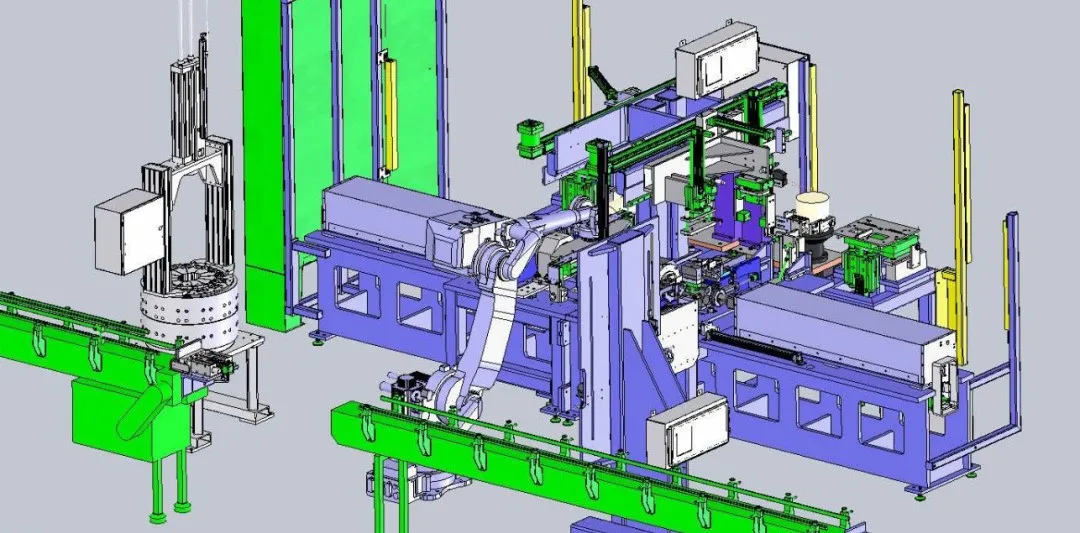
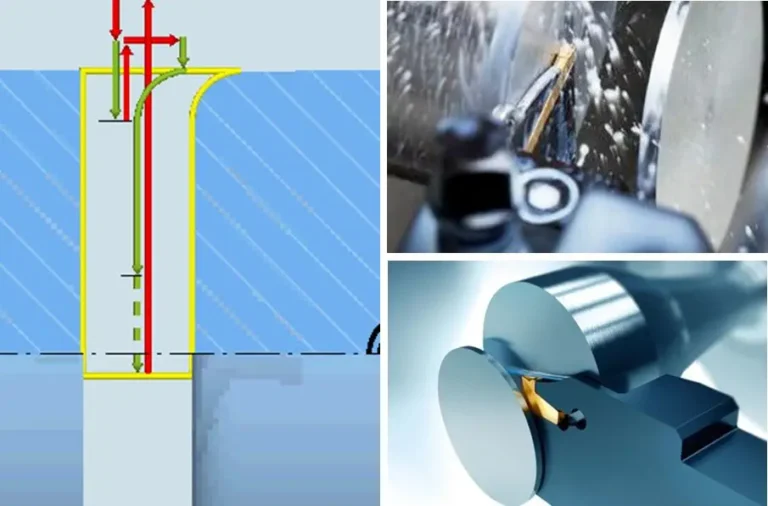
Industrial design, product design, and mechanical design are related yet different; they are done by completely different groups of people, and very few people can be proficient in all three of these different jobs at the same time.
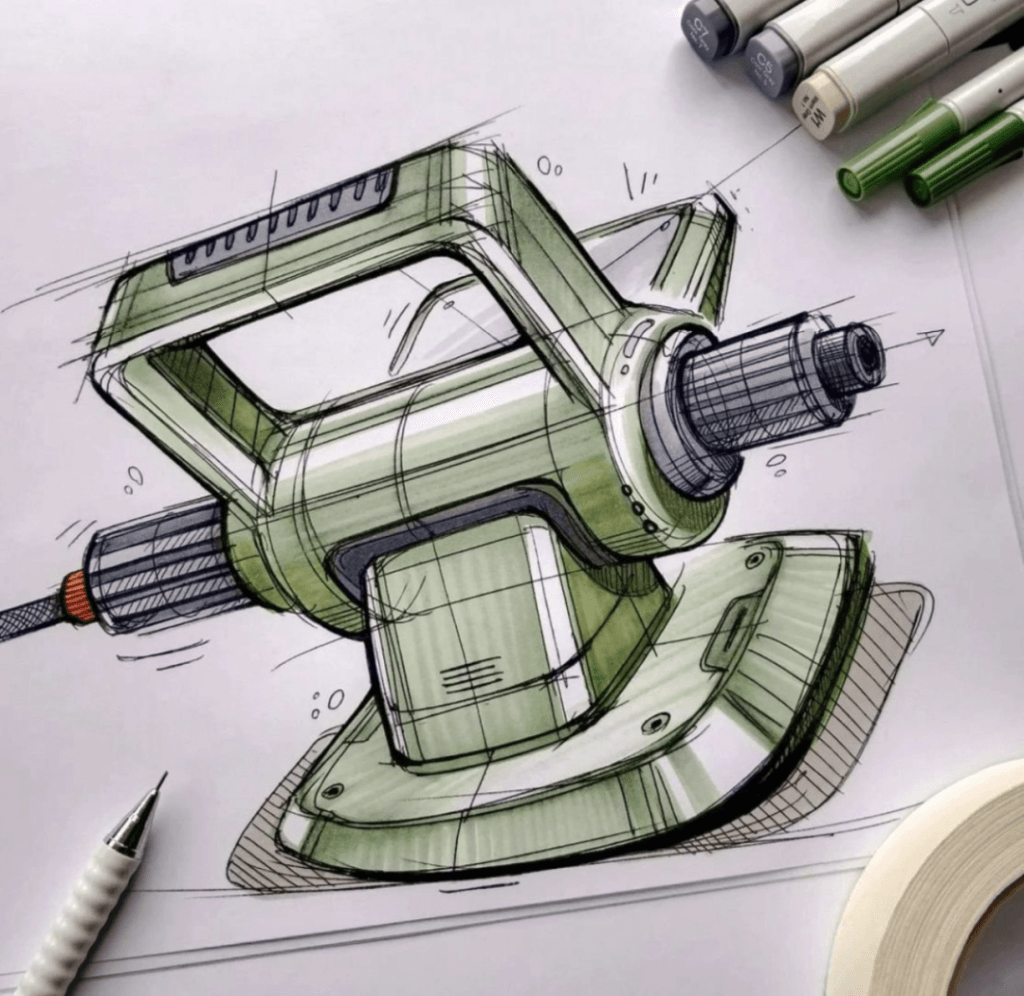
Industrial design
Essentially the design of an industrial product, involves the design and expression of its shape, the spatial relationships between its features, materials, colors, and surface treatments. It primarily focuses on aesthetics and is widely used in various industries, including industrial products, handicrafts, and daily necessities.
A truly excellent industrial designer, besides possessing strong aesthetic skills, should also understand and be familiar with the working principles, functionalities, internal structure, manufacturing processes, and mold-making methods of the product they are designing.
Only then can the designed appearance be considered reliable and commercially viable; otherwise, it’s just a joke, a piece of waste paper.
Product design
Product design generally refers to the design of the product’s internal structure, the support, connection, and positional relationships between parts, as well as the realization of the overall function. It is generally applied to the structural design of non-transmission components. In some special cases, product design also includes appearance design, and then combines it with structural design to cover all aspects.
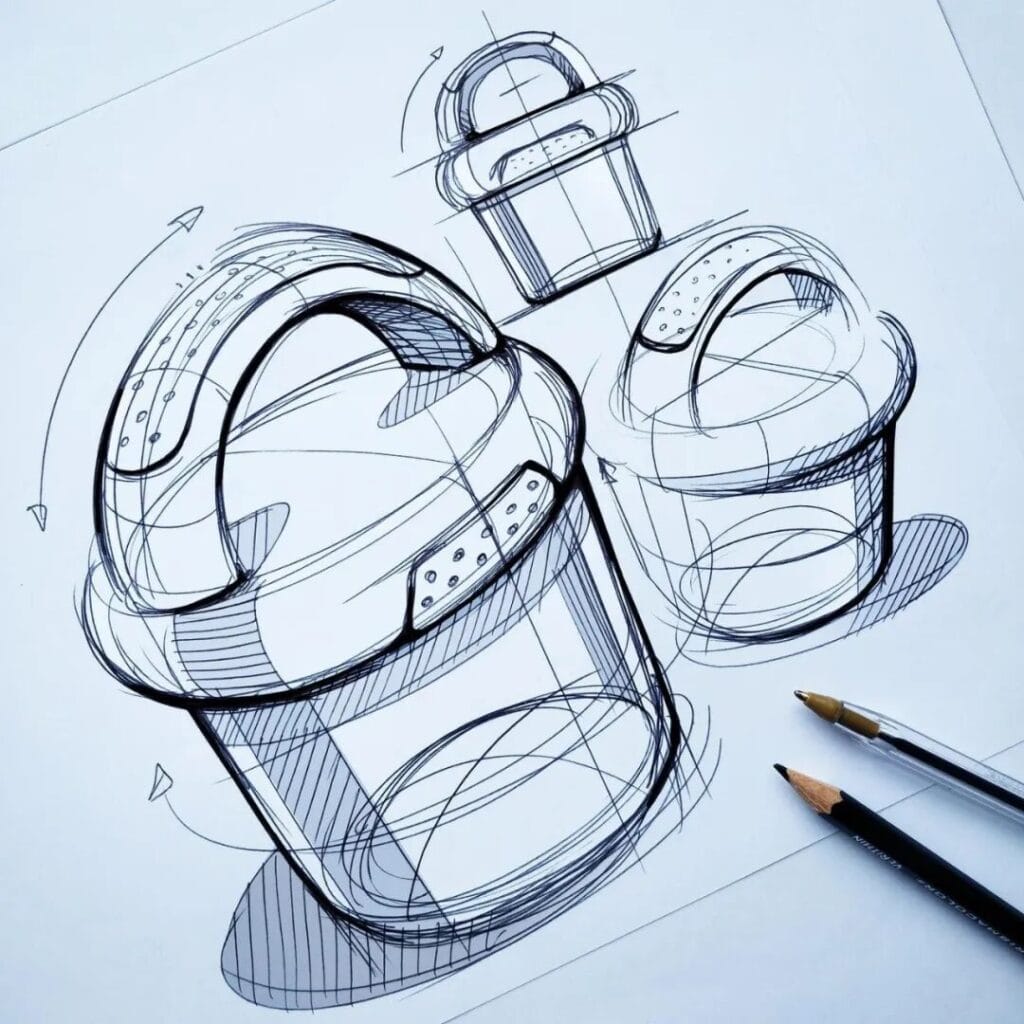

It also requires a comprehensive understanding of various aspects; otherwise, it will remain just theoretical, leading to numerous defects such as an unrealizable product, a clumsy design, excessively high costs, or low reliability.
In short, the difference between an excellent product and a poor one is enormous in the eyes of professionals. Product design focuses on aspects such as product appearance, workmanship details, and cost control. For example, mobile phones, despite their relatively simple structure, are of very high quality, with meticulous attention to detail.
Mechanical design
It is primarily used in industries such as non-standard automated equipment, mechanical equipment, and robotics. It mainly focuses on products with many moving parts, characterized by complexity, high unit price, and relatively high technical content, but production batches are generally not large. This position requires a solid foundation in mechanical principles, mechanics analysis, motion simulation, and knowledge of each component, making it a relatively high-barrier-to-entry role.
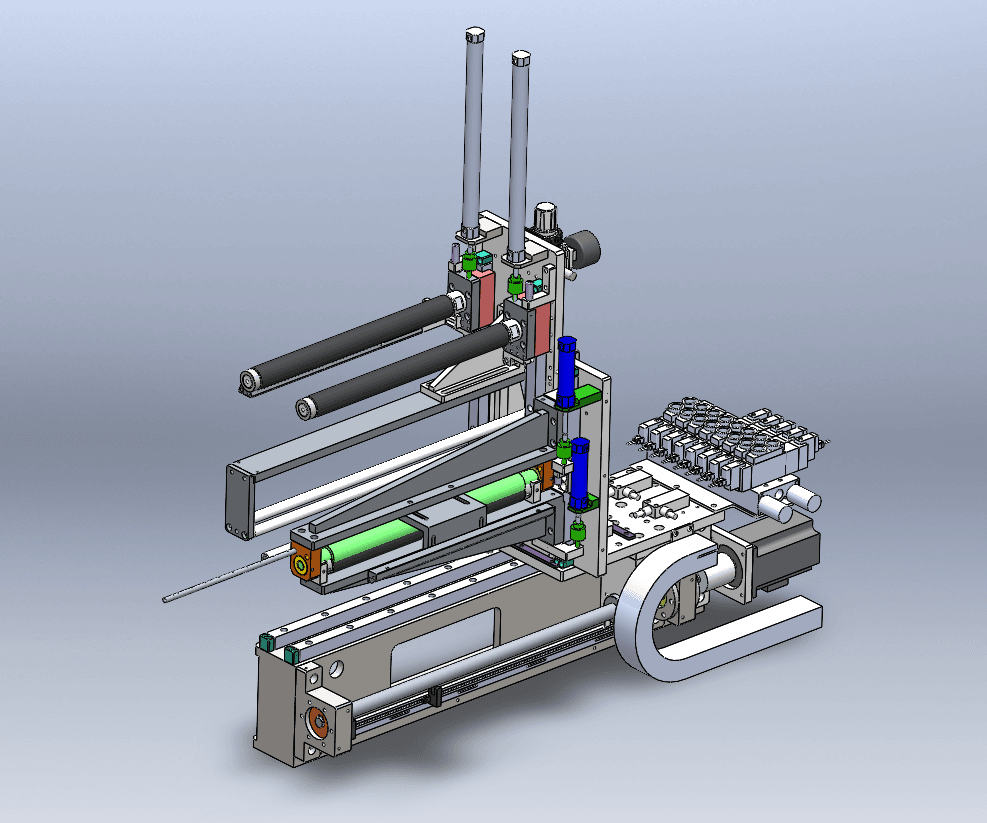
The product focus of mechanical design is on functional implementation, reliability, and performance parameters, while requirements for industrial design, user experience, and appearance quality are relatively lower. For example, designing a machine tool has extremely high requirements for reliability and performance.
Final words from Gaofeng
The three different positions mentioned above are related but also distinct. No one can master them all. It would take a lifetime to learn any one of them. Don’t be greedy!