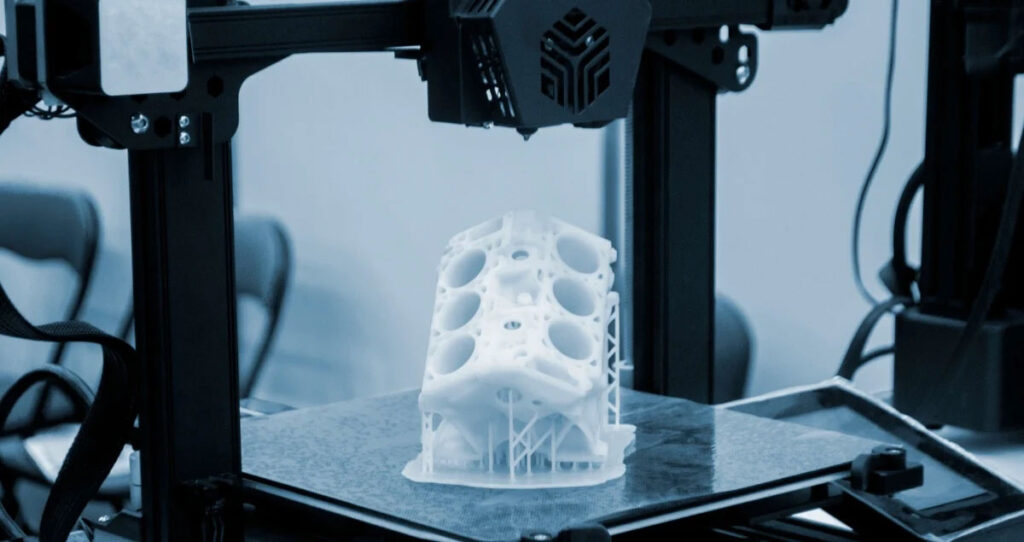

Before you start, let’s first understand the definition of 3D printing prototypes:
During the product design process, after we have completed the design drawings, the thing we want to do most is to know what the actual object of our design will look like, whether the appearance is consistent with our design ideas, whether the structural design is reasonable, etc.
In layman’s terms, a prototype is one or more functional samples made based on the product appearance drawings or structural drawings before a mold is made, used to check the rationality of the appearance or structure. Classification of prototypes Early prototypes were restricted by various conditions, mainly manifested in that most of the work was done manually, which made the prototypes take a long time to make and it was difficult to strictly meet the dimensional requirements of the appearance and structural drawings.
CNC prototype: Its main workload is completed by CNC machine tools, and according to the different equipment used, it can be divided into 3D printing prototypes (RP, Rapid Prototyping) and machining center (CNC) prototypes.
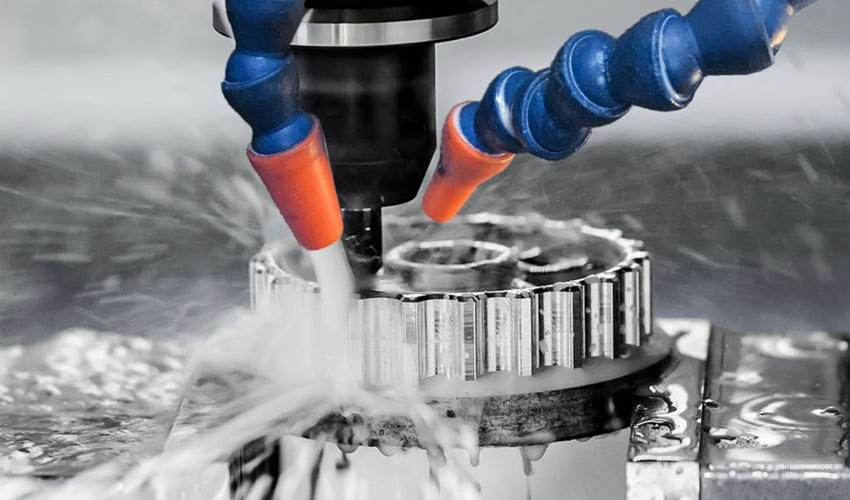

Numerical Control Machine Tools refers to machine tools equipped with computer numerical control systems, referred to as CNC machine tools or machining centers.
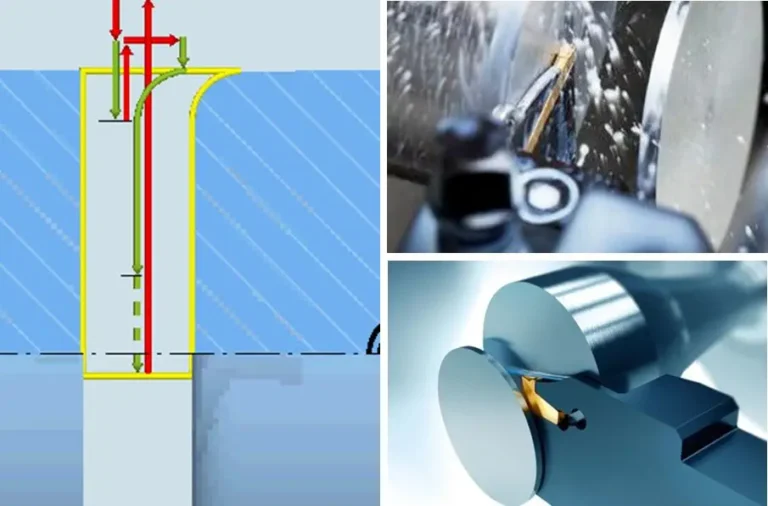
Differences Between 3D Printing and CNC Machining
| Items | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
| Principle | Additive | Subtractive |
| Material Utilization | Very High | Not High |
| Process Features | 1. Capable of processing various complex surfaces and irregular structures | 1. Ordinary CNC cannot process complex shapes |
| 2. Single-step forming, can achieve what traditional machining cannot | 2. Multi-step forming | |
| 3. No need to consider fixture usage | 3. Requires specialized personnel to design and use fixtures | |
| Cost Structure | 1. Import STI file for printing, no manual leveling required | 1. Requires professional programming and machining personnel |
| 2. Can process multiple parts at once if the tray size allows | 2. Can only process one part at a time | |
| Material Types | 1. Multiple color options available | 1. Clear advantage with metal materials |
| 2. 3D printing uses modified plastics with overall performance superior to photosensitive resin or other materials |
Specific comparison between 3D printed prototypes and CNC prototypes:
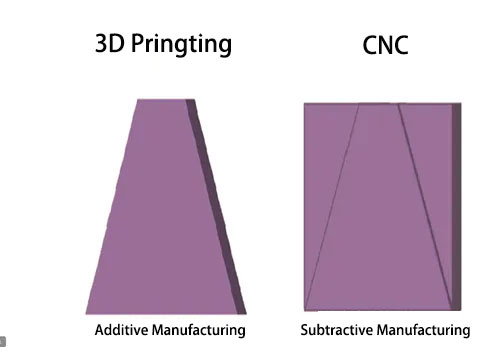
Materials
3D Printing
1. Extremely high material utilization, no waste
2. Real ABS plastic, multiple colors available
CNC Machining
1. The utilization rate is not high, and a lot of materials are wasted
Process Comparison
3D Printing:
1. Can process various complex curved surfaces and special-shaped structures
2. One-step molding, after removing the support, you can get a complete sample
3. No need to consider any fixture design CNC
4. Ordinary three-axis CNC cannot process such complex shapes
5. Complex parts need to be formed multiple times and need to be split and programmed, which requires a lot of work
6. Consider the cost structure of fixture design and manufacturing 3D printing
7. The built-in driver software can quickly calculate the printing time and required materials, without the need for professional training
8. As long as the XYZ molding area is large enough, multiple parts can be processed at one time, without manual supervision
9. What you see is what you get, high precision, no processing errors
10. No complicated maintenance is required, and the workbench material wire can be cleaned quickly and easily after printing.
CNC:
1. Professional programmers, professional machine operators and fixture design are required.
2. Only one part can be processed at a time, and at least three people are involved from design to manufacturing, which results in high labor costs.
3. There may be processing errors caused by human operating errors or poor clamping
4. After processing is completed, a special person is required to clean the machine tool, remove waste, etc., which takes a long time (labor cost).